|
Electron Beam Lithography
Electron-beam lithography (often abbreviated as e-beam lithography, EBL) is the practice of scanning a focused beam of electrons to draw custom shapes on a surface covered with an electron-sensitive film called a resist (exposing). The electron beam changes the solubility of the resist, enabling selective removal of either the exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist by immersing it in a solvent (developing). The purpose, as with photolithography, is to create very small structures in the resist that can subsequently be transferred to the substrate material, often by etching. The primary advantage of electron-beam lithography is that it can draw custom patterns (direct-write) with sub-10 nm resolution. This form of maskless lithography has high resolution and low throughput, limiting its usage to photomask fabrication, low-volume production of semiconductor devices, and research and development. Systems Electron-beam lithography systems used in commercial applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (physics)
In physics, the cross section is a measure of the probability that a specific process will take place when some kind of radiant excitation (e.g. a particle beam, sound wave, light, or an X-ray) intersects a localized phenomenon (e.g. a particle or density fluctuation). For example, the Rutherford cross-section is a measure of probability that an alpha particle will be deflected by a given angle during an interaction with an atomic nucleus. Cross section is typically denoted ( sigma) and is expressed in units of area, more specifically in barns. In a way, it can be thought of as the size of the object that the excitation must hit in order for the process to occur, but more exactly, it is a parameter of a stochastic process. In classical physics, this probability often converges to a deterministic proportion of excitation energy involved in the process, so that, for example, with light scattering off of a particle, the cross section specifies the amount of optical power scattere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximity Effect (electron Beam Lithography)
The proximity effect in electron beam lithography (EBL) is the phenomenon that the exposure dose distribution, and hence the developed pattern, is wider than the scanned pattern due to the interactions of the primary beam electrons with the resist and substrate. These cause the resist outside the scanned pattern to receive a non-zero dose. Important contributions to weak-resist polymer chain scission (for positive resists) or crosslinking (for negative resists) come from electron forward scattering and backscattering. The forward scattering process is due to electron-electron interactions which deflect the primary electrons by a typically small angle, thus statistically broadening the beam in the resist (and further in the substrate). The majority of the electrons do not stop in the resist but penetrate the substrate. These electrons can still contribute to resist exposure by scattering back into the resist and causing subsequent inelastic or exposing processes. This backscattering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens Flare
A lens flare happens when light is scattered or flared in a lens system, often in response to a bright light, producing a sometimes undesirable artifact in the image. This happens through light scattered by the imaging mechanism itself, for example through internal reflection and forward scatter from material imperfections in the lens. Lenses with large numbers of elements such as zooms tend to have more lens flare, as they contain a relatively large number of interfaces at which internal scattering may occur. These mechanisms differ from the focused image generation mechanism, which depends on rays from the refraction of light from the subject itself. There are two types of flare: visible artifacts and glare across the image. The glare makes the image look "washed out" by reducing contrast and color saturation (adding light to dark image regions, and adding white to saturated regions, reducing their saturation). Visible artifacts, usually in the shape of the aperture made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backscattering
In physics, backscatter (or backscattering) is the reflection of waves, particles, or signals back to the direction from which they came. It is usually a diffuse reflection due to scattering, as opposed to specular reflection as from a mirror, although specular backscattering can occur at normal incidence with a surface. Backscattering has important applications in astronomy, photography, and medical ultrasonography. The opposite effect is forward scatter, e.g. when a translucent material like a cloud diffuses sunlight, giving soft light. Backscatter of waves in physical space Backscattering can occur in quite different physical situations, where the incoming waves or particles are deflected from their original direction by different mechanisms: *Diffuse reflection from large particles and Mie scattering, causing alpenglow and gegenschein, and showing up in weather radar; *Inelastic collisions between electromagnetic waves and the transmitting medium (Brillouin scattering and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monte Carlo Simulations
Monte Carlo methods, or Monte Carlo experiments, are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. The underlying concept is to use randomness to solve problems that might be deterministic in principle. They are often used in physical and mathematical problems and are most useful when it is difficult or impossible to use other approaches. Monte Carlo methods are mainly used in three problem classes: optimization, numerical integration, and generating draws from a probability distribution. In physics-related problems, Monte Carlo methods are useful for simulating systems with many coupled degrees of freedom, such as fluids, disordered materials, strongly coupled solids, and cellular structures (see cellular Potts model, interacting particle systems, McKean–Vlasov processes, kinetic models of gases). Other examples include modeling phenomena with significant uncertainty in inputs such as the calculation of risk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polaron
A polaron is a quasiparticle used in condensed matter physics to understand the interactions between electrons and atoms in a solid material. The polaron concept was proposed by Lev Landau in 1933 and Solomon Pekar in 1946 to describe an electron moving in a dielectric crystal where the atoms displace from their equilibrium positions to effectively screen the charge of an electron, known as a phonon cloud. This lowers the electron mobility and increases the electron's effective mass. The general concept of a polaron has been extended to describe other interactions between the electrons and ions in metals that result in a bound state, or a lowering of energy compared to the non-interacting system. Major theoretical work has focused on solving Fröhlich and Holstein Hamiltonians. This is still an active field of research to find exact numerical solutions to the case of one or two electrons in a large crystal lattice, and to study the case of many interacting electrons. Experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, Elasticity (physics), elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter physics, condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical Quantization (physics), quantization of the mode of vibration, modes of vibrations for elastic structures of interacting particles. Phonons can be thought of as quantized sound waves, similar to photons as quantized light waves. The study of phonons is an important part of condensed matter physics. They play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter systems, such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, as well as in models of neutron scattering and related effects. The concept of phonons was introduced in 1932 by Soviet Union, Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The name ''phonon'' comes from the Ancient Greek language, Greek word (), which translates to ''so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization Potential
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected. Uses Everyday examples of gas ionization are such as within a fluorescent lamp or other electrical discharge lamps. It is also used in radiation detectors such as the Geiger-Müller counter or the ionization chamber. The ionizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poly(methyl Methacrylate)
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Astariglas, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex, among several others ( see below). This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes. Although not a type of familiar silica-based glass, the substance, like many thermoplastics, is often technically classified as a type of glass, in that it is a non-crystalline vitreous substance—hence its occasional historic designation as ''acrylic glass''. Chemically, it is the synthetic polymer of methyl methacrylate. It was developed in 1928 in several different laboratories by many chemists, such as William Chalmers, Otto Röhm, and Walter Bauer, and first brought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Charge
Space charge is an interpretation of a collection of electric charges in which excess electric charge is treated as a continuum of charge distributed over a region of space (either a volume or an area) rather than distinct point-like charges. This model typically applies when charge carriers have been emitted from some region of a solid—the cloud of emitted carriers can form a space charge region if they are sufficiently spread out, or the charged atoms or molecules left behind in the solid can form a space charge region. Space charge only occurs in dielectric media (including vacuum) because in a conductive medium the charge tends to be rapidly neutralized or screened. The sign of the space charge can be either negative or positive. This situation is perhaps most familiar in the area near a metal object when it is heated to incandescence in a vacuum. This effect was first observed by Thomas Edison in light bulb filaments, where it is sometimes called the Edison effect. Space c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
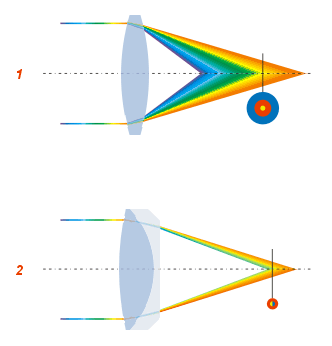
Optical Aberration
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses, that causes light to be spread out over some region of space rather than focused to a point. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred or distorted, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which is not sharp. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration. Aberration can be anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |