|
Eotyrannus
''Eotyrannus'' (meaning "dawn tyrant") is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur hailing from the Early Cretaceous Wessex Formation beds, included in Wealden Group, located in the southwest coast of the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom. The remains (MIWG1997.550), consisting of assorted skull, axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton elements, from a juvenile or subadult, found in a plant debris clay bed, were described by Hutt ''et al.'' in early 2001. The etymology of the generic name refers to the animal's classification as an early tyrannosaur or "tyrant lizard", while the specific name honors the discoverer of the fossil. Discovery and naming The exact location of the discovery of the holotype specimen has not been revealed due to its importance and the possibility of new material to be collected as the coastline recedes. From what is mentioned in the description, the specimen was found on the southwestern coast of the Isle of Wight, between Atherfield Point and Hano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eotyrannus 2 NT
''Eotyrannus'' (meaning "dawn tyrant") is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur hailing from the Early Cretaceous Wessex Formation beds, included in Wealden Group, located in the southwest coast of the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom. The remains (MIWG1997.550), consisting of assorted skull, axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton elements, from a juvenile or subadult, found in a plant debris clay bed, were described by Hutt ''et al.'' in early 2001. The etymology of the generic name refers to the animal's classification as an early tyrannosaur or "tyrant lizard", while the specific name honors the discoverer of the fossil. Discovery and naming The exact location of the discovery of the holotypic, holotype specimen has not been revealed due to its importance and the possibility of new material to be collected as the coastline recedes. From what is mentioned in the description, the specimen was found on the southwestern coast of the Isle of Wight, between Atherfield Point a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eotyrannus
''Eotyrannus'' (meaning "dawn tyrant") is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur hailing from the Early Cretaceous Wessex Formation beds, included in Wealden Group, located in the southwest coast of the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom. The remains (MIWG1997.550), consisting of assorted skull, axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton elements, from a juvenile or subadult, found in a plant debris clay bed, were described by Hutt ''et al.'' in early 2001. The etymology of the generic name refers to the animal's classification as an early tyrannosaur or "tyrant lizard", while the specific name honors the discoverer of the fossil. Discovery and naming The exact location of the discovery of the holotype specimen has not been revealed due to its importance and the possibility of new material to be collected as the coastline recedes. From what is mentioned in the description, the specimen was found on the southwestern coast of the Isle of Wight, between Atherfield Point and Hano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosauroid
Tyrannosauroidea (meaning 'tyrant lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that includes the family Tyrannosauridae as well as more basal relatives. Tyrannosauroids lived on the Laurasian supercontinent beginning in the Jurassic Period. By the end of the Cretaceous Period, tyrannosauroids were the dominant large predators in the Northern Hemisphere, culminating in the gigantic ''Tyrannosaurus''. Fossils of tyrannosauroids have been recovered on what are now the continents of North America, Europe and Asia, with fragmentary remains possibly attributable to tyrannosaurs also known from South America and Australia. Tyrannosauroids were bipedal carnivores, as were most theropods, and were characterized by numerous skeletal features, especially of the skull and pelvis. Early in their existence, tyrannosauroids were small predators with long, three-fingered forelimbs. Late Cretaceous genera became much larger, including some of the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosauroidea
Tyrannosauroidea (meaning 'tyrant lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that includes the family Tyrannosauridae as well as more basal relatives. Tyrannosauroids lived on the Laurasian supercontinent beginning in the Jurassic Period. By the end of the Cretaceous Period, tyrannosauroids were the dominant large predators in the Northern Hemisphere, culminating in the gigantic ''Tyrannosaurus''. Fossils of tyrannosauroids have been recovered on what are now the continents of North America, Europe and Asia, with fragmentary remains possibly attributable to tyrannosaurs also known from South America and Australia. Tyrannosauroids were bipedal carnivores, as were most theropods, and were characterized by numerous skeletal features, especially of the skull and pelvis. Early in their existence, tyrannosauroids were small predators with long, three-fingered forelimbs. Late Cretaceous genera became much larger, including some of the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darren Naish
Darren William Naish is a British vertebrate palaeontologist, author and science communicator. As a researcher, he is best known for his work describing and reevaluating dinosaurs and other Mesozoic reptiles, including '' Eotyrannus'', '' Xenoposeidon'', and azhdarchid pterosaurs. Much of his research has focused on Wealden Group fossils from the Isle of Wight. He is founder of the vertebrate palaeozoology blog Tetrapod Zoology, and has written several popular science books. Naish also makes frequent media appearances and is a scientific consultant and advisor for film, television, museums and exhibitions. Naish is also known for his skepticism and work examining cryptozoology and sea monster sightings and beliefs from a scientific perspective. Research He obtained a geology degree at the University of Southampton and later studied vertebrate palaeontology under British palaeontologist David Martill at the University of Portsmouth, where he obtained both an M. Phil. and PhD. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
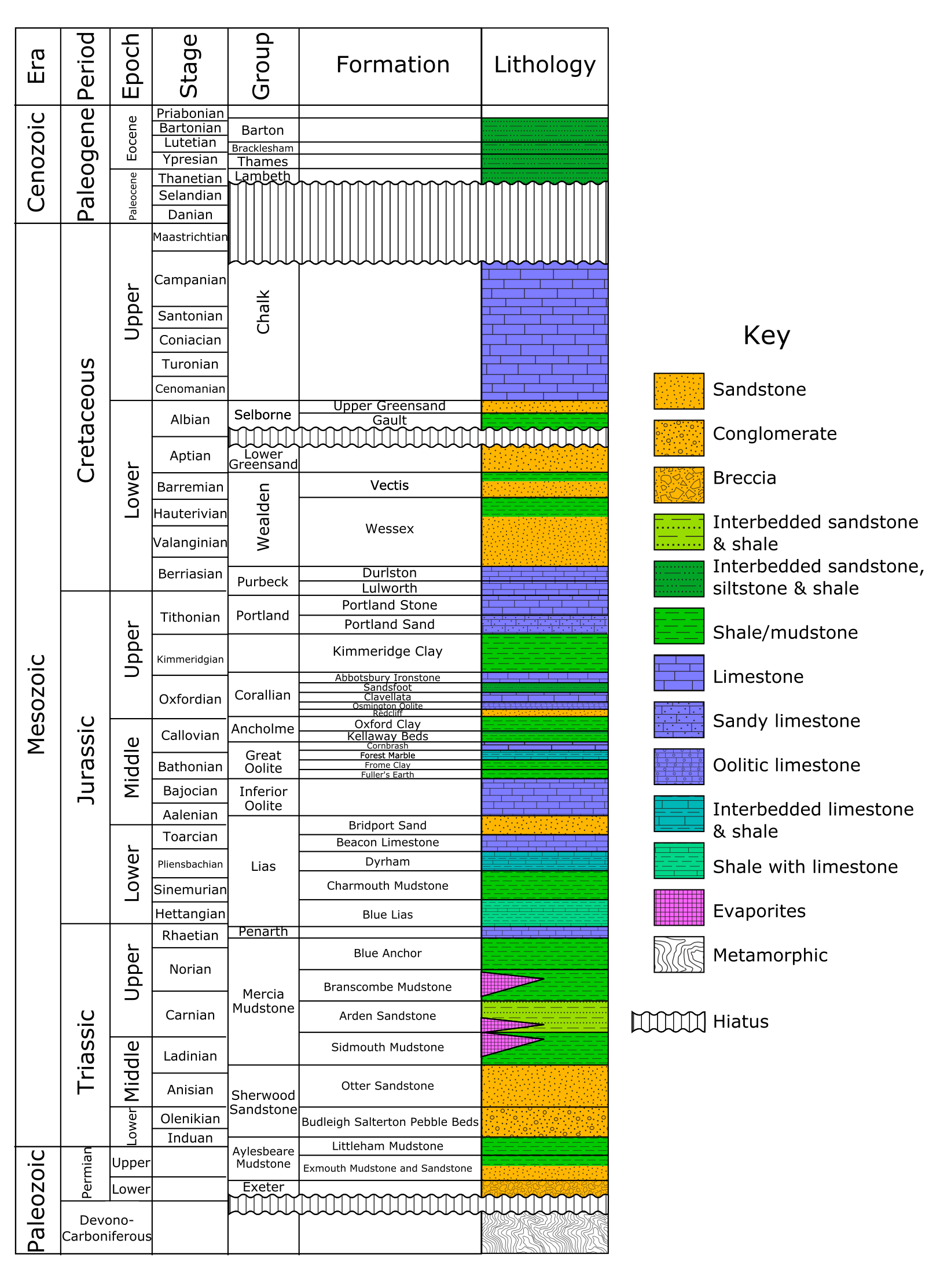
Wessex Formation
The Wessex Formation is a fossil-rich English geological formation that dates from the Berriasian to Barremian stages (about 145–125 million years ago) of the Early Cretaceous. It forms part of the Wealden Group and underlies the younger Vectis Formation and overlies the Durlston Formation. The dominant lithology of this unit is mudstone with some interbedded sandstones. It is part of the strata of the Wessex Basin, exposed in both the Isle of Purbeck and the Isle of Wight. While the Purbeck sections are largely barren of vertebrate remains, the Isle of Wight sections are well known for producing the richest and most diverse fauna in Early Cretaceous Europe. Nomenclatural History The Wessex Formation has historically alternately been called the "Variegated Marls And Sandstones", a name used by W. J. Arkell in his 1947 map of the Isle of Purbeck as well as the "Wealden Marls" It was given its current formal name by Daley and Stewart in 1979 Stratigraphy and Lithology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossa (anatomy)
In anatomy, a fossa (; plural ''fossae'' ( or ); from Latin ''fossa'', "ditch" or "trench") is a depression or hollow, usually in a bone, such as the hypophyseal fossa (the depression in the sphenoid bone).Venieratos D, Anagnostopoulou S, Garidou A., A new morphometric method for the sella turcica and the hypophyseal fossa and its clinical relevance.;Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2005 Nov;64(4):240-7. Some examples include: In the Skull: * Cranial fossa ** Anterior cranial fossa ** Middle cranial fossa *** Interpeduncular fossa ** Posterior cranial fossa * Hypophyseal fossa * Temporal bone fossa ** Mandibular fossa ** Jugular fossa * Infratemporal fossa * Pterygopalatine fossa * Pterygoid fossa * Lacrimal fossa ** Fossa for lacrimal gland ** Fossa for lacrimal sac * Mandibular fossa * Scaphoid fossa * Jugular fossa * Condyloid fossa * Rhomboid fossa In the Mandible: * Retromolar fossa In the Torso: * Fossa ovalis (heart) * Infraclavicular fossa * Pyriform fossa * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute '' tibia''. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body. Structure In human anatomy, the tibia is the second largest bone next to the femur. As in other vertebrates the tibia is one of two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula, and is a component of the knee and ankle joints. The ossification or formation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct amniotes. Foramina inside the body of typically allow , |