|
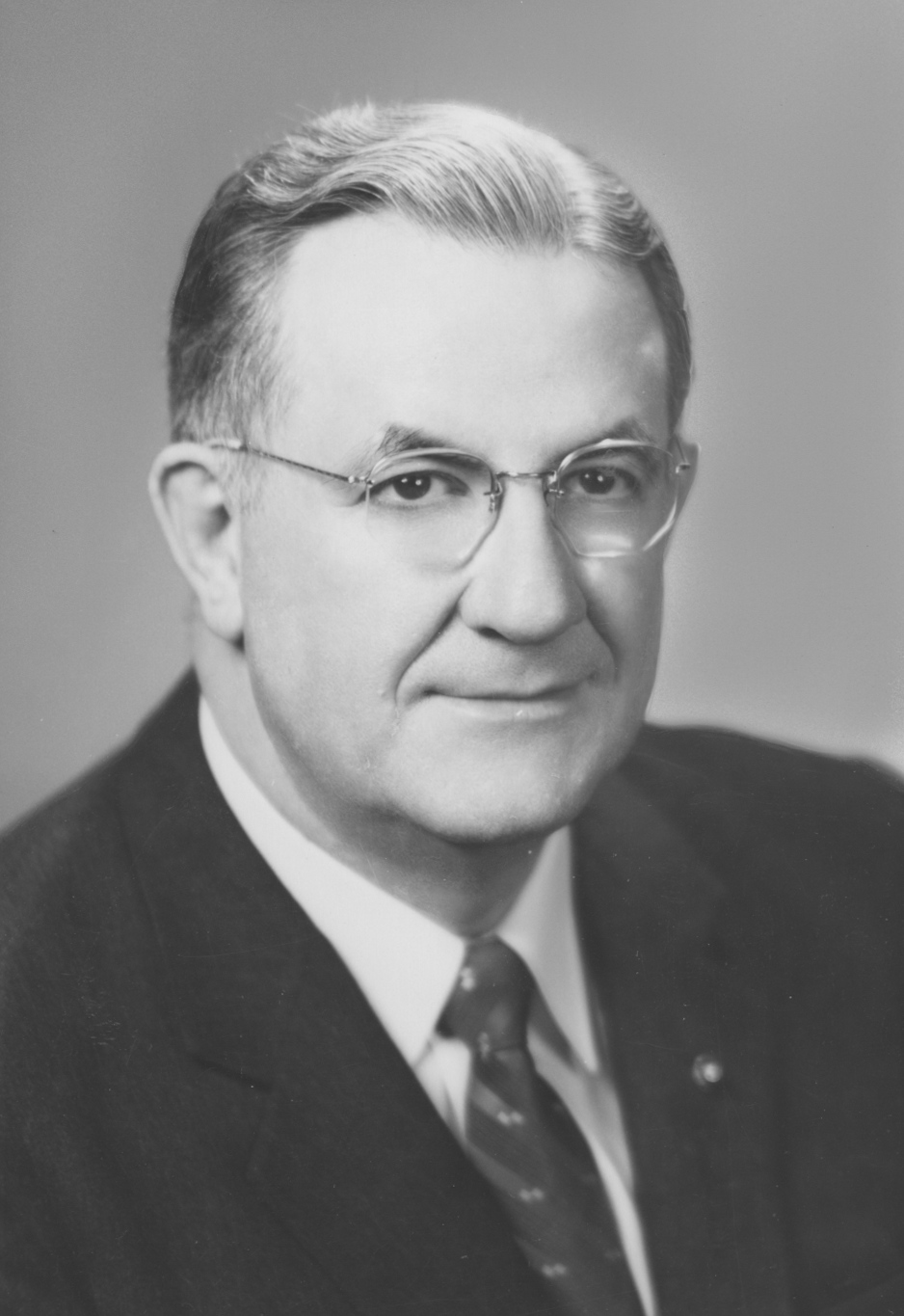
Edward V. Long
Edward Vaughn Long (July 18, 1908November 6, 1972) was a United States Senator from Missouri and a member of the United States Democratic Party, Democratic Party. He served in the United States Senate from 1960 until 1968. One of his most notable accomplishments as a US Senator writing the final draft of the Freedom of Information Act (United States), Freedom of Information Act which passed in 1966 after 11 years of research, creation, and fight by the "Father of the Freedom of Information Act", Representative John E. Moss (D) of Sacramento, California. Biography Born in rural Lincoln County, Missouri near Whiteside, Missouri, Whiteside, he was educated at Culver-Stockton College and the University of Missouri. After holding various local offices in Bowling Green, Missouri, Bowling Green and Pike County, Missouri, Pike County, Long was elected to the Missouri State Senate, where he served from 1945 to 1955; he was elected majority floor leader in 1952 and President pro tempore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas to the south and Oklahoma, Kansas and Nebraska to the west. In the south are the Ozarks, a forested highland, providing timber, minerals, and recreation. The Missouri River, after which the state is named, flows through the center into the Mississippi River, which makes up the eastern border. With more than six million residents, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 19th-most populous state of the country. The largest urban areas are St. Louis, Kansas City, Missouri, Kansas City, Springfield, Missouri, Springfield and Columbia, Missouri, Columbia; the Capital city, capital is Jefferson City, Missouri, Jefferson City. Humans have inhabited w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowling Green, Missouri
Bowling Green is a city in Pike County, Missouri, United States. The population was 5,334 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Pike County. History Bowling Green was settled in 1819, and designated county seat in 1824. Settled chiefly by migrants from Kentucky and Virginia, it was named after Bowling Green, Kentucky. The James Beauchamp Clark House was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976. Geography Highways * U.S. Route 54 * U.S. Route 61 * Route 161 Bowling Green lies at the junction of US highways 54 and 61. US 54 links Bowling Green with Illinois to the east and Jefferson City and the Lake of the Ozarks to the south and west, while US 61 connects the city with Hannibal to the north and the St. Louis area to the south. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which, is land and is water. Climate Demographics 2010 census As of the census of 2010, there were 5,334 people, 1,316 households, and 81 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classes Of United States Senators
The 100 seats in the United States Senate are divided into three classes for the purpose of determining which seats will be up for election in any two-year cycle, with only one class being up for election at a time. With senators being elected to fixed terms of six years, the classes allow about a third of the seats to be up for election in any presidential or midterm election year instead of having all 100 be up for election at the same time every six years. The seats are also divided in such a way that any given state's two senators are in different classes so that each seat's term ends in different years. Class 1and 2 consist of 33 seats each, while class3 consists of 34 seats. Elections for class1 seats took place most recently in 2018, class2 in 2020, and the elections for class3 seats in 2022. The three classes were established by ArticleI, Section 3, Clause2 of the U.S. Constitution. The actual division was originally performed by the Senate of the 1st Congress in May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Senator
The United States Senate is the Upper house, upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives being the Lower house, lower chamber. Together they compose the national Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the United States. The composition and powers of the Senate are established by Article One of the United States Constitution. The Senate is composed of #Membership, senators, each of whom represents a single U.S. state, state in its entirety. Each of the 50 states is equally represented by two senators who serve Classes of United States senators, staggered terms of six years, for a total of 100 senators. The Vice President of the United States, vice president of the United States serves as presiding officer and president of the Senate by Ex officio member, virtue of that office, despite not being a senator, and has a vote only if the Senate is equally divided. In the vice president's absence, the Presiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1956 Missouri Lieutenant Gubernatorial Election ...
The 1956 Missouri lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1956. Democratic nominee Edward V. Long defeated Republican nominee Richard M. Webster with 53.49% of the vote. Primary elections Primary elections were held on August 7, 1956. Democratic primary Candidates * Edward V. Long, State Senator *Tom A. Shockley *Harry E. Kemp *Charles C. Hurst *John Hosmer *Samuel Van D. Williams Results General election Candidates *Edward V. Long, Democratic *Richard M. Webster, Republican Results References {{1956 United States elections, state=collapsed 1956 Gubernatorial Missouri Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand View Burial Park, Hannibal
Grand View Burial Park is a cemetery in Hannibal, Missouri, developed in 1934 as a memorial cemetery.Grand View Funeral Home & Burial Park accessed September 19, 2009 The first burial was on May 11, 1934. Two more burials were performed in May and 19 more during the rest of 1934. During an average year, approximately 225 burials are performed. In 1981 Grand View Funeral Home was opened adjacent to the memorial park. In 2021 the total number of interments in the memorial park exceeded 13,000. Notable burials * Arthur J. Forrest (1895–1964), World War I |
Supreme Court Of The United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point of federal law. It also has original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, specifically "all Cases affecting Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, and those in which a State shall be Party." The court holds the power of judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statute for violating a provision of the Constitution. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or statutory law. However, it may act only within the context of a case in an area of law over which it has jurisdiction. The court may decide cases having political overtones, but has ruled that it does not have power to decide non-justiciable political questions. Established by Article Three of the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurgood Marshall
Thurgood Marshall (July 2, 1908 – January 24, 1993) was an American civil rights lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1967 until 1991. He was the Supreme Court's first African-American justice. Prior to his judicial service, he was an attorney who fought for civil rights, leading the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund. Marshall coordinated the assault on racial segregation in schools. He won 29 of the 32 civil rights cases he argued before the Supreme Court, culminating in the Court's landmark 1954 decision in ''Brown v. Board of Education'', which rejected the separate but equal doctrine and held segregation in public education to be unconstitutional. President Lyndon B. Johnson appointed Marshall to the Supreme Court in 1967. A staunch liberal, he frequently dissented as the Court became increasingly conservative. Born in Baltimore, Maryland, Marshall attended Lincoln University and the Howard Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting Rights Act Of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement on August 6, 1965, and Congress later amended the Act five times to expand its protections. Designed to enforce the voting rights guaranteed by the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments to the United States Constitution, the Act sought to secure the right to vote for racial minorities throughout the country, especially in the South. According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the Act is considered to be the most effective piece of federal civil rights legislation ever enacted in the country. It is also "one of the most far-reaching pieces of civil rights legislation in U.S. history." The act contains numerous provisions that regulate elections. The act's "general provisions" provide nationwide protections for voting rights. Section 2 is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
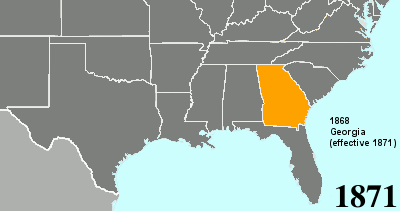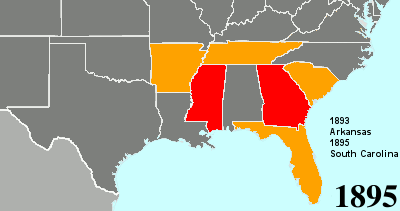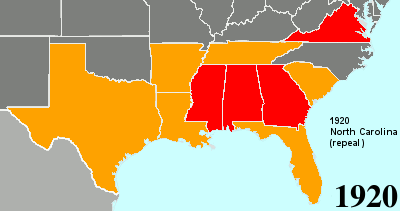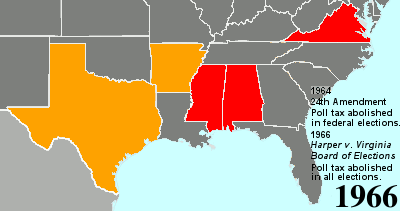
Twenty-fourth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Twenty-fourth Amendment (Amendment XXIV) of the United States Constitution prohibits both Congress and the states from conditioning the right to vote in federal elections on payment of a poll tax or other types of tax. The amendment was proposed by Congress to the states on August 27, 1962, and was ratified by the states on January 23, 1964. Southern states of the former Confederate States of America adopted poll taxes in laws of the late 19th century and new constitutions from 1890 to 1908, after the Democratic Party had generally regained control of state legislatures decades after the end of Reconstruction, as a measure to prevent African Americans and often poor whites (and following passage of the Nineteenth Amendment, women) from voting. Use of the poll taxes by states was held to be constitutional by the Supreme Court of the United States in the 1937 decision ''Breedlove v. Suttles''. When the 24th Amendment was ratified in 1964, five states still retained a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Act Of 1968
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a landmark law in the United States signed into law by United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots. Titles II through VII comprise the Indian Civil Rights Act, which applies to the Native American tribes of the United States and makes many but not all of the guarantees of the U.S. Bill of Rights applicable within the tribes. (that Act appears today in Title 25, sections 1301 to 1303 of the United States Code). Titles VIII and IX are commonly known as the Fair Housing Act, which was meant as a follow-up to the Civil Rights Act of 1964 (this is different legislation than the Housing and Urban Development Act of 1968, which expanded housing funding programs). While the Civil Rights Act of 1866 prohibited discrimination in housing, there were no federal enforcement provisions. The 1968 act expanded on previous acts and prohibited discrimination concerning the sale, rental, and financing of housing based on rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |