|
EnOcean
The EnOcean technology is an energy harvesting wireless technology used primarily in building automation systems, but also in other application fields such as industry, transportation, logistics or smart homes solutions. The energy harvesting wireless modules are manufactured and marketed by the company EnOcean, headquartered in Oberhaching near Munich. The modules combine micro energy converters with ultra low power electronics and wireless communications and enable batteryless, wireless sensors, switches, and controls. In March 2012, the EnOcean wireless standard was ratified as the international standard ISO/ IEC 14543-3-10, which is optimized for wireless solutions with ultra-low power consumption and energy harvesting. The standard covers the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) layers 1-3 which are the physical, data link and networking layers. EnOcean is offering its technology and licenses for the patented features within the EnOcean Alliance framework. Technology EnOcean t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
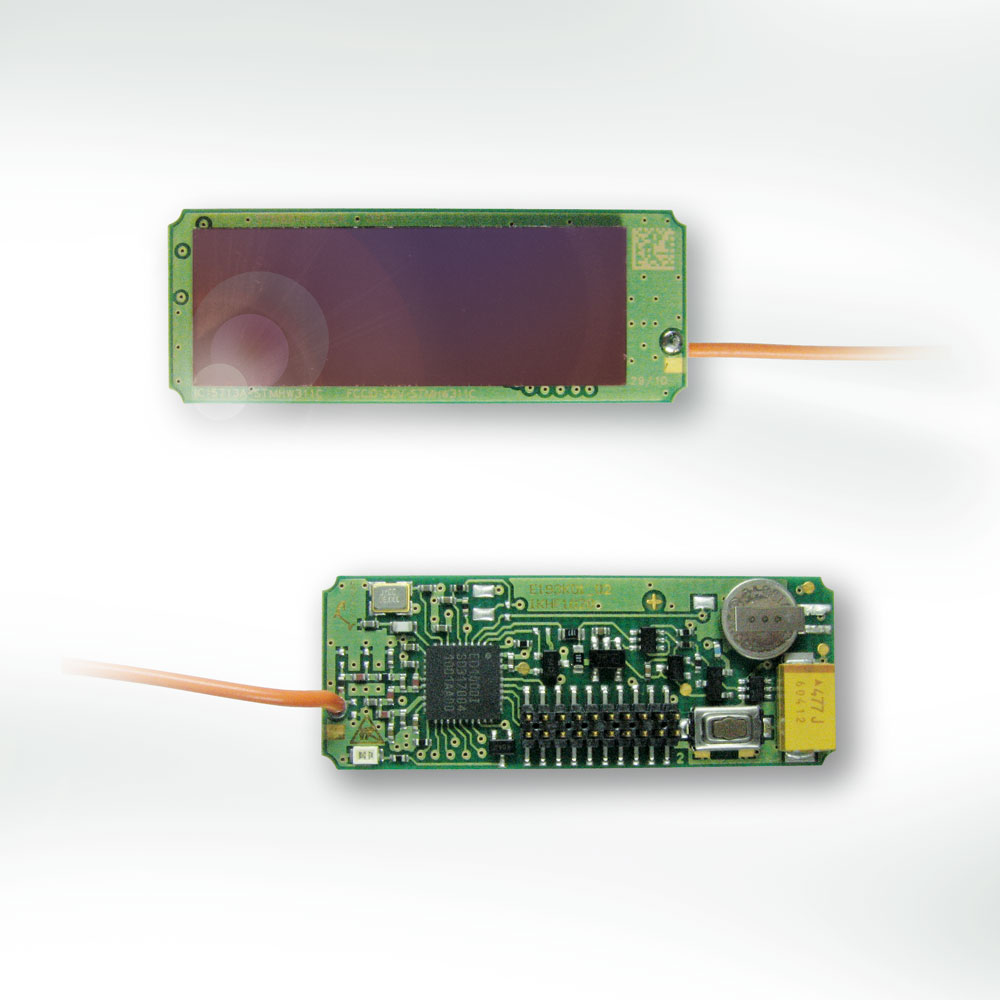
EnOcean STM310 Mit Solarzelle White
The EnOcean technology is an energy harvesting wireless technology used primarily in building automation systems, but also in other application fields such as industry, transportation, logistics or Home automation, smart homes solutions. The energy harvesting wireless modules are manufactured and marketed by the company EnOcean, headquartered in Oberhaching near Munich. The modules combine micro energy converters with ultra low power electronics and wireless communications and enable batteryless, Wireless sensor network, wireless sensors, switches, and controls. In March 2012, the EnOcean wireless standard was ratified as the international standard International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC 14543-3-10, which is optimized for wireless solutions with ultra-low power consumption and energy harvesting. The standard covers the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) layers 1-3 which are the physical, data link and networking layers. EnOc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EnOcean ECT310
The EnOcean technology is an energy harvesting wireless technology used primarily in building automation systems, but also in other application fields such as industry, transportation, logistics or smart homes solutions. The energy harvesting wireless modules are manufactured and marketed by the company EnOcean, headquartered in Oberhaching near Munich. The modules combine micro energy converters with ultra low power electronics and wireless communications and enable batteryless, wireless sensors, switches, and controls. In March 2012, the EnOcean wireless standard was ratified as the international standard ISO/IEC 14543-3-10, which is optimized for wireless solutions with ultra-low power consumption and energy harvesting. The standard covers the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) layers 1-3 which are the physical, data link and networking layers. EnOcean is offering its technology and licenses for the patented features within the EnOcean Alliance framework. Technology EnOcean te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enocean Eco200
The EnOcean technology is an energy harvesting wireless technology used primarily in building automation systems, but also in other application fields such as industry, transportation, logistics or smart homes solutions. The energy harvesting wireless modules are manufactured and marketed by the company EnOcean, headquartered in Oberhaching near Munich. The modules combine micro energy converters with ultra low power electronics and wireless communications and enable batteryless, wireless sensors, switches, and controls. In March 2012, the EnOcean wireless standard was ratified as the international standard ISO/IEC 14543-3-10, which is optimized for wireless solutions with ultra-low power consumption and energy harvesting. The standard covers the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) layers 1-3 which are the physical, data link and networking layers. EnOcean is offering its technology and licenses for the patented features within the EnOcean Alliance framework. Technology EnOcean te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Harvesting
Energy harvesting (EH, also known as power harvesting or energy scavenging or ambient power) is the process by which energy is derived from external sources (e.g., solar power, thermal energy, wind energy, salinity gradients, and kinetic energy, also known as ambient energy), and then captured, and stored for small, wireless autonomous devices, like those used in wearable electronics and wireless sensor networks. Energy harvesters usually provide a very small amount of power for low-energy electronics. While the input fuel to some large-scale generation costs resources (oil, coal, etc.), the energy source for energy harvesters is present as ambient background. For example, temperature gradients exist from the operation of a combustion engine and in urban areas, there is a large amount of electromagnetic energy in the environment because of radio and television broadcasting. One of the earliest applications of ambient power collected from ambient electromagnetic radiation (EMR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio ''wireless technology'' include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Automation
Building automation (BAS), also known as building management system (BMS) or building energy management system (BEMS), is the automatic centralized control of a building's HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning), electrical, lighting, shading, Access Control, Security Systems, and other interrelated systems. Some objectives of building automation are improved occupant comfort, efficient operation of building systems, reduction in energy consumption, reduced operating and maintaining costs and increased security. BAS functionality may keep a buildings climate within a specified range, provide light to rooms based on an occupancy, monitor performance and device failures, and provide malfunction alarms to building maintenance staff. A BAS works to reduce building energy and maintenance costs compared to a non-controlled building. Most commercial, institutional, and industrial buildings built after 2000 include a BAS, whilst older buildings may be retrofitted with a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osram
Osram Licht AG is a German company that makes electric lights, headquartered in Munich and Premstätten (Austria). Osram positions itself as a high-tech photonics company that is increasingly focusing on sensor technology, visualization and treatment by light. The company serves customers in the consumer, automotive, healthcare and industrial technology sectors. The operating company of Osram is Osram GmbH. Osram was founded in 1919 by the merger of the lighting businesses of Auergesellschaft, Siemens & Halske and Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft (AEG). Osram was a wholly owned subsidiary of Siemens AG from 1978 to 2013. On 5 July 2013, Osram was spun off from Siemens, and the listing of its stock began on Frankfurt Stock Exchange on 8 July 2013. Osram's business with conventional light sources was spun off in 2016 under the name Ledvance and sold to a Chinese consortium. After a bidding war with Bain Capital, Osram was taken over by Austrian company AMS in July 2020. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Sensor
A carbon dioxide sensor or CO2 sensor is an instrument for the measurement of carbon dioxide gas. The most common principles for CO2 sensors are infrared gas sensors ( NDIR) and chemical gas sensors. Measuring carbon dioxide is important in monitoring indoor air quality, the function of the lungs in the form of a capnograph device, and many industrial processes. Nondispersive infrared (NDIR) CO2 sensors NDIR sensors are spectroscopic sensors to detect CO2 in a gaseous environment by its characteristic absorption. The key components are an infrared source, a light tube, an interference (wavelength) filter, and an infrared detector. The gas is pumped or diffuses into the light tube, and the electronics measure the absorption of the characteristic wavelength of light. NDIR sensors are most often used for measuring carbon dioxide.Carbonate Based CO2 Sensors with High Performance, Th. Lang, H.-D. Wiemhöfer and W. Göpel, Conf.Proc.Eurosensors IX, Stockholm (S) (1995); Sensors and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens Building Technologies
Siemens Building Technologies is an Operating Division of Siemens. It provides automation technologies and services for commercial, industrial and public buildings and infrastructures. The division is headquartered in Zug, Switzerland, and employs 28,069 people worldwide (September 2018) . History Siemens Building Technologies resulted from the 1998 acquisition of the industrial activities of Elektrowatt Ltd. ( Zurich, Switzerland), Cerberus Ltd. (Männdedorf, Switzerland), and of Staefa Control System Ltd. ( Stäfa, Switzerland) by Siemens.Siemens Building Technologies About UHistory Siemens Building Technology The newly built Siemens Building Technologies CPS Software House was opened in Chicago in October 2017, built for $20 million as an R&D facility. In 2018, the division made a number of acquisitions, including Comfy in Oakland, and the smart-building companies J2 Innovations and Enlightened. President of the Siemens Building Technologies division was Dave Hopping. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens AG
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad. The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''Energy'', ''Healthcare'' (Siemens Healthineers), and ''Infrastructure & Cities'', which represent the main activities of the corporation. The corporation is a prominent maker of medical diagnostics equipment and its medical health-care division, which generates about 12 percent of the corporation's total sales, is its second-most profitable unit, after the industrial automation division. In this area, it is regarded as a pioneer and the company with the highest revenue in the world. The corporation is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Siemens and its subsidiaries employ approximately 303,000 people worldwide and reported global revenue of around €62 billion in 2021 according to its earnings release. History 1847 to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberhaching
Oberhaching is a municipality in Bavaria, Germany, with 13,638 inhabitants (2020) on an area of . It is located south of Munich city centre and has a 1,250 year history. Architecture The most important buildings are the originally Romanesque church St Stephan in the centre of Oberhaching, the Gothic church Mariae Geburt in Oberbiberg, the Baroque church Holy Cross in Kreuzpullach and the Renaissance Wittelsbach mansion in Laufzorn. The small palace was built by Albert VI, Duke of Bavaria and later served as a residence for his nephew Maximilian Philipp Hieronymus, Duke of Bavaria-Leuchtenberg. Sports Oberhaching is home to the basketball team TSV Oberhaching Tropics who play in Germany's ProB league. The Paraguay national football team was stationed in Oberhaching during the 2006 FIFA World Cup. Transport Oberhaching has its own motorway exit on the A 995, which connects the motorway junction Munich-South (and thus the A 99 and the A 8) with the Munich district of Obergies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)