|
Electronic Circuit Design
Electronic circuit design comprises the analysis and synthesis of electronic circuits. Methods To design any electrical circuit, either Analogue electronics, analog or Digital circuit, digital, Electrical engineering, electrical engineers need to be able to predict the voltages and currents at all places within the circuit. Linear circuits, that is, circuits wherein the outputs are linearly dependent on the inputs, can be analyzed by hand using complex analysis. Simple nonlinear circuits can also be analyzed in this way. Specialized software has been created to analyze circuits that are either too complicated or too nonlinear to analyze by hand. Circuit simulation software allows engineers to design circuits more efficiently, reducing the time cost and risk of error involved in building circuit prototypes. Some of these make use of hardware description languages such as VHDL or Verilog. Network simulation software More complex circuits are analyzed with circuit simulation softw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Analogue Electronics
Analogue electronics () are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term ''analogue'' describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word ''analogue'' is derived from the Greek word meaning ''proportional''. Analogue signals An analogue signal uses some attribute of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses the angular position of a needle on top of a contracting and expanding box as the signal to convey the information of changes in atmospheric pressure. Electrical signals may represent information by changing their voltage, current, frequency, or total charge. Information is converted from some other physical form (such as sound, light, temperature, pressure, position) to an electrical signal by a transducer which converts one type of energy into another (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PLECS
PLECS ( Piecewise Linear Electrical Circuit Simulation) is a software tool for system-level simulations of electrical circuits developed by Plexim. It is especially designed for power electronics but can be used for any electrical network. PLECS includes the possibility to model controls and different physical domains (thermal, magnetic and mechanical) besides the electrical system. Most circuit simulation programs model switches as highly nonlinear elements. Due to steep voltage and current transient, the simulation becomes slow when switches are commutated. In most simplistic applications, switches are modelled as variable resistors that alternate between a very small and a very large resistance. In other cases, they are represented by a sophisticated semiconductor model. When simulating complex power electronic systems, however, the processes during switching are of little interest. In these situations it is more appropriate to use ideal switches that toggle instantaneous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
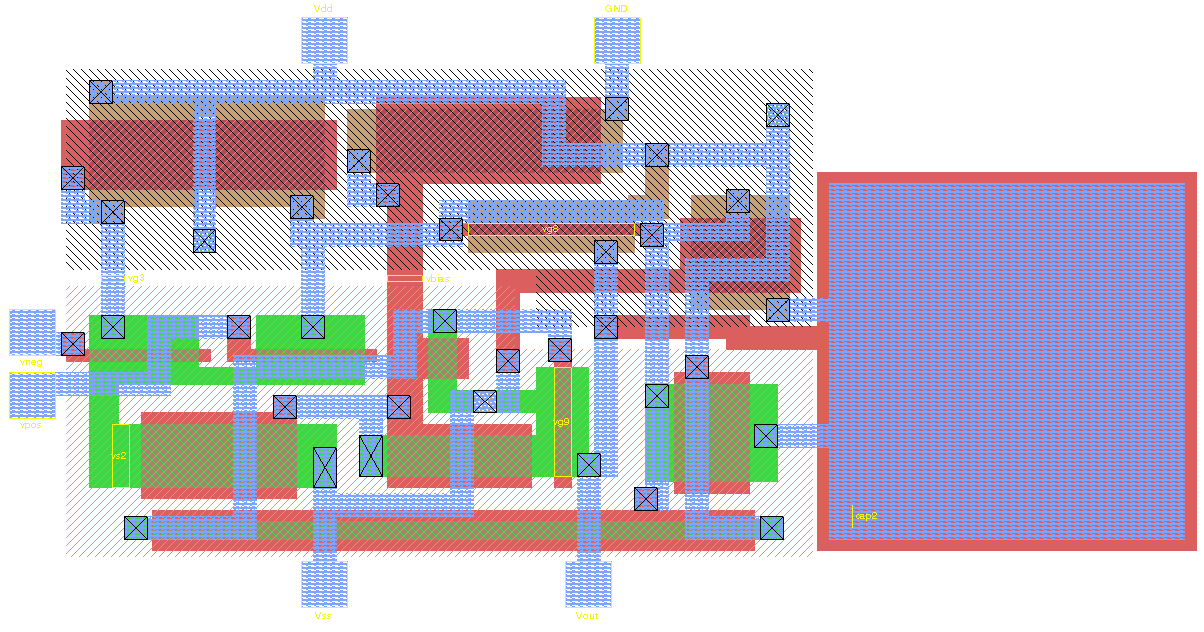
Integrated Circuit Design
Integrated circuit design, semiconductor design, chip design or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular Boolean logic, logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits (ICs). An IC consists of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography. IC design can be divided into the broad categories of Digital data, digital and analog electronics, analog IC design. Digital IC design is to produce components such as microprocessors, FPGAs, memories (Random-access memory, RAM, Read-only memory, ROM, and flash memory, flash) and digital Application-specific integrated circuit, ASICs. Digital design focuses on logical correctness, maximizing circuit density, and placing circuits so that clock and timing signals are routed efficiently. Analog IC design also has specializations in power IC design and Radio frequency, RF IC design. Analog IC design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Circuit Design
In electrical engineering, the process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit. One person can often do the design process without needing a planned or structured design process for simple circuits. Still, teams of designers following a systematic approach with intelligently guided computer simulation are becoming increasingly common for more complex designs. In integrated circuit design automation, the term "circuit design" often refers to the step of the design cycle which outputs the schematics of the integrated circuit. Typically this is the step between logic design and physical design. Process Traditional circuit design usually involves several stages. Sometimes, a design specification is written after liaising with the customer. A technical proposal may be written to meet the requirements of the customer specification. The next stage involves synthesising on pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Logic Synthesis
In computer engineering, logic synthesis is a process by which an abstract specification of desired circuit behavior, typically at register transfer level (RTL), is turned into a design implementation in terms of logic gates, typically by a computer program called a ''synthesis tool''. Common examples of this process include synthesis of designs specified in hardware description languages, including VHDL and Verilog. Some synthesis tools generate bitstreams for programmable logic devices such as PALs or FPGAs, while others target the creation of ASICs. Logic synthesis is one step in circuit design in the electronic design automation, the others are place and route and verification and validation. History The roots of logic synthesis can be traced to the treatment of logic by George Boole (1815 to 1864), in what is now termed Boolean algebra. In 1938, Claude Shannon showed that the two-valued Boolean algebra can describe the operation of switching circuits. In the early d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hardware Description Language
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, usually to design application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and to program field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). A hardware description language enables a precise, Formal language, formal description of an electronic circuit that allows for the automated analysis and Electronic circuit simulation, simulation of the circuit. It also allows for the Logic synthesis, synthesis of an HDL description into a netlist (a specification of physical electronic components and how they are connected together), which can then be Place and route, placed and routed to produce the Mask set, set of masks used to create an integrated circuit. A hardware description language looks much like a programming language such as C (programming language), C or ALGOL; it is a textual description consisting of expressions, statements and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance in one direction and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a Crystallinity, crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. It has an Exponential function, exponential current–voltage characteristic. Semiconductor diodes were the first Semiconductor device, semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a Crystal, crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Piecewise Linear Function
In mathematics, a piecewise linear or segmented function is a real-valued function of a real variable, whose graph is composed of straight-line segments. Definition A piecewise linear function is a function defined on a (possibly unbounded) interval of real numbers, such that there is a collection of intervals on each of which the function is an affine function. (Thus "piecewise linear" is actually defined to mean "piecewise affine".) If the domain of the function is compact, there needs to be a finite collection of such intervals; if the domain is not compact, it may either be required to be finite or to be locally finite in the reals. Examples The function defined by : f(x) = \begin -x - 3 & \textx \leq -3 \\ x + 3 & \text-3 < x < 0 \\ -2x + 3 & \text0 \leq x < 3 \\ 0.5x - 4.5 & \textx \geq 3 \end is piecewise linear with four pieces. The graph of this function is shown to the right. Since the graph of an affine(*) function is a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Simulink
Simulink is a MATLAB-based graphical programming environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing multidomain dynamical systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool and a customizable set of block libraries. It offers tight integration with the rest of the MATLAB environment and can either drive MATLAB or be scripted from it. Simulink is widely used in automatic control and digital signal processing for multidomain simulation and model-based design. Add-on products MathWorks and other third-party hardware and software products can be used with Simulink. For example, Stateflow extends Simulink with a design environment for developing state machines and flow charts. Coupled with another of their products, Simulink can automatically generate C source code for real-time implementation of systems. As the efficiency and flexibility of the code improves, this is becoming more widely adopted for production systems, in addition to being a tool for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kirchhoff's Current Law
Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two Equality (mathematics), equalities that deal with the Electric current, current and potential difference (commonly known as voltage) in the lumped element model of electrical circuits. They were first described in 1845 by German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. This generalized the work of Georg Ohm and preceded the work of James Clerk Maxwell. Widely used in electrical engineering, they are also called Kirchhoff's rules or simply Kirchhoff's laws. These laws can be applied in time and frequency domains and form the basis for Network analysis (electrical circuits), network analysis. Both of Kirchhoff's laws can be understood as corollaries of Maxwell's equations in the low-frequency limit. They are accurate for DC circuits, and for AC circuits at frequencies where the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are very large compared to the circuits. Kirchhoff's current law This law, also called Kirchhoff's first law, or Kirchhoff's junction rule, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Digital Circuit
In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematical model for digital logic circuits. Circuits are defined by the gates they contain and the values the gates can produce. For example, the values in a Boolean circuit are Boolean values, and the circuit includes conjunction, disjunction, and negation gates. The values in an integer circuit are sets of integers and the gates compute set union, set intersection, and set complement, as well as the arithmetic operations addition and multiplication. Formal definition A circuit is a triplet (M, L, G), where * M is a set of values, * L is a set of gate labels, each of which is a function from M^ to M for some non-negative integer i (where i represents the number of inputs to the gate), and * G is a labelled graph, labelled directed acyclic gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steady State
In systems theory, a system or a process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties ''p'' of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero and remains so: : \frac = 0 \quad \text t. In discrete time, it means that the first difference of each property is zero and remains so: : p_t-p_=0 \quad \text t. The concept of a steady state has relevance in many fields, in particular thermodynamics, economics, and engineering. If a system is in a steady state, then the recently observed behavior of the system will continue into the future. In stochastic systems, the probabilities that various states will be repeated will remain constant. For example, see ' for the derivation of the steady state. In many systems, a steady state is not achieved until some time after the system is started or initiated. This initial sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |