|
Edward Teach
Edward Teach (alternatively spelled Edward Thatch, – 22 November 1718), better known as Blackbeard, was an English pirate who operated around the West Indies and the eastern coast of Britain's North American colonies. Little is known about his early life, but he may have been a sailor on privateer ships during Queen Anne's War before he settled on the Bahamian island of New Providence, a base for Captain Benjamin Hornigold, whose crew Teach joined around 1716. Hornigold placed him in command of a sloop that he had captured, and the two engaged in numerous acts of piracy. Their numbers were boosted by the addition to their fleet of two more ships, one of which was commanded by Stede Bonnet; but Hornigold retired from piracy toward the end of 1717, taking two vessels with him. Teach captured a French slave ship known as , renamed her ''Queen Anne's Revenge'', equipped her with 40 guns, and crewed her with over 300 men. He became a renowned pirate. His nickname derived from h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Anne's Revenge
''Queen Anne's Revenge'' was an early-18th-century ship, most famously used as a flagship by Edward Teach, better known by his nickname Blackbeard. Although the date and place of the ship's construction are uncertain, it was originally believed she was built for merchant service in Bristol, England in 1710 and named ''Concord'', later captured by Kingdom of France, French privateers and renamed ''La Concorde''. After several years' service by French sailors (both as a naval frigate and as a merchant vessel – much of the time as a slave ship, slave trading ship), she was captured by Blackbeard in 1717. Blackbeard used the ship for less than a year, but captured numerous prize (law), prizes using her as his flagship. In May 1718, Blackbeard ran the ship aground at Topsail Inlet, now known as Beaufort, North Carolina, Beaufort Inlet, North Carolina, United States, in the present-day Carteret County, North Carolina, Carteret County. After the grounding, her crew and supplies were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Hornigold
Captain Benjamin Hornigold (1680–1719) was an English pirate who operated during the tail end of the Golden Age of Piracy. Born in England in the late 17th century, Hornigold began his pirate career in 1713, attacking merchant ships in the Bahamas. He helped to establish the "Republic of Pirates" in Nassau and by 1717 was the captain of one of the most heavily armed ships in the region, called the ''Ranger''. It was at this time he appointed Edward Teach, best known in history books as "Blackbeard", as his second-in-command. Mindful not to attack British-led ships during his career, his crew eventually grew tired of the tactic and Hornigold was voted out as captain. In December 1718, Hornigold accepted a King's Pardon for his crimes and became a pirate hunter, pursuing his former allies on behalf of the Governor of the Bahamas, Woodes Rogers. He was killed when his ship was wrecked on a reef near New Spain during the hurricane season of 1719. Early career Hornigold's early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
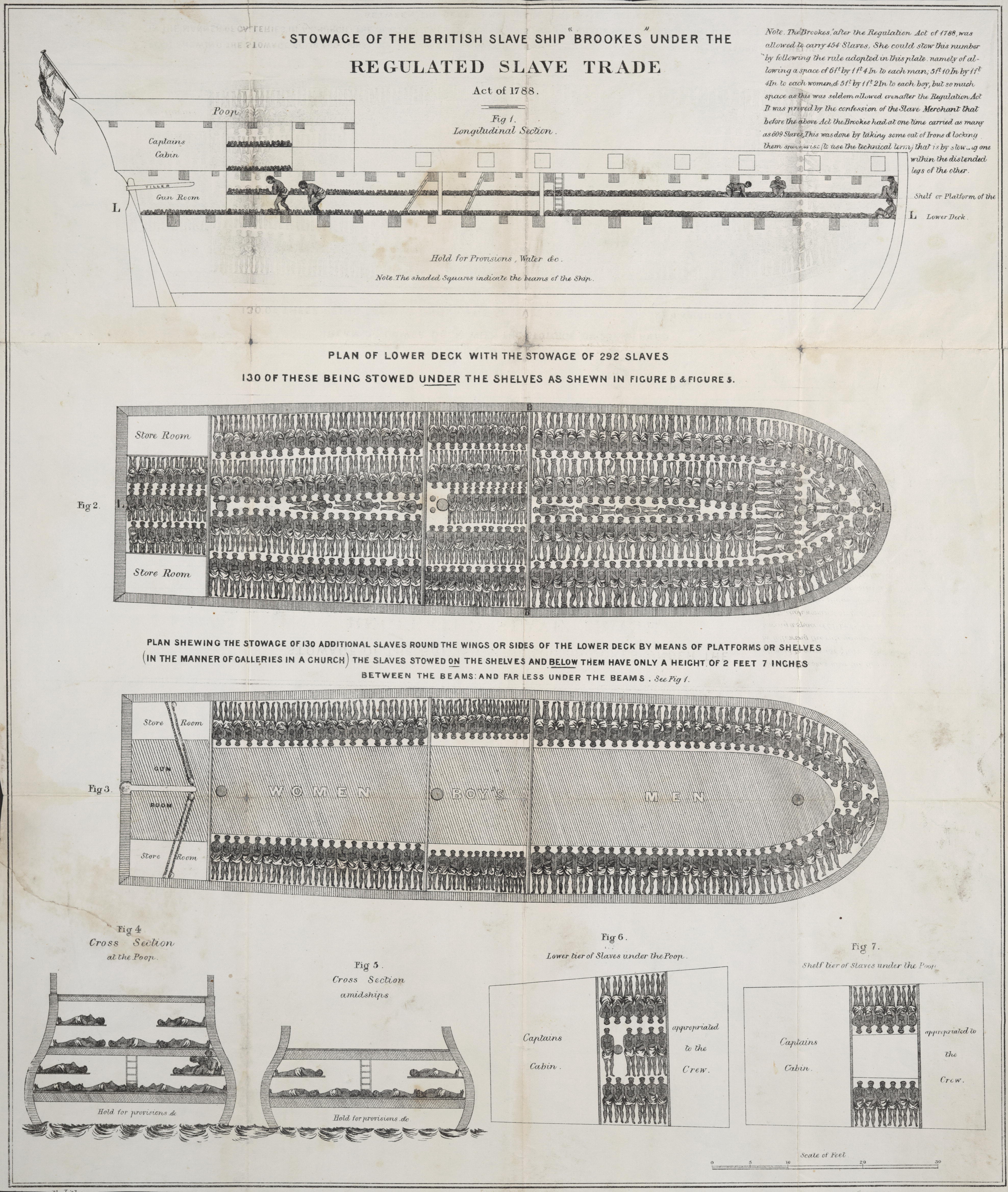
Slave Ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta Marie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
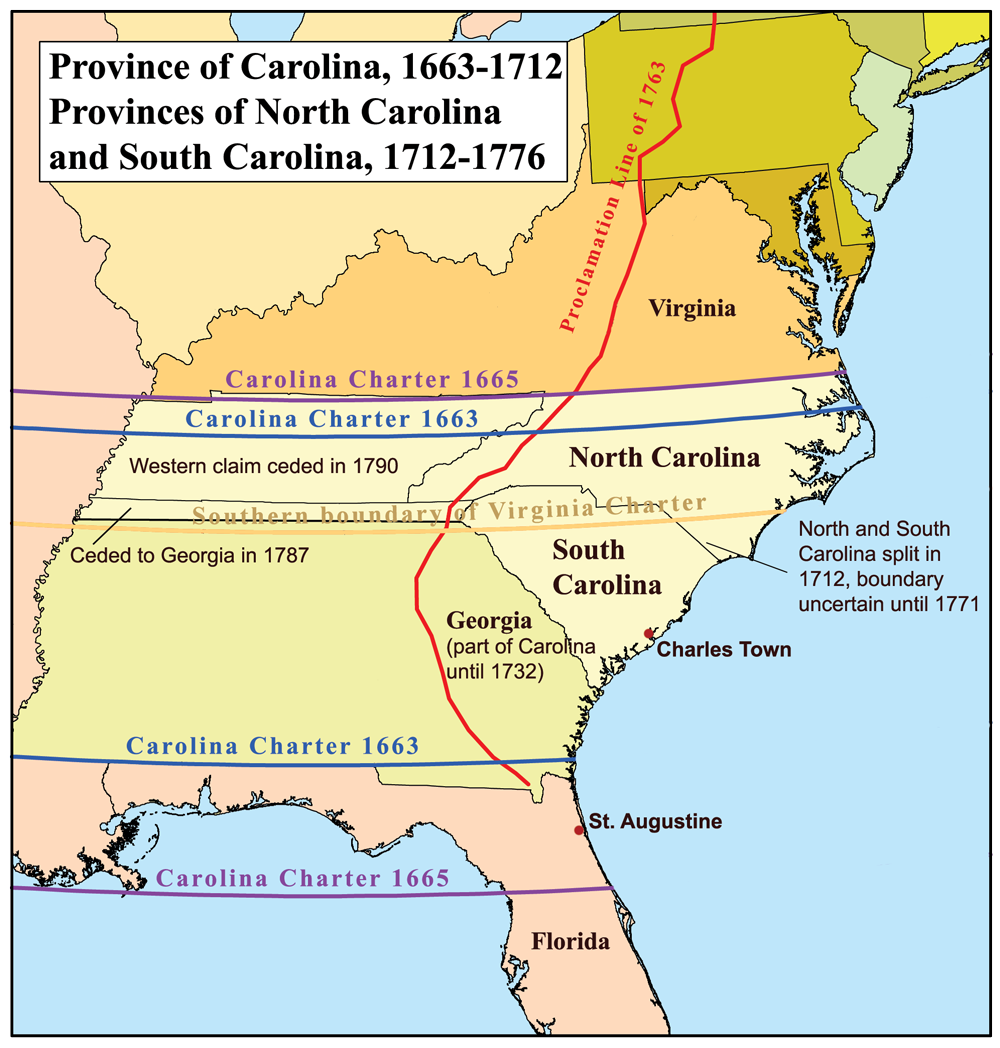
Province Of Carolina
Province of Carolina was a province of England (1663–1707) and Great Britain (1707–1712) that existed in North America and the Caribbean from 1663 until partitioned into North and South on January 24, 1712. It is part of present-day Alabama, Georgia, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and The Bahamas. Etymology "Carolina" is taken from the Latin word for " Charles" ( Carolus), honoring King CharlesI. and was first named in the 1663 Royal Charter granting to Edward, Earl of Clarendon; George, Duke of Albemarle; William, Lord Craven; John, Lord Berkeley; Anthony, Lord Ashley; Sir George Carteret, Sir William Berkeley, and Sir John Colleton the right to settle lands in the present-day U.S. states of North Carolina, Tennessee, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and Florida. Background On October 30, 1629, King Charles I of England granted a patent to Sir Robert Heath for the lands south of 36 degrees and north of 31 degrees, " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from Central and West Africa that had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders,Thornton, p. 112. while others had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids; Europeans gathered and imprisoned the enslaved at forts on the African coast and then brought them to the Americas. Except for the Portuguese, European slave traders generally did not participate in the raids because life expectancy for Europeans in sub-Saharan Africa was less than one year during the period of the slave trade (which was prior to the widespread availability of quini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Maynard
Robert Maynard (19 September 1684 – 4 January 1751) was a British lieutenant, and later captain, in the Royal Navy. Little is known about Maynard's early life, other than he was born in England in 1684 and then later joined the English Navy. He was made a lieutenant in January 1707, and by 1709 was the third lieutenant on . In November 1718, Maynard was tasked with hunting down and killing the notorious pirate Blackbeard. While leading , Maynard lured Blackbeard into attacking his ship off the coast of North Carolina, and in the ensuing struggle Maynard and his crew killed Blackbeard. Expecting to be rewarded for his actions, Maynard was never fully compensated or paid for the expedition. He was eventually promoted to commander in 1739, and to captain in 1740, before dying at the age of 66 in his home county of Kent, England. Early life Maynard was born in Dartford, Kent, England on 19 September 1684. Naval commands and battles Governor Alexander Spotswood of the Colony of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor Of Virginia
The governor of the Commonwealth of Virginia serves as the head of government of Virginia for a four-year term. The incumbent, Glenn Youngkin, was sworn in on January 15, 2022. Oath of office On inauguration day, the Governor-elect takes the following oath of office: ''"I do solemnly swear (or affirm) that I will support the Constitution of the United States, and the Constitution of the Commonwealth of Virginia, and that I will faithfully and impartially discharge all the duties incumbent upon me as Governor of the Commonwealth of Virginia, according to the best of my ability. (So help me, God.)"'' Qualifications Article V, Section 3 of the Virginia Constitution lists the following qualifications for a person to be elected Governor of Virginia: * Be a citizen of the United States * Be at least thirty years old * Be a resident and a registered voter in the Commonwealth of Virginia for at least five years before the election Unlike other state governors, Virginia governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Spotswood
Alexander Spotswood (12 December 1676 – 7 June 1740) was a British Army officer, explorer and lieutenant governor of Colonial Virginia; he is regarded as one of the most significant historical figures in British North American colonial history. After a brilliant but unsatisfactory military career, in 1710 he was nominated colonial governor of Virginia, a post which he held for twelve years. During that period, Spotswood engaged in the exploration of the territories beyond the western border, of which he was the first to see the economic potentials. In 1716 he organised and led an expedition west of the mountains, known as Knights of the Golden Horseshoe Expedition, with which he established the Crown's dominion over the territory between the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Shenandoah Valley, thus taking a decisive step for the future British expansion to the West. As the governor of Virginia, Spotswood's first preoccupation was to make sea routes safe and fight against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Pardon (piracy)
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the jurisdiction. Pardons can be granted in many countries when individuals are deemed to have demonstrated that they have "paid their debt to society", or are otherwise considered to be deserving of them. In some jurisdictions of some nations, accepting a pardon may ''implicitly'' constitute an admission of guilt; the offer is refused in some cases. Cases of wrongful conviction are in recent times more often dealt with by appeal rather than by pardon; however, a pardon is sometimes offered when innocence is undisputed in order to avoid the costs that are associated with a retrial. Clemency plays a critical role when capital punishment exists in a jurisdiction. Pardons are sometimes seen as a mechanism for combating corruption, allowing a parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath, North Carolina
Bath is a town in Beaufort County, North Carolina, United States. Located on the Pamlico River, it developed a trade in naval stores, furs, and tobacco. The population was 249 as of 2010. North Carolina’s first town and port of entry, it was chartered on March 8, 1705. Historically, Bath is often counted as North Carolina's first capital, as it was nominally so designated in 1712, when the Province of North Carolina was separated from the Province of Carolina and granted its own governor, though no permanent government institutions were located there. The capital was officially moved to Edenton in 1722, though the meetings of the General Assembly would still periodically occur in Bath through the eighteenth century. Bath was the site of Cary's Rebellion in 1711, and later served as one of many bases for notorious pirate Blackbeard. Bath waned in population, as its importance as both a port and government center were surpassed by the nearby city of New Bern; its pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort, North Carolina
Beaufort ( ) is a town in and the county seat of Carteret County, North Carolina, Carteret County, North Carolina, United States. Established in 1713 and incorporated in 1723, Beaufort is the fourth oldest town in North Carolina (after Bath, North Carolina, Bath, New Bern, North Carolina, New Bern and Edenton, North Carolina, Edenton). On February 1, 2012, Beaufort was ranked as "America's Coolest Small Town" by readers of ''Budget Travel Magazine.'' The population was 4,039 at the 2010 census. It is sometimes confused with Beaufort, South Carolina, a city of the same name in South Carolina; the two are distinguished by different pronunciations. Beaufort is located in North Carolina's "Inner Banks" region. The town is home to the North Carolina Maritime Museum, the Duke University Marine Laboratory (Nicholas School of the Environment), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Center for Coastal Fisheries and Habitat Research. It is also the location of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)



