|
Enteromyxum
''Enteromyxum'' is a genus of myxozoans. Species The World Register of Marine Species includes the following species in the genus: * '' Enteromyxum fugu'' (Tun, Yokoyama, Ogawa & Wakayabashi, 2002) * ''Enteromyxum leei ''Enteromyxum leei'' is a species of myxozoan, histozoic parasite that infects the intestinal tract and sometimes associated organs, like gall bladder and liver, of several teleostean fish species. Myxozoans are microscopic metazoans, with an obl ...'' (Diamant, Lom & Dyková, 1994) * '' Enteromyxum scophthalmi'' Palenzuela, Redondo & Alvarez-Pellitero, 2002 References Myxidiidae Cnidarian genera {{myxozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteromyxum Leei
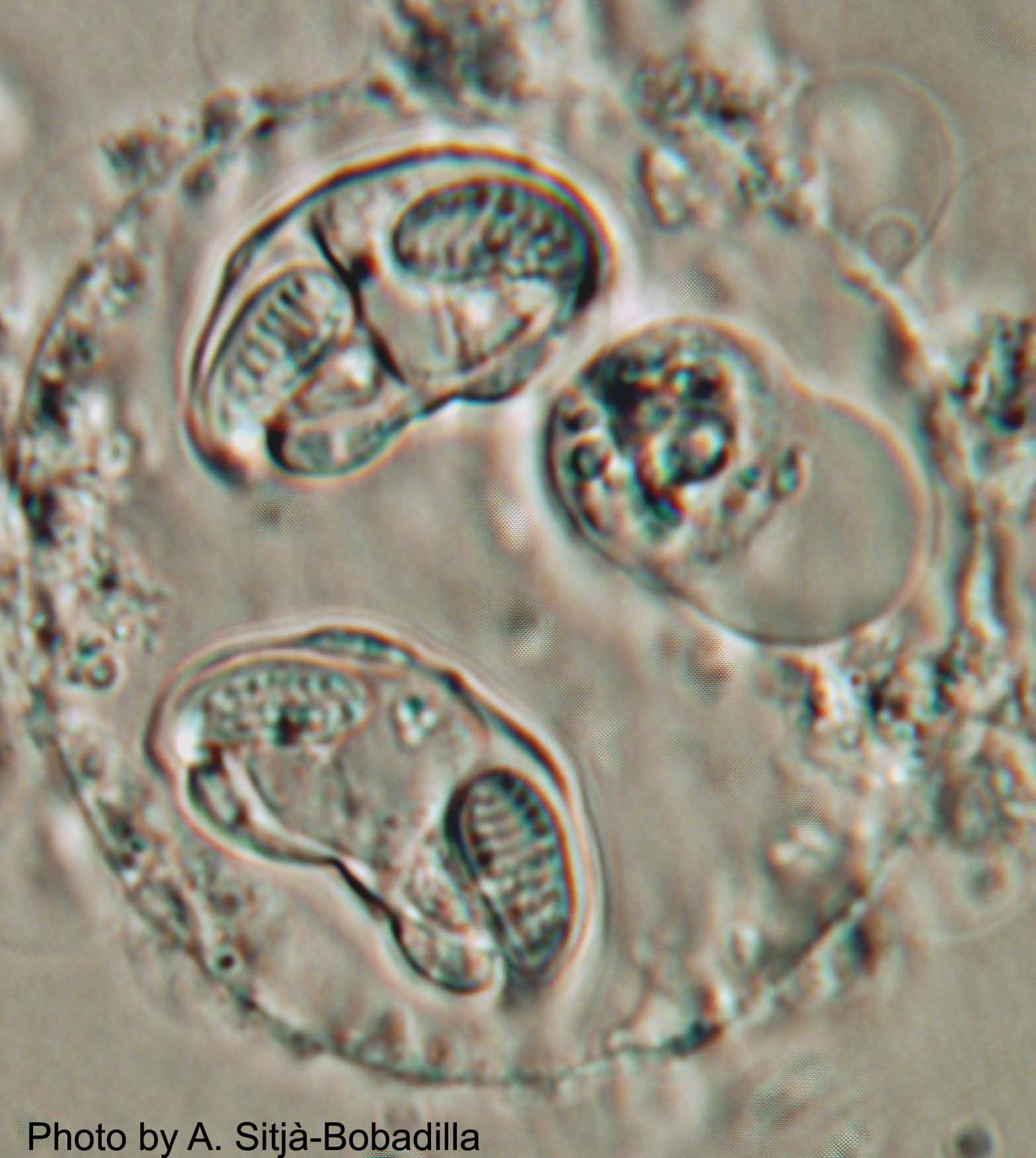
''Enteromyxum leei'' is a species of myxozoan, histozoic parasite that infects the intestinal tract and sometimes associated organs, like gall bladder and liver, of several teleostean fish species. Myxozoans are microscopic metazoans, with an obligate parasitic life-style. The parasite stages of this species live in the paracelullar space between fish enterocytes. It is the causative agent of enteromyxosis, or emaciative disease, also known as "razor blade syndrome" in sparid fish. ''E. leei'' has a wide host and geographical range within marine fish (at least 60 species from 22 different families, mainly Perciforms), and even freshwater fish have been infected experimentally. ''E. leei'' initially emerged in the Mediterranean in the late 1980s and it is believed to have been unintentionally introduced into the Red Sea.Diamant, A. (1997). Fish-to-fish transmission of a marine myxosporean. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 30, 99-105. Its pathogenicity and economic impact depend on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteromyxum Scophthalmi
''Enteromyxum scophthalmi'' is a species of parasitic myxozoan, a pathogen of fish. It is an intestinal parasite of the turbot (''Scophthalmus maximus'') and can cause outbreaks of disease in farmed fish. It causes a cachectic syndrome characterised by loss of weight, muscle atrophy, weakness and fatigue. Taxonomy This parasite was first described in 2002 by Palenzuela, Redondo & Alvarez-Pellitero using material obtained from the gut of a turbot (''Scophthalmus maximus''). The fish were obtained from a farm in northwestern Spain. After examination with light and electron microscopy, and by comparing its ribosomal DNA with that of similar myxozoan species, it was established that this species was closely related to ''Myxidium leei'', another enteric parasite of marine fish, but not to other members of the genus ''Myxidium''. A combination of morphological data and data from molecular analysis resulted in the new genus ''Enteromyxum'' being created to include both the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteromyxum Fugu
''Enteromyxum'' is a genus of myxozoans. Species The World Register of Marine Species includes the following species in the genus: * '' Enteromyxum fugu'' (Tun, Yokoyama, Ogawa & Wakayabashi, 2002) * ''Enteromyxum leei'' (Diamant, Lom & Dyková, 1994) * ''Enteromyxum scophthalmi ''Enteromyxum scophthalmi'' is a species of parasitic myxozoan, a pathogen of fish. It is an intestinal parasite of the turbot (''Scophthalmus maximus'') and can cause outbreaks of disease in farmed fish. It causes a cachectic syndrome char ...'' Palenzuela, Redondo & Alvarez-Pellitero, 2002 References Myxidiidae Cnidarian genera {{myxozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxozoa
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. Over 2,180 species have been described and some estimates have suggested at least 30,000 undiscovered species. Many have a two-host lifecycle, involving a fish and an annelid worm or a bryozoan. The average size of a myxosporean spore usually ranges from 10 μm to 20 μm, whereas that of a malacosporean (a subclade of the Myxozoa) spore can be up to 2 mm. Myxozoans can live in both freshwater and marine habitats. Myxozoans are highly derived cnidarians that have undergone dramatic evolution from a free swimming, self-sufficient jellyfish-like creature into their current form of obligate parasites composed of very few cells – sometimes only a single cell. As myxozoans evolved into microscopic parasites, they lost many g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxidiidae
Myxidiidae is a family of myxozoans. Genera The World Register of Marine Species includes the following genera in the family: * ''Enteromyxum'' Palenzuela, Redondo & Alvarez-Pellitero, 2002 * ''Myxidium ''Myxidium'' is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Myxidiidae. The genus has cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world ...'' Buetschli, 1882 * '' Sigmomyxa'' Karlsbakk & Køie, 2012 * '' Zschokkella'' Auerbach, 1909 References Cnidarian families Variisporina {{parasitic animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Register Of Marine Species
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms. Content The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scientific specialists on each group of organism. These taxonomists control the quality of the information, which is gathered from the primary scientific literature as well as from some external regional and taxon-specific databases. WoRMS maintains valid names of all marine organisms, but also provides information on synonyms and invalid names. It is an ongoing task to maintain the registry, since new species are constantly being discovered and described by scientists; in addition, the nomenclature and taxonomy of existing species is often corrected or changed as new research is constantly being published. Subsets of WoRMS content are made available, and can have separate badging and their own home/launch pages, as "subregisters", such as the ''World List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |