|
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic ( Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Latin-script Digraphs
This is a list of digraphs used in various Latin alphabets. Capitalisation involves only the first letter (''ch'' becomes ''Ch'') unless otherwise stated (''ij'' becomes ''IJ''). Letters with diacritics are arranged in alphabetic order according to their base: is alphabetised with , not at the end of the alphabet, as it would be in Danish, Norwegian and Swedish. Substantially-modified letters, such as (a variant of ) and (based on ), are placed at the end. Apostrophe (capital ) is used in Bari for . (capital ) is used in Bari for . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for when it appears in a dark or ''yin'' tone. It is also often written as . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark (capital ) is used in Bari and Hausa (in Nigeria) for , but in Niger, Hausa is replaced with . A is used in Taa, where it represents the glottalized o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rh (digraph)
This is a list of digraphs used in various Latin alphabets. Capitalisation involves only the first letter (''ch'' becomes ''Ch'') unless otherwise stated (''ij'' becomes ''IJ''). Letters with diacritics are arranged in alphabetic order according to their base: is alphabetised with , not at the end of the alphabet, as it would be in Danish, Norwegian and Swedish. Substantially-modified letters, such as (a variant of ) and (based on ), are placed at the end. Apostrophe (capital ) is used in Bari for . (capital ) is used in Bari for . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for when it appears in a dark or ''yin'' tone. It is also often written as . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark (capital ) is used in Bari and Hausa (in Nigeria) for , but in Niger, Hausa is replaced with . A is used in Taa, where it represents the glottalized o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian English
Canadian English (CanE, CE, en-CA) encompasses the varieties of English native to Canada. According to the 2016 census, English was the first language of 19.4 million Canadians or 58.1% of the total population; the remainder spoke French (20.8%) or other languages (21.1%). In Quebec, 7.5% of the population are anglophone, as most of Quebec's residents are native speakers of Quebec French. Phonologically, Canadian and American English are classified together as North American English, emphasizing the fact that most cannot distinguish the typical accents of the two countries by sound alone. While Canadian English tends to be closer to American English in most regards,Labov, p. 222. it does possess elements from British English and some uniquely Canadian characteristics.Dollinger, Stefan (2008). "New-Dialect Formation in Canada". Amsterdam: Benjamins, . p. 25. The precise influence of American English, British English and other sources on Canadian English varieties has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
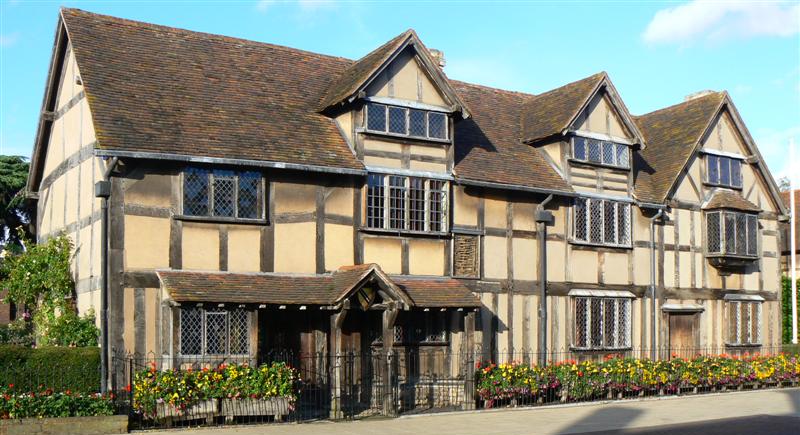
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the " Bard of Avon" (or simply "the Bard"). His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. He remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted. Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18, he married Anne Hathaway, with whom he had three children: Susanna, and twins Hamnet and Judith. Sometime between 1585 and 1592, he began a successful career in London as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiberno-English
Hiberno-English (from Latin '' Hibernia'': "Ireland"), and in ga, Béarla na hÉireann. or Irish English, also formerly Anglo-Irish, is the set of English dialects native to the island of Ireland (including both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland). In the Republic of Ireland, English is one of two official languages, along with the Irish language, and is the country's working language. Irish English's writing standards, such as its spelling, align with British English. However, Irish English's diverse accents and some of its grammatical structures and vocabulary are unique, with some influences deriving from the Irish language and some notably conservative phonological features: features no longer common in the accents of England or North America. Phonologists today often divide Irish English into four or five overarching dialects or accents:Hickey, Raymond. ''A Sound Atlas of Irish English'', Volume 1. Walter de Gruyter: 2004pp. 57–60. Ulster accents, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a comprehensive resource to scholars and academic researchers, as well as describing usage in its many variations throughout the world. Work began on the dictionary in 1857, but it was only in 1884 that it began to be published in unbound Serial (literature), fascicles as work continued on the project, under the name of ''A New English Dictionary on Historical Principles; Founded Mainly on the Materials Collected by The Philological Society''. In 1895, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' was first used unofficially on the covers of the series, and in 1928 the full dictionary was republished in 10 bound volumes. In 1933, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' fully replaced the former name in all occurrences in its reprinting as 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances is the de facto common language used in government, education and commerce. Since the 20th century, American English has become the most influential form of English worldwide. American English varieties include many patterns of pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar and particularly spelling that are unified nationwide but distinct from other English dialects around the world. Any American or Canadian accent perceived as lacking noticeably local, ethnic or cultural markers is popularly called "General" or "Standard" American, a fairly uniform accent continuum native to certain regions of the U.S. and associated nationally with broadcast mass media and highly educated speech. However, historical and present linguistic evidence does not sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the '' Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first fully phonemic script, the Proto-Sinaitic script, later known as the Phoenician alphabet, is considered to be the first alphabet and is the ancestor of most modern alphabets, including Arabic, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Latin, and possibly Brahmic. It was created by Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in the Sinai Peninsula (as the Proto-Sinaitic script), by selecting a small number of hieroglyphs commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values of the Canaanite languages. However, Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |