|
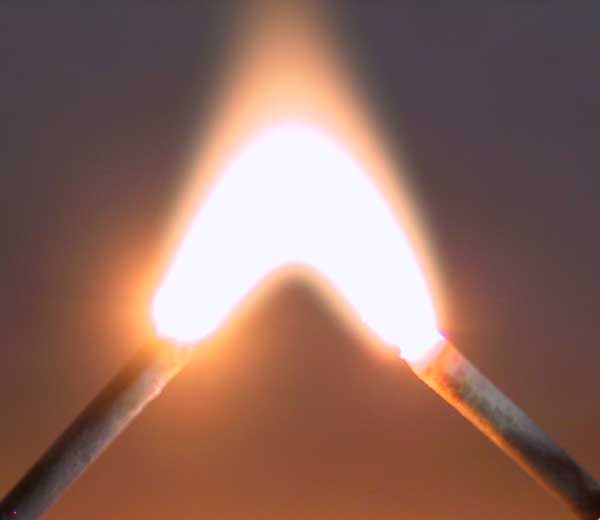
Electric Discharge
An electric discharge is the release and transmission of electricity in an applied electric field through a medium such as a gas (ie., an outgoing flow of electric current through a non-metal medium).American Geophysical Union, National Research Council (U.S.). Geophysics Study Committee (1986) ''The earth's electrical environment''. National Academy Press, Washington, DC, p. 263. Applications The properties and effects of electric discharges are useful over a wide range of magnitudes. Tiny pulses of current are used to detect ionizing radiation in a Geiger–Müller tube. A low steady current can be used to illustrate the spectrum of gases in a gas-filled tube. A neon lamp is an example of a gas-discharge lamp, useful both for illumination and as a voltage regulator. A flashtube generates a short pulse of intense light useful for photography by sending a heavy current through a gas arc discharge. Corona discharges are used in photocopiers. Electric discharges can convey substan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glow Discharge Current-voltage Curve English
Glow or GLOW may refer to: In science and technology In computing and telecommunications * Glow (JavaScript library), an open-source JavaScript library created by the BBC * Glow (Scottish Schools National Intranet), a telecommunications project in Scotland In physics * Incandescence, the emission of electromagnetic radiation from a hot object * Luminescence, any form of light emission ''not'' resulting from heat * List of light sources Other uses in science and technology * Glow or Bloom (shader effect), computer graphics effect * GLOW (gross lift-off weight), see maximum takeoff weight In arts and entertainment In film and television * ''The Glow'' (film), a 2002 TV film starring Portia de Rossi * ''Glow'' (2000 film), a film starring Frankie Ingrassia * ''Glow'' (2011 film), a film starring Tony Lo Bianco * ''The Glow'' (TV series), a 2000s television series starring Dean Cain * GLOW TV, a syndicated televised version of the Gorgeous Ladies of Wrestling events from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Welding
Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a binding of the metals. It is a type of welding that uses a welding power supply to create an electric arc between a metal stick ("electrode") and the base material to melt the metals at the point of contact. Arc welders can use either direct (DC) or alternating (AC) current, and consumable or non-consumable electrodes. The welding area is usually protected by some type of shielding gas (e.g. an inert gas), vapor, or slag. Arc welding processes may be manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated. First developed in the late part of the 19th century, arc welding became commercially important in shipbuilding during the Second World War. Today it remains an important process for the fabrication of steel structures and vehicles. Power supplies To supply the electrical energy necessary for arc welding processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electric charge, electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the land, ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an average of one Joule, gigajoule of energy. This discharge may produce a wide range of electromagnetic radiation, from heat created by the rapid movement of electrons, to brilliant flashes of visible light in the form of black-body radiation. Lightning causes thunder, a sound from the shock wave which develops as gases in the vicinity of the discharge experience a sudden increase in pressure. Lightning occurs commonly during thunderstorms as well as other types of energetic weather systems, but volcanic lightning can also occur during volcanic eruptions. The three main kinds of lightning are distinguished by where they occur: either inside a single Cumulonimbus cloud, thundercloud (intra-cloud), between two clouds (cloud-to-cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townsend Discharge
The Townsend discharge or Townsend avalanche is a gas ionisation process where free electrons are accelerated by an electric field, collide with gas molecules, and consequently free additional electrons. Those electrons are in turn accelerated and free additional electrons. The result is an avalanche breakdown, avalanche multiplication that permits electrical conduction through the gas. The discharge requires a source of free electrons and a significant electric field; without both, the phenomenon does not occur. The Townsend discharge is named after John Sealy Townsend, who discovered the fundamental ionisation mechanism by his work circa 1897 at the Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge. General description of the phenomenon The avalanche occurs in a gaseous medium that can be ionization, ionised (such as air). The electric field and the mean free path of the electron must allow free electrons to acquire an energy level (velocity) that can cause impact ionisation. If the electric fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Arc
A vacuum arc can arise when the surfaces of metal electrodes in contact with a good vacuum begin to emit electrons either through heating (thermionic emission) or in an electric field that is sufficient to cause field electron emission. Once initiated, a vacuum arc can persist, since the freed particles gain kinetic energy from the electric field, heating the metal surfaces through high-speed particle collisions. This process can create an incandescent cathode spot, which frees more particles, thereby sustaining the arc. At sufficiently high currents an incandescent anode spot may also be formed. Electric discharge in vacuum is important for certain types of vacuum tubes and for high-voltage vacuum switches. The thermionic vacuum arc (TVA) is a new type of plasma source, which generates a plasma containing ions with a directed energy. TVA discharges can be ignited in high-vacuum conditions between a heated cathode (electron gun) and an anode (tungsten crucible) containing the mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streamer Discharge
A streamer discharge, also known as ''filamentary discharge'', is a type of transient electrical discharge which forms at the surface of a conductive electrode carrying a high voltage in an insulating medium such as air. Streamers are luminous writhing branching sparks, plasma channels composed of ionized air molecules, which repeatedly strike out from the electrode into the air. Like the related corona discharges and brush discharges, a streamer discharge represents a region around a high voltage conductor where the air has suffered electrical breakdown and become conductive (ionized), so electric charge is leaking off the electrode into the air. It occurs when the electric field at the surface of a conductor exceeds the dielectric strength of air, around 30 kilovolts per centimeter. When the electric field created by the applied voltage reaches this threshold, accelerated electrons strike air molecules with enough energy to knock other electrons off them, ionizing them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Discharge
In electrical engineering, partial discharge (PD) is a localized dielectric breakdown (DB) (which does not completely bridge the space between the two conductors) of a small portion of a solid or fluid electrical insulation (EI) system under high voltage (HV) stress. While a corona discharge (CD) is usually revealed by a relatively steady glow or brush discharge (BD) in air, partial discharges within solid insulation system are not visible. PD can occur in a gaseous, liquid, or solid insulating medium. It often starts within gas voids, such as voids in solid epoxy insulation or bubbles in transformer oil. Protracted partial discharge can erode solid insulation and eventually lead to breakdown of insulation. Discharge mechanism PD usually begins within voids, cracks, or inclusions within a solid dielectric, at conductor-dielectric interfaces within solid or liquid dielectrics, or in bubbles within liquid dielectrics. Since PDs are limited to only a portion of the insulation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leader (spark)
A leader is a hot, highly conductive channel of plasma that plays a critical part during dielectric breakdown within a long electric spark. Mechanism When a gas is subjected to high voltage stress, the electric field is often quite non-uniform near one, or both, of the high voltage electrodes making up a spark gap. Breakdown initially begins with the formation of corona discharges near the electrode with the highest electrical stress. If the electrical field is further increased, longer length ''cold'' discharges (called '' streamers'' or ''burst corona'') sporadically form near the stressed electrode. Streamers attract multiple electron avalanches into a single channel, propagating forward quickly via photon emission which leads to photoelectrons producing new avalanches. Streamers redistribute charge within the surrounding gas, temporarily forming regions of excess charge ( space charges) in the regions surrounding the discharges. If the electrical field is sufficiently high, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Discharge In Gases
Electric discharge in gases occurs when electric current flows through a gaseous medium due to ionization of the gas. Depending on several factors, the discharge may radiate visible light. The properties of electric discharges in gases are studied in connection with design of lighting sources and in the design of high voltage electrical equipment. Discharge types In cold cathode tubes, the electric discharge in gas has three regions, with distinct current–voltage characteristics:Reference Data for Engineers: Radio, Electronics, Computers and Communications By Wendy Middleton, Mac E. Van Valkenburg, p. 16-42, Newnes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden and momentary flow of electric current between two electrically charged objects caused by contact, an short circuit, electrical short or dielectric breakdown. A buildup of static electricity can be caused by tribocharging or by electrostatic induction. The ESD occurs when differently-charged objects are brought close together or when the dielectric between them breaks down, often creating a visible electric spark, spark. ESD can create spectacular electric sparks (lightning, with the accompanying sound of thunder, is a large-scale ESD event), but also less dramatic forms which may be neither seen nor heard, yet still be large enough to cause damage to sensitive electronic devices. Electric sparks require a field strength above approximately 40 kV/cm in air, as notably occurs in lightning strikes. Other forms of ESD include corona discharge from sharp electrodes and brush discharge from blunt electrodes. ESD can cause harmful effects of imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Arc
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The electric current, current through a normally Electrical conductance, nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma (physics), plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge and relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. An archaic term is voltaic arc, as used in the phrase "voltaic arc lamp". Techniques for arc suppression can be used to reduce the duration or likelihood of arc formation. In the late 19th century, Arc lamp, electric arc lighting was in wide use for Street light#Arc lamps, public lighting. Some low-pressure electric arcs are used in many applications. For example, fluorescent lamp, fluorescent tubes, mercury, sodium, and metal-halide lamps are used for lighting; xenon arc lamps have been used for movie projectors. Electric a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Glow Discharge
A glow discharge is a plasma formed by the passage of electric current through a gas. It is often created by applying a voltage between two electrodes in a glass tube containing a low-pressure gas. When the voltage exceeds a value called the striking voltage, the gas ionization becomes self-sustaining, and the tube glows with a colored light. The color depends on the gas used. Glow discharges are used as a source of light in devices such as neon lights, fluorescent lamps, and plasma-screen televisions. Analyzing the light produced with spectroscopy can reveal information about the atomic interactions in the gas, so glow discharges are used in plasma physics and analytical chemistry. They are also used in the surface treatment technique called sputtering. Electrical conduction in gas Conduction in a gas requires charge carriers, which can be either electrons or ions. Charge carriers come from ionizing some of the gas molecules. In terms of current flow, glow discharge falls b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |