|
Engine Test Stand
An engine test stand is a facility used to develop, characterize and test engines. The facility, often offered as a product to automotive OEMs, allows engine operation in different operating regimes and offers measurement of several physical variables associated with the engine operation. A sophisticated engine test stand houses several sensors (or transducers), data acquisition features and actuators to control the engine state. The sensors would measure several physical variables of interest which typically include: * crankshaft torque and angular velocity * intake air and fuel consumption rates, often detected using volumetric and/or gravimetric measurement methods * air-fuel ratio for the intake mixture, often detected using an exhaust gas oxygen sensor * environment pollutant concentrations in the exhaust gas such as carbon monoxide, different configurations of hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter * temperatures and gas pressures at severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
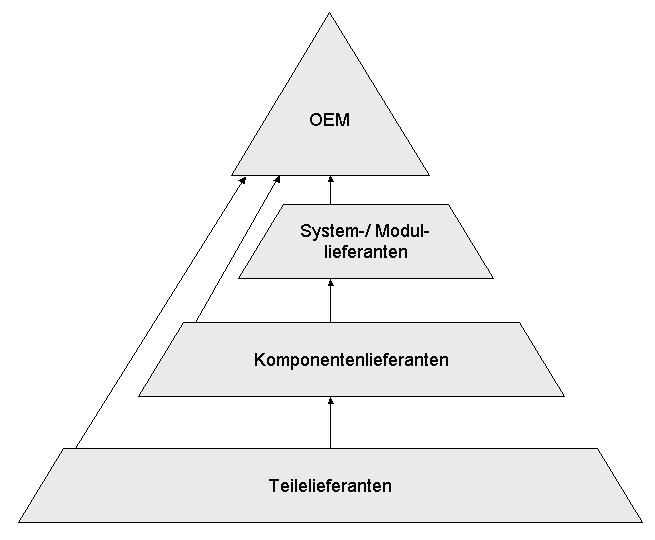
Original Equipment Manufacturer
An original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is generally perceived as a company that produces non-aftermarket parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. It is a common industry term recognized and used by many professional organizations such as SAE International, ISO, and others. However, the term is also used in several other ways, which causes ambiguity. It sometimes means the maker of a system that includes other companies' subsystems, an end-product producer, an automotive part that is manufactured by the same company that produced the original part used in the automobile's assembly, or a value-added reseller.Ken Olsen: PDP-1 and PDP-8 (page 3) , economicadventure.com Automotive parts When referring to auto parts, OEM refers to the manufactur ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressures
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch ( psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Manometric uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Doppler Velocimetry
Laser Doppler velocimetry, also known as laser Doppler anemometry, is the technique of using the Doppler shift in a laser beam to measure the velocity in transparent or semi-transparent fluid flows or the linear or vibratory motion of opaque, reflecting surfaces. The measurement with laser Doppler anemometry is absolute and linear with velocity and requires no pre-calibration. Technology origin The development of the helium–neon laser (He-Ne) in 1962 at the Bell Telephone Laboratories provided the optics community with a continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source that was highly concentrated at a wavelength of 632.8 nanometers (nm) in the red portion of the visible spectrum. It was discovered that fluid flow measurements could be made using the Doppler effect on a He-Ne beam scattered by small polystyrene spheres in the fluid. At the Research Laboratories of Brown Engineering Company (later Teledyne Brown Engineering), this phenomenon was used to develop the first laser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Test Cycles
An emission test cycle is a protocol contained in an emission standard to allow repeatable and comparable measurement of exhaust emissions for different engines or vehicles. Test cycles specify the specific conditions under which the engine or vehicle is operated during the emission test. There are many different test cycles issued by various national and international governments and working groups. Specified parameters in a test cycle include a range of operating temperature, speed, and load. Ideally these are specified so as to accurately and realistically represent the range of conditions under which the vehicle or engine will be operated in actual use. Because it is impractical to test an engine or vehicle under every possible combination of speed, load, and temperature, this may not actually be the case. Vehicle and engine manufacturers may exploit the limited number of test conditions in the cycle by programming their engine management systems to control emissions to regulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, which in turn may vary per application, and this spectrum of variance is often illustrated as a continuous energy profile. Non-transportation applications, such as industry, benefit from increased fuel efficiency, especially fossil fuel power plants or industries dealing with combustion, such as ammonia production during the Haber process. In the context of transport, fuel economy is the energy efficiency of a particular vehicle, given as a ratio of distance traveled per unit of fuel consumed. It is dependent on several factors including engine efficiency, transmission design, and tire design. In most countries, using the metric system, fuel economy is stated as "fuel consumption" in liters per 100 kilometers (L/100 km) or kilometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feedback Mechanism
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a Signal chain (signal processing chain), chain of Causality, cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems: History Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback had started to enter Economics, economic theory in Britain by the 18th century, but it was not at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so did not have a name. The first ever known artificial feedback device was a Ballcock, float valve, for maintaining water at a constant level, invented in 270 BC in Alexandria, Ancient Egypt, Egypt. This device illustrated the principle of feedback: a low water level opens the valve, the rising water then provides feedback into the system, closing the valve when the required level is reached. This then reoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips. In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). An SoC may connect the external microcontroller chips as the motherboard components, but an SoC usually integrates the advanced peripherals like graphics processing unit (GPU) and Wi-Fi interface controller as its internal microcontroller unit circuits. Microcontrollers are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induction Motor
An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding. An induction motor can therefore be made without electrical connections to the rotor. An induction motor's rotor can be either wound type or squirrel-cage type. Three-phase squirrel-cage induction motors are widely used as industrial drives because they are self-starting, reliable and economical. Single-phase induction motors are used extensively for smaller loads, such as household appliances like fans. Although traditionally used in fixed-speed service, induction motors are increasingly being used with variable-frequency drives (VFD) in variable-speed service. VFDs offer especially important energy savings opportunities for existing and prospective induction motors in variable-torque centrifugal fan, pump and compressor load applications. Squirrel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intake Manifold
In automotive engineering, an inlet manifold or intake manifold (in American English) is the part of an engine that supplies the fuel/air mixture to the cylinders. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' epeatedly and refers to the multiplying of one (pipe) into many.manifold, (adv.) "in the proportion of many to one, by many times". AD1526 ''Oxford English Dictionary'', In contrast, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into a smaller number of pipes – often down to one pipe. The primary function of the intake manifold is to ''evenly'' distribute the combustion mixture (or just air in a direct injection engine) to each intake port in the cylinder head(s). Even distribution is important to optimize the efficiency and performance of the engine. It may also serve as a mount for the carburetor, throttle body, fuel injectors and other components of the engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |