|
Ekman Transport
Ekman transport is part of Ekman motion theory, first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Winds are the main source of energy for ocean circulation, and Ekman Transport is a component of wind-driven ocean current. Ekman transport occurs when ocean surface waters are influenced by the friction force acting on them via the wind. As the wind blows it casts a friction force on the ocean surface that drags the upper 10-100m of the water column with it. However, due to the influence of the Coriolis force, Coriolis effect, the ocean water moves at a 90° angle from the direction of the surface wind. The direction of transport is dependent on the hemisphere: in the Northern Hemisphere, northern hemisphere, transport occurs at 90° clockwise from wind direction, while in the Southern Hemisphere, southern hemisphere it occurs at 90° anticlockwise.Colling, pp 42-44 This phenomenon was first noted by Fridtjof Nansen, who recorded that ice transport appeared to occur at an angle to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Layer
The Ekman layer is the layer in a fluid where there is a force balance between pressure gradient force, Coriolis force and turbulent drag. It was first described by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Ekman layers occur both in the atmosphere and in the ocean. There are two types of Ekman layers. The first type occurs at the surface of the ocean and is forced by surface winds, which act as a drag on the surface of the ocean. The second type occurs at the bottom of the atmosphere and ocean, where frictional forces are associated with flow over rough surfaces. History Ekman developed the theory of the Ekman layer after Fridtjof Nansen observed that ice drifts at an angle of 20°–40° to the right of the prevailing wind direction while on an Arctic expedition aboard the Fram. Nansen asked his colleague, Vilhelm Bjerknes to set one of his students upon study of the problem. Bjerknes tapped Ekman, who presented his results in 1902 as his doctoral thesis. Mathematical formulation The mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barotropic
In fluid dynamics, a barotropic fluid is a fluid whose density is a function of pressure only. The barotropic fluid is a useful model of fluid behavior in a wide variety of scientific fields, from meteorology to astrophysics. The density of most liquids is nearly constant (isopycnic), so it can be stated that their densities vary only weakly with pressure and temperature. Water, which varies only a few percent with temperature and salinity, may be approximated as barotropic. In general, air is not barotropic, as it is a function of temperature and pressure; but, under certain circumstances, the barotropic assumption can be useful. In astrophysics, barotropic fluids are important in the study of stellar interiors or of the interstellar medium. One common class of barotropic model used in astrophysics is a polytropic fluid. Typically, the barotropic assumption is not very realistic. In meteorology, a barotropic atmosphere is one that for which the density of the air depends only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harald Sverdrup (oceanographer)
Harald Ulrik Sverdrup (15 November 1888 – 21 August 1957) was a Norwegian oceanographer and meteorologist. He was director of Scripps Institution of Oceanography and director of the Norwegian Polar Institute. Background He was born at Sogndal in Sogn og Fjordane, Norway. He was the son of Lutheran theologian Edvard Sverdrup (1861–1923) and Maria Vollan (1865–1891). His sister Mimi Sverdrup Lunden (1894–1955) was an educator and author. His brother Leif Sverdrup (1898–1976) was a General with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. His brother Einar Sverdrup (1895–1942) was CEO of Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani. Sverdrup was a student at Bergen Cathedral School in 1901 before graduating in 1906 at Kongsgård School in Stavanger. He graduated cand. real. in 1914 from University of Oslo. He studied under Vilhelm Bjerknes and earned his Dr. Philos. at the University of Leipzig in 1917. Career He was the scientific director of the North Polar expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostrophic Wind
In atmospheric science, geostrophic flow () is the theoretical wind that would result from an exact balance between the Coriolis force and the pressure gradient force. This condition is called '' geostrophic equilibrium'' or ''geostrophic balance'' (also known as ''geostrophy''). The geostrophic wind is directed parallel to isobars (lines of constant pressure at a given height). This balance seldom holds exactly in nature. The true wind almost always differs from the geostrophic wind due to other forces such as friction from the ground. Thus, the actual wind would equal the geostrophic wind only if there were no friction (e.g. above the atmospheric boundary layer) and the isobars were perfectly straight. Despite this, much of the atmosphere outside the tropics is close to geostrophic flow much of the time and it is a valuable first approximation. Geostrophic flow in air or water is a zero-frequency inertial wave. Origin A useful heuristic is to imagine air starting from res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garbage Patch
A garbage patch is a gyre of marine debris particles caused by the effects of ocean currents and increasing plastic pollution by human populations. These human-caused collections of plastic and other debris, cause ecosystem and environmental problems that affect marine life, contaminate oceans with toxic chemicals, and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Once waterborne, marine debris becomes mobile. Flotsam can be blown by the wind, or follow the flow of ocean currents, often ending up in the middle of oceanic gyres where currents are weakest. Garbage patches grow because of widespread loss of plastic from human trash collection systems. The United Nations Environmental Program estimated that "for every square mile of ocean" there are about "46,000 pieces of plastic." The 10 largest emitters of oceanic plastic pollution worldwide are, from the most to the least, China, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Egypt, Malaysia, Nigeria, and Bangladesh, largely thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Gyre
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the '' wind stress curl'' (torque). ''Gyre'' can refer to any type of vortex in an atmosphere or a sea, even one that is human-created, but it is most commonly used in terrestrial oceanography to refer to the major ocean systems. Major gyres The following are the five most notable ocean gyres:The five most notable gyres PowerPoint Presentation * Indian Ocean Gyre * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Wind
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled colonial expansion into the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. In meteorology, they act as the steering flow for tropical storms that form over the Atlantic, Pacific, and southern Indian oceans and make landfall in North America, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar and East Africa. Shallow cumulus clouds are seen within trade wind regimes and are capped from becoming taller by a trade wind inversion, which is caused by descending air aloft from within the subtropical ridge. The we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
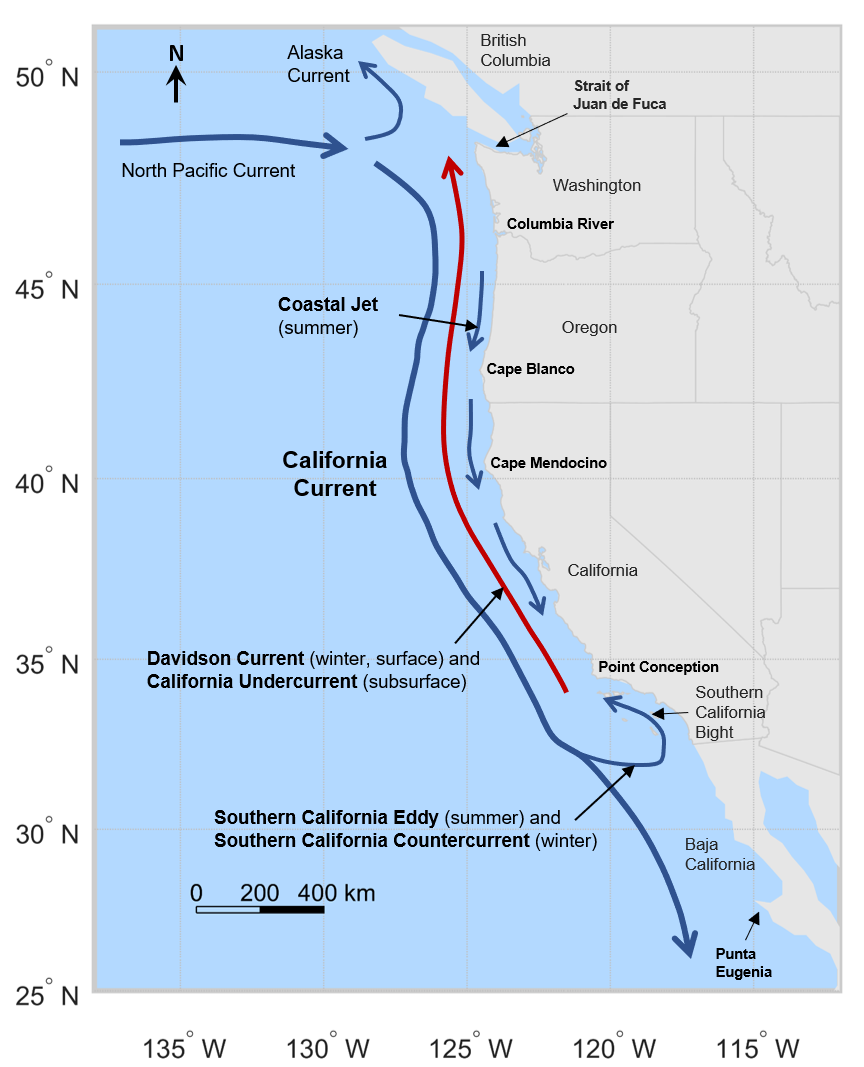
California Current
The California Current is a cold water Pacific Ocean current that moves southward along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia and ending off southern Baja California Sur. It is considered an Eastern boundary current due to the influence of the North American coastline on its course. It is also one of five major coastal currents affiliated with strong upwelling zones, the others being the Humboldt Current, the Canary Current, the Benguela Current, and the Somali Current. The California Current is part of the North Pacific Gyre, a large swirling current that occupies the northern basin of the Pacific. Physical properties The movement of Alaskan and northern ocean currents southward down the west coast results in much cooler ocean temperatures than at comparable latitudes on the east coast of the United States, where ocean currents come from the Caribbean and tropical Atlantic. The cooler ocean current along the west coast also makes summ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt Current
The Humboldt Current, also called the Peru Current, is a cold, low-salinity ocean current that flows north along the western coast of South America.Montecino, Vivian, and Carina B. Lange. "The Humboldt Current System: Ecosystem components and processes, fisheries, and sediment studies." ''Progress in Oceanography'' 83.1 (2009): 65-79. DOI10.1016/j.pocean.2009.07.041/ref> It is an eastern boundary current flowing in the direction of the equator, and extends offshore. The Humboldt Current is named after the German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt even though it was discovered by José de Acosta 250 years before Humboldt. In 1846, von Humboldt reported measurements of the cold-water current in his book '' Cosmos''. The current extends from southern Chile (~45th parallel south) to northern Peru (~4th parallel south) where cold, upwelled, waters intersect warm tropical waters to form the Equatorial Front. Sea surface temperatures off the coast of Peru, around 5th parallel south, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Ice Sheet
The Antarctic ice sheet is one of the two polar ice caps of Earth. It covers about 98% of the Antarctic continent and is the largest single mass of ice on Earth, with an average thickness of over 2 kilometers. It covers an area of almost and contains of ice. A cubic kilometer of ice weighs approximately 0.92 metric gigatonnes, meaning that the ice sheet weighs ~24,380,000 gigatonnes. It holds approximately 61% of all fresh water on Earth, equivalent to about 58 meters of sea level rise if all the ice were above sea level. In East Antarctica, the ice sheet rests on a major land mass, while in West Antarctica the bed can extend to more than 2,500 m below sea level. Satellite measurements by NASA indicate a still increasing sheet thickness above the continent, outweighing the losses at the edge. The reasons for this are not fully understood, but suggestions include the climatic effects on ocean and atmospheric circulation of the ozone hole, and/or cooler ocean surface temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |