|
Elongated Square Gyrobicupola
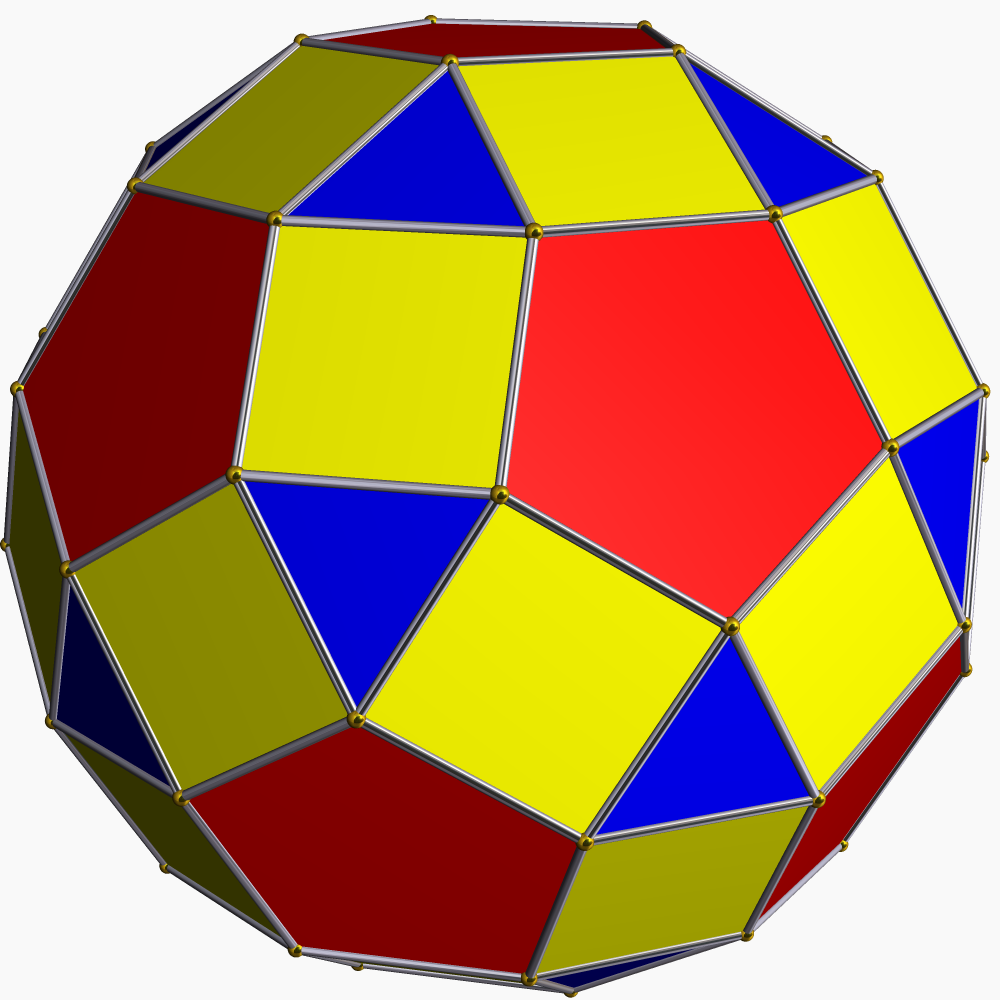
In geometry, the elongated square gyrobicupola or pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron is one of the Johnson solids (). It is not usually considered to be an Archimedean solid, even though its faces consist of regular polygons that meet in the same pattern at each of its vertices, because unlike the 13 Archimedean solids, it lacks a set of global symmetries that map every vertex to every other vertex (though Grünbaum has suggested it should be added to the traditional list of Archimedean solids as a 14th example). It strongly resembles, but should not be mistaken for, the rhombicuboctahedron, which ''is'' an Archimedean solid. It is also a canonical polyhedron. This shape may have been discovered by Johannes Kepler in his enumeration of the Archimedean solids, but its first clear appearance in print appears to be the work of Duncan Sommerville in 1905. It was independently rediscovered by J. C. P. Miller by 1930 (by mistake while attempting to construct a model of the rhombi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each vertex. An example of a Johnson solid is the square-based pyramid with equilateral sides ( ); it has 1 square face and 4 triangular faces. Some authors require that the solid not be uniform (i.e., not Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, uniform prism, or uniform antiprism) before they refer to it as a “Johnson solid”. As in any strictly convex solid, at least three faces meet at every vertex, and the total of their angles is less than 360 degrees. Since a regular polygon has angles at least 60 degrees, it follows that at most five faces meet at any vertex. The pentagonal pyramid () is an example that has a degree-5 vertex. Although there is no obvious restriction that any given regular polygon cannot be a face of a Johnson solid, it turns out that the faces of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branko Grünbaum
Branko Grünbaum ( he, ברנקו גרונבאום; 2 October 1929 – 14 September 2018) was a Croatian-born mathematician of Jewish descentBranko Grünbaum Hrvatska enciklopedija LZMK. and a professor at the in . He received his Ph.D. in 1957 from Hebrew University of Jerusalem< ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrate Rhombicosidodecahedron
In geometry, the gyrate rhombicosidodecahedron is one of the Johnson solids (). It is also a canonical polyhedron. Related polyhedron It can be constructed as a rhombicosidodecahedron with one pentagonal cupola rotated through 36 degrees. They have the same faces around each vertex, but vertex configurations along the rotation become a different order, . Alternative Johnson solids, constructed by rotating different cupolae of a rhombicosidodecahedron, are: * The parabigyrate rhombicosidodecahedron () where two opposing cupolae are rotated; * The metabigyrate rhombicosidodecahedron () where two non-opposing cupolae are rotated; * And the trigyrate rhombicosidodecahedron In geometry, the trigyrate rhombicosidodecahedron is one of the Johnson solids (). It contains 20 triangles, 30 squares and 12 pentagons. It is also a Midsphere#Canonical polyhedron, canonical polyhedron. It can be constructed as a rhombicosi ... () where three cupolae are rotated. External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Cupola
