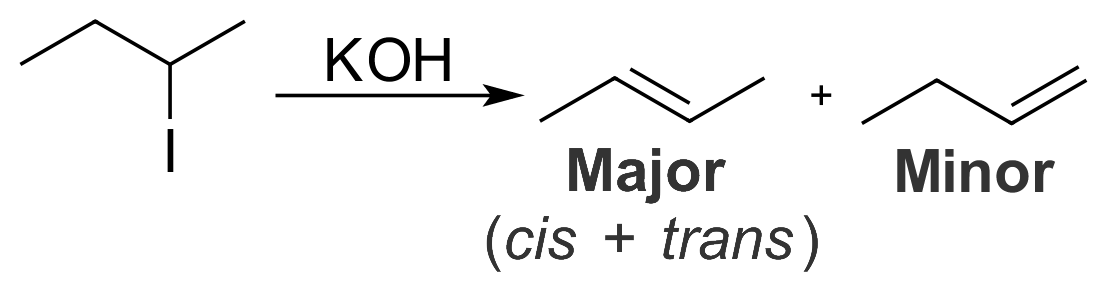|
Ei Mechanism
In organic chemistry, the Ei mechanism (Elimination Internal/Intramolecular), also known as a thermal syn elimination or a pericyclic syn elimination, is a special type of elimination reaction in which two vicinal (adjacent) substituents on an alkane framework leave simultaneously via a cyclic transition state to form an alkene in a ''syn'' elimination. This type of elimination is unique because it is thermally activated and does not require additional reagents, unlike regular eliminations, which require an acid or base, or would in many cases involve charged intermediates. This reaction mechanism is often found in pyrolysis. General features Compounds that undergo elimination through cyclic transition states upon heating, with no other reagents present, are given the designation as Ei reactions. Depending on the compound, elimination takes place through a four, five, or six-membered transition state.Carey, F. A.; Sunburg, R. J. ''Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reaction and Synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired electron, unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemical reaction, chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimer (chemistry), dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and methylene radical, triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, Plasma (ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept. For example, butanol , methyl propyl ether , and diethyl ether have the same molecular formula but are three distinct structural isomers. The concept applies also to polyatomic ions with the same total charge. A classical example is the cyanate ion and the fulminate ion . It is also extended to ionic compounds, so that (for example) ammonium cyanate and urea are considered structural isomers,William F. Bynum, E. Janet Browne, Roy Porter (2014): ''Dictionary of the History of Science''. 530 pages. and so are methylammonium formate and ammonium acetate . Structural isomerism is the most radical type of isomerism. It is opposed to stereoisomerism, in which the atoms and bonding s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis–trans Isomerism
''Cis''–''trans'' isomerism, also known as geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism, is a term used in chemistry that concerns the spatial arrangement of atoms within molecules. The prefixes "''cis''" and "''trans''" are from Latin: "this side of" and "the other side of", respectively. In the context of chemistry, ''cis'' indicates that the functional groups (substituents) are on the same side of some plane, while ''trans'' conveys that they are on opposing (transverse) sides. ''Cis''–''trans'' isomers are stereoisomers, that is, pairs of molecules which have the same formula but whose functional groups are in different orientations in three-dimensional space. ''Cis-trans'' notation does not always correspond to ''E''–''Z'' isomerism, which is an '' absolute'' stereochemical description. In general, ''cis''–''trans'' stereoisomers contain double bonds that do not rotate, or they may contain ring structures, where the rotation of bonds is restricted or prevente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newman Projections Of Cyclic Transition States
Newman is a surname of English origin and may refer to many people: The surname Newman is widespread in the core Anglosphere. A *Abram Newman (1736–1799), British grocer *Adrian Newman (other), multiple people *Al Newman (born 1960), American baseball player *Alan Newman (baseball) (born 1969), American baseball player *Alec Newman (born 1974), Scottish actor * Alfred Newman (other), multiple people * Ali Newman (born 1977), better known as Brother Ali, American rapper *Alison Newman (born 1968), British actress * Allen George Newman (1875–1940), American sculptor * Alysha Newman (born 1994), Canadian pole vaulter * Amy Hauck Newman, American medicinal chemist *Andrea Newman (1938–2019), British author *Andrew Newman (other), multiple people * Angelia Thurston Newman (1837–1910), American poet and writer *Anne B. Newman (born 1955), American gerontologist *Arnold Newman (1918–2006), American photographer * Aubrey Newman (1903–1994), Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Stability
In chemistry, chemical stability is the thermodynamic stability of a chemical system. Thermodynamic stability occurs when a system is in its lowest energy state A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The te ..., or in chemical equilibrium with its environment. This may be a dynamic equilibrium in which individual atoms or molecules change form, but their overall number in a particular form is conserved. This type of chemical thermodynamic equilibrium will persist indefinitely unless the system is changed. Chemical systems might undergo changes in the phase of matter or a set of chemical reactions. State A is said to be more thermodynamically stable than state B if the Gibbs free energy of the change from A to B is positive. Versus reactivity Thermodynamic stability appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugated System
In theoretical chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases stability. It is conventionally represented as having alternating single and multiple bonds. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the system, which may be cyclic, acyclic, linear or mixed. The term "conjugated" was coined in 1899 by the German chemist Johannes Thiele. Conjugation is the overlap of one p-orbital with another across an adjacent σ bond (in transition metals, d-orbitals can be involved). A conjugated system has a region of overlapping p-orbitals, bridging the interjacent locations that simple diagrams illustrate as not having a π bond. They allow a delocalization of π electrons across all the adjacent aligned p-orbitals. The π electrons do not belong to a single bond or atom, but rather to a group of atoms. Molecules containing conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steric Effects
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions and molecules. Steric effects complement electronic effects, which dictate the shape and reactivity of molecules. Steric repulsive forces between overlapping electron clouds result in structured groupings of molecules stabilized by the way that opposites attract and like charges repel. Steric hindrance Steric hindrance is a consequence of steric effects. Steric hindrance is the slowing of chemical reactions due to steric bulk. It is usually manifested in ''intermolecular reactions'', whereas discussion of steric effects often focus on ''intramolecular interactions''. Steric hindrance is often exploited to control selectivity, such as slowing unwanted side-reactions. Steric hindrance between adjacent groups can also affect torsiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaitsev's Rule
In organic chemistry, Zaitsev's rule (or Saytzeff's rule, Saytzev's rule) is an empirical rule for predicting the favored alkene product(s) in elimination reactions. While at the University of Kazan, Russian chemist Alexander Zaitsev studied a variety of different elimination reactions and observed a general trend in the resulting alkenes. Based on this trend, Zaitsev proposed that the alkene formed in greatest amount is that which corresponded to removal of the hydrogen from the alpha-carbon having the fewest hydrogen substituents. For example, when 2-iodobutane is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH), 2-butene is the major product and 1-butene is the minor product. : More generally, Zaitsev's rule predicts that in an elimination reaction the most substituted product will be the most stable, and therefore the most favored. The rule makes no generalizations about the stereochemistry of the newly formed alkene, but only the regiochemistry of the elimination reaction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |