|
Elkosh
Elkosh ( he, אֶלְקוֹשׁ) is a moshav in northern Israel. Located near Ma'alot-Tarshiha and the Lebanese border, it falls under the jurisdiction of Ma'ale Yosef Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The village was established in 1949 by immigrants from Yemen. It is located on the land of the Palestinian villages of Dayr al-Qassi and Al-Mansura, both depopulated in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. It was named after the biblical city of Elkosh, birth-town of prophet Nahum ( Nahum 1:1), which was located in the area.Carta's Official Guide to Israel and Complete Gazetteer to all Sites in the Holy Land. (3rd edition 1993) Jerusalem, Carta, p. 144, The founders were later joined by more immigrants from Kurdistan Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish la .... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dayr Al-Qassi
Dayr al-Qassi or Deir el-Qasi ( ar, دير القاسي), was a Palestinian Arab village located 26 km northeast of the city of Acre, which was depopulated during 1948 Arab-Israeli war. Geography The village was located 26 km northeast of the city of Acre, on a rocky hill about 5 km south of the Lebanese border. It was linked by a paved road to Fassuta in the north and Tarshiha in the southwest. The road divided the town into an eastern and one western quarter, or ''haras,'' the eastern quarter being higher up.Khalidi, 1992, p. 12 History The first part of the village name, ''Dayr'' ("monastery") suggest that the village might have had a monastery and a Christian population. However, in modern times the population was Muslim. According to the residents of the village, ancient artifacts from the Canaanite, Israelite and Roman period were unearthed in the Ottoman and British Mandate period. Ceramics from the late Roman and the Byzantine eras have been found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahum
Nahum ( or ; he, נַחוּם ''Naḥūm'') was a minor prophet whose prophecy is recorded in the ''Tanakh'', also called the Hebrew Bible and The Old Testament. His book comes in chronological order between Micah and Habakkuk in the Bible. He wrote about the end of the Assyrian Empire, and its capital city, Nineveh, in a vivid poetic style. Life Little is known about Nahum's personal history. His name means "comforter," and he was from the town of Alqosh (Nahum 1:1), which scholars have attempted to identify with several cities, including the modern Alqosh in northern Iraq and Capernaum of northern Galilee. He was a very nationalistic Hebrew, however, and lived amongst the Elkoshites in peace. Nahum, called "the Elkoshite", is the seventh in order of the minor prophets. Works Nahum's writings could be taken as prophecy or as history. One account suggests that his writings are a prophecy written in about 615 BC, just before the downfall of Assyria, while another account sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mansura, Acre
:''See Mansura (other) for other places with similar names.'' Al-Mansura ( ar, المنصورة), was a Palestinian village that was depopulated by the Israeli army during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. In 1945, it had a population of 2,300 together with the neighboring villages of Dayr al-Qassi (also depopulated) and Fassuta. The population was predominantly Christians, Christian and most its residents live in what is now the state of Israel. It was situated on the northern end of a mountain in the Upper Galilee whose summit was behind the village to the south. It was connected to the coastal Acre, Israel, Acre-Ras al-Naqoura highway via a secondary road. History The village was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1517; in 1596 it appeared under the name of ''al-Mansura'' in the Defter, tax registers as part of the ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Jira in the ''Sanjak'' (district) of Safad. It had an all Muslim population, consisting of 17 households and 5 bachelors. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma'ale Yosef Regional Council
The Ma'ale Yosef Regional Council ( he, מועצה אזורית מעלה יוסף, ''Mo'atza Azorit Ma'aleh Yosef'') is a regional council in the Upper Galilee, part of the Northern District of Israel, situated between the towns of Ma'alot-Tarshiha and Shlomi. Its offices are located in Gornot HaGalil. The council was established in 1963, although most of its settlements were founded in the 1950s. It was named for Yosef Weiz, Zionist pioneer of the Second Aliyah and director of the Jewish National Fund following the First World War. Geography The council runs along the Israel-Lebanon border. It is bounded on the west by the Mateh Asher Regional Council and Kafr Yasif, on the south by the Misgav Regional Council, and on the east by the Merom HaGalil Regional Council. Within its geographic area are several Druze and other Israeli-Arab villages. List of settlements The regional council provides municipal services for the populations within its territory, who live on mosha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Northern District (Israel)
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places Established In 1949
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshavim
A moshav ( he, מוֹשָׁב, plural ', lit. ''settlement, village'') is a type of Israeli town or settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms settler, pioneered by the Labor Zionism, Labour Zionists between 1904 and 1914, during what is known as the Second Aliyah, second wave of ''aliyah''. A resident or a member of a moshav can be called a "moshavnik" (). The moshavim are similar to kibbutzim with an emphasis on community labour. They were designed as part of the Zionist state-building programme following the green revolution Yishuv ("settlement") in the Mandatory Palestine, British Mandate of Palestine during the early 20th century, but in contrast to the collective farming kibbutzim, farms in a moshav tended to be individually owned but of fixed and equal size. Workers produced crops and other goods on their properties through individual or pooled labour with the profit and foodstuffs going to provide for themselves. Mosha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish languages, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros Mountains, Zagros and the eastern Taurus Mountains, Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey (Turkish Kurdistan, Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq (Iraqi Kurdistan, Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran (Iranian Kurdistan, Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria (Syrian Kurdistan, Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern South Caucasus, Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalism, Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Palestine Studies
The Institute for Palestine Studies (IPS) is the oldest independent nonprofit public service research institute in the Arab world. It was established and incorporated in Beirut, Lebanon, in 1963 and has since served as a model for other such institutes in the region. It is the only institute in the world solely concerned with analyzing and documenting Palestinian affairs and the Arab–Israeli conflict. It also publishes scholarly journals and has published over 600 books, monographs, and documentary collections in English, Arabic and French—as well as its renowned #Publications, quarterly academic journals: ''Journal of Palestine Studies'', ''Jerusalem Quarterly'', and ''Majallat al-Dirasat al-Filistiniyyah''. IPS's Library in Beirut is the largest in the Arab world specializing in Palestinian affairs, the Arab–Israeli conflict, and Judaica. It is led by a Board of Trustees comprising some forty scholars, businessmen, and public figures representing almost all Arab countries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington D
Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough ** Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Washington, Wisconsin (other) * Fort Washington (disambiguatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
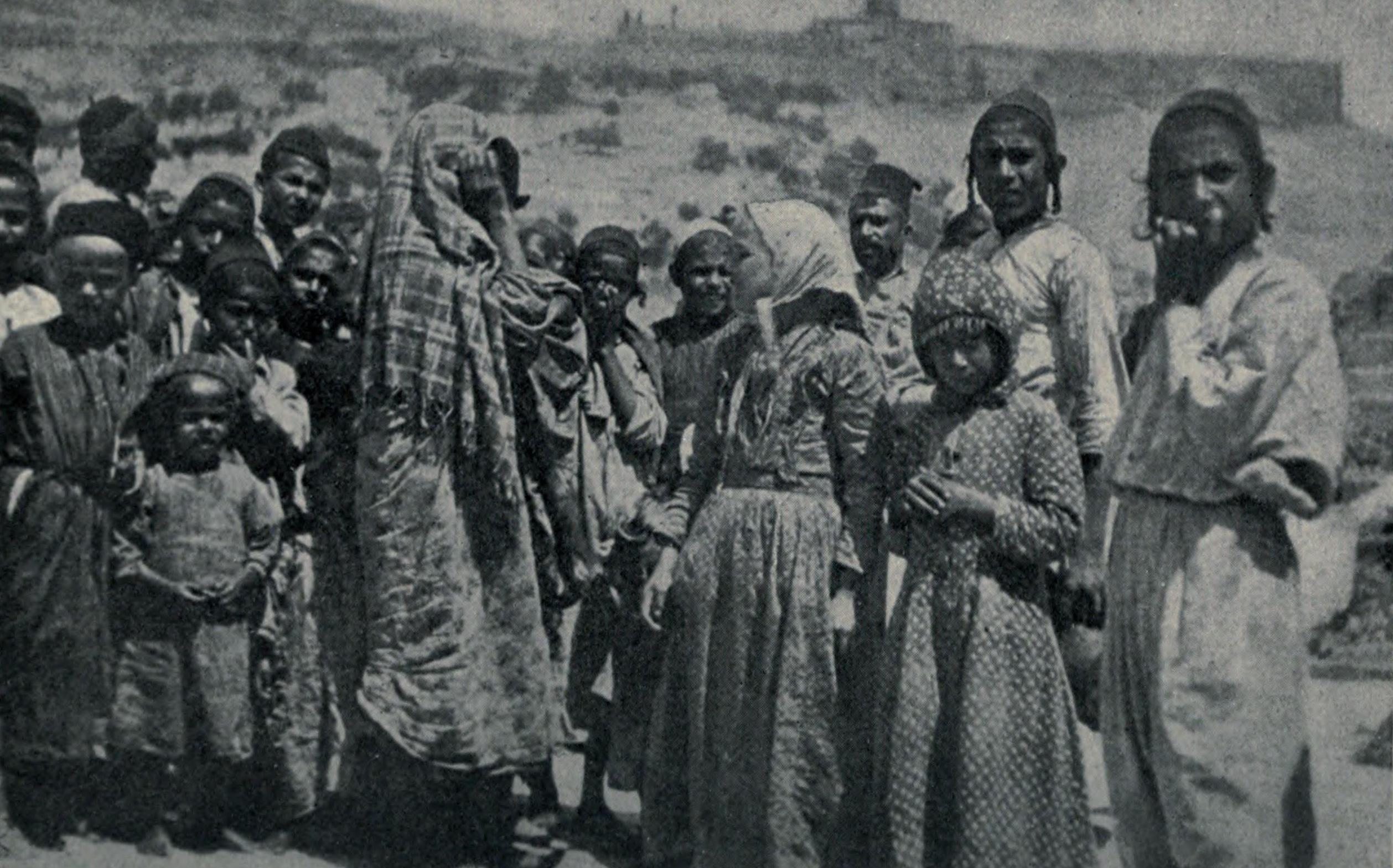
Yemenite Jews
Yemenite Jews or Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ''Yehudei Teman''; ar, اليهود اليمنيون) are those Jews who live, or once lived, in Yemen, and their descendants maintaining their customs. Between June 1949 and September 1950, the overwhelming majority of Yemen's Jewish population immigrated to Israel in Operation Magic Carpet. After several waves of persecution throughout Yemen, the vast majority of Yemenite Jews now live in Israel, while smaller communities live in the United States and elsewhere. Only a handful remain in Yemen. The few remaining Jews experience intense, and at times violent, anti-Semitism on a daily basis. Yemenite Jews have a unique religious tradition that distinguishes them from Ashkenazi Jews, Sephardi Jews, and other Jewish groups. They have been described as "the most Jewish of all Jews" and "the ones who have preserved the Hebrew language the best". Yemenite Jews fall within the "Mizrahi" (eastern) category of Jews, though they differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