In geometry, the square cupola, sometimes called lesser dome, is one of the Johnson solids (). It can be obtained as a slice of the rhombicuboctahedron. As in all cupolae, the base polygon has twice as many edges and vertices as the top; in this case the base polygon is an octagon. Formulae The following formulae for the circumradius, surface area, volume, and height can be used if all faces are regular, with edge length ''a'': :C=\left(\frac\sqrt\right)a\approx1.39897a, :A=\left(7+2\sqrt+\sqrt\right)a^2\approx11.56048a^2, :V=\left(1+\frac\right)a^3\approx1.94281a^3. :h = \fraca \approx 0.70711a Related polyhedra and honeycombs Other convex cupolae Dual polyhedron The dual of the square cupola has 8 triangular and 4 kite faces: Crossed square cupola The crossed square cupola is one of the nonconvex Johnson solid isomorphs, being topologically identical to the convex square cupola. It can be obtained as a slice of the nonconvex great rhombicuboctahedron or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudorhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the elongated square gyrobicupola or pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron is one of the Johnson solids (). It is not usually considered to be an Archimedean solid, even though its faces consist of regular polygons that meet in the same pattern at each of its vertices, because unlike the 13 Archimedean solids, it lacks a set of global symmetries that map every vertex to every other vertex (though Grünbaum has suggested it should be added to the traditional list of Archimedean solids as a 14th example). It strongly resembles, but should not be mistaken for, the rhombicuboctahedron, which ''is'' an Archimedean solid. It is also a canonical polyhedron. This shape may have been discovered by Johannes Kepler in his enumeration of the Archimedean solids, but its first clear appearance in print appears to be the work of Duncan Sommerville in 1905. It was independently rediscovered by J. C. P. Miller by 1930 (by mistake while attempting to construct a model of the rhombicubocta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploded Rhombicuboctahedron
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume associated with an extreme outward release of energy, usually with the generation of high temperatures and release of high-pressure gases. Supersonic explosions created by high explosives are known as detonations and travel through shock waves. Subsonic explosions are created by low explosives through a slower combustion process known as deflagration. Causes Explosions can occur in nature due to a large influx of energy. Most natural explosions arise from volcanic or stellar processes of various sorts. Explosive volcanic eruptions occur when magma rises from below, it has very dissolved gas in it. The reduction of pressure as the magma rises and causes the gas to bubble out of solution, resulting in a rapid increase in volume. Explosions also occur as a result of impact events and in phenomena such as hydrothermal explosions (also due to volcanic processes). Explosions can also occur outside of Earth in the universe in events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |