|
Edmund O'Meara
Edmund O'Meara ( ga, Éamonn Ó Meadhra, also known as Edmund Meara; 1614–1681) was an Irish physiologist and one of the last prominent champions of the medical ideas of Galen. Son of Dermod O'Meara who was a physician, poet and author. O'Meara is remembered today for his criticism of vivisection, stating that the agony suffered by lab animals distorted the research results, using this as a basis to reject William Harvey's ideas about the circulatory system and defend the earlier theories of Galen.Arthur J. Donovan "Richard Lower, M.D., Physician and Surgeon (1631–1691)" ''World Journal of Surgery'' Volume 28, Number 9 / September 2004 pages 938–945 O'Meara wrote an epitaph for Malachy Ó Caollaidhe, but was unable to locate his grave. See also * Barry Edward O'Meara, surgeon, 1786–1836. * Kathleen O'Meara, catholic writer, 1839–1888. References * ''O'Meara, Edmund'', p. 808, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography 41 – Norbury – Osborn'', Oxford Ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Ethnicity
The Irish ( ga, Muintir na hÉireann or ''Na hÉireannaigh'') are an ethnic group and nation native to the island of Ireland, who share a common history and culture. There have been humans in Ireland for about 33,000 years, and it has been continually inhabited for more than 10,000 years (see Prehistoric Ireland). For most of Ireland's recorded history, the Irish have been primarily a Gaelic people (see Gaelic Ireland). From the 9th century, small numbers of Vikings settled in Ireland, becoming the Norse-Gaels. Anglo-Normans also conquered parts of Ireland in the 12th century, while England's 16th/17th century conquest and colonisation of Ireland brought many English and Lowland Scots to parts of the island, especially the north. Today, Ireland is made up of the Republic of Ireland (officially called Ireland) and Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom). The people of Northern Ireland hold various national identities including British, Irish, Northern Irish or some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiologist
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all medical researchers of antiquity, Galen influenced the development of various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and neurology, as well as philosophy and logic. The son of Aelius Nicon, a wealthy Greek architect with scholarly interests, Galen received a comprehensive education that prepared him for a successful career as a physician and philosopher. Born in the ancient city of Pergamon (present-day Bergama, Turkey), Galen traveled extensively, exposing himself to a wide variety of medical theories and discoveries before settling in Rome, where he served prominent members of Roman society and eventually was given the position of personal physician to several emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermod O'Meara
Dermod O'Meara ( ga, Diarmaid Ó Meadhra; fl. 1610–46) was an Irish physician and poet, author of the first medical work printed in Dublin in 1619. He was the father of Edmund O'Meara. Biography He was a son of Domhnaill O'Meara, lord of the Ó Meadhra lineage and foster-father to Thomas Butler. His family were hereditary physicians and poets to the Earls of Ormond. O'Meara's first published work—also the first book of Latin verse published in Ireland—was ''Ormonius'', published in 1614. It is a praise poem in the epic style about the life of Thomas Butler. In it, O'Meara describes himself as one of the vates, and claims that Thomas was suckled as a baby by Áine Áine () is an Irish goddess of summer, wealth and sovereignty. She is associated with midsummer and the sun,MacKillop, James (1998) ''Dictionary of Celtic Mythology'' Oxford: Oxford University Press pp.10, 16, 128 and is sometimes represent ..., an Irish goddess. Subsequently, O'Meara studied medicine a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
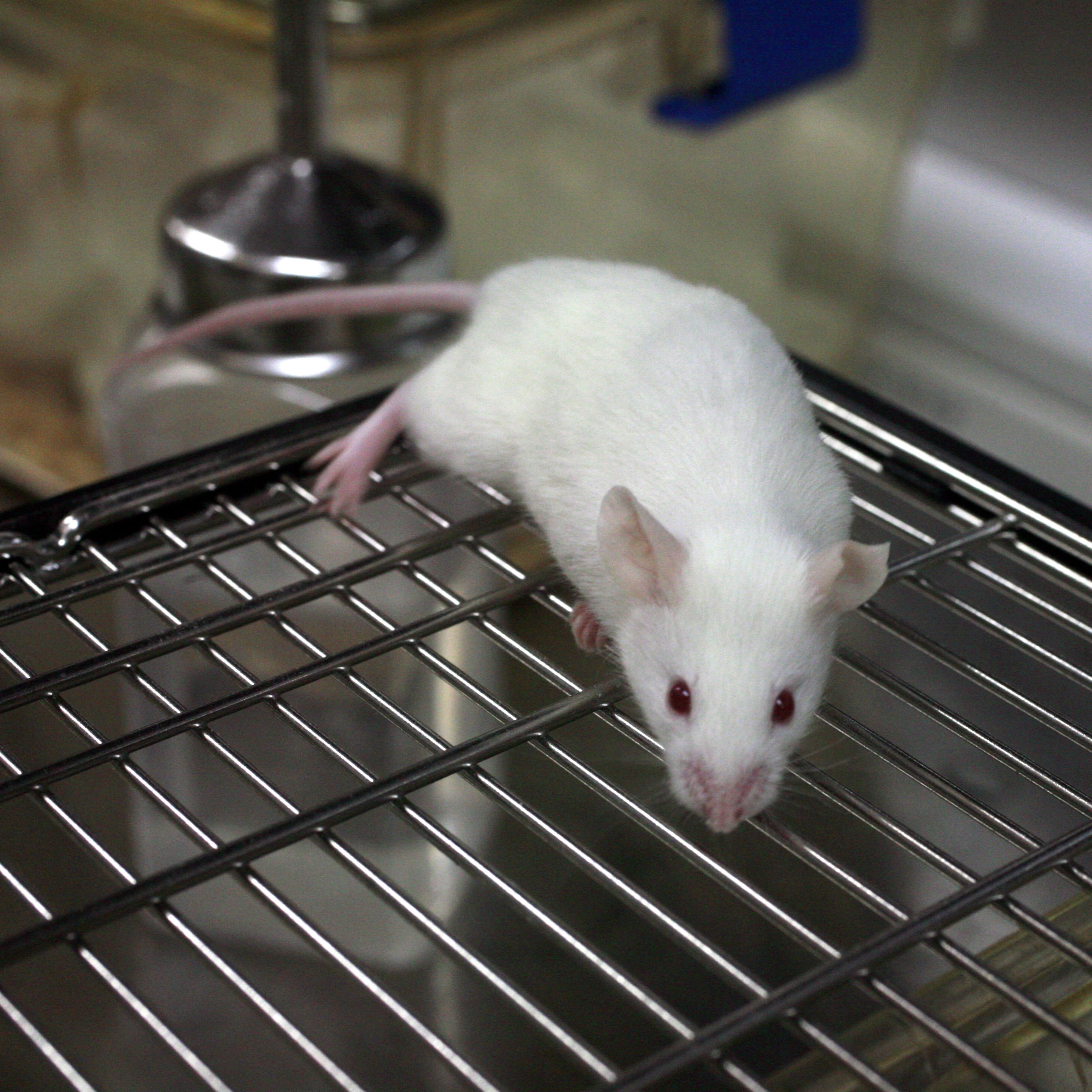
Vivisection
Vivisection () is surgery conducted for experimental purposes on a living organism, typically animals with a central nervous system, to view living internal structure. The word is, more broadly, used as a pejorative catch-all term for experimentation on live animalsTansey, E.MReview of ''Vivisection in Historical Perspective by Nicholaas A. Rupke, book reviews, National Center for Biotechnology Information, p. 226. by organizations opposed to animal experimentation,Yarri, Donna''The Ethics of Animal Experimentation: A Critical Analysis and Constructive Christian Proposal, Oxford University Press, 2005, p. 163. but the term is rarely used by practising scientists. Human vivisection, such as live organ harvesting, has been perpetrated as a form of torture. Animal vivisection Research requiring vivisection techniques that cannot be met through other means is often subject to an external ethics review in conception and implementation, and in many jurisdictions use of anesthesia is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions in anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, the systemic circulation and properties of blood being pumped to the brain and the rest of the body by the heart, though earlier writers, such as Realdo Colombo, Michael Servetus, and Jacques Dubois, had provided precursors of the theory. Family William's father, Thomas Harvey, was a jurat of Folkestone where he served as mayor in 1600. Records and personal descriptions delineate him as an overall calm, diligent, and intelligent man whose "sons... revered, consulted and implicitly trusted in him... (they) made their father the treasurer of their wealth when they acquired great estates...(He) kept, employed, and improved their gainings to their great advantage." Thomas Harvey's portrait can still be seen in the central panel of a wall of the dining room at Rolls Park, Chig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The Closed circulatory system, circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malachy Ó Caollaidhe
Malachy Ó Caollaidhe, also known as Malachy Queally, Malachias Quælly, O'Queely or O'Quechly (died 1645) was an Irish Roman Catholic archbishop of Tuam; he was called by Irish writers Maelseachlainn Ua Cadhla, by John Colgan Queleus, and erroneously by Thomas Carte, O'Kelly. Life Malachy Ó Caollaidhe was born in the barony of Corcomroe in County Clare. He belonged to a family which ruled Connemara till 1238, when they were conquered by the O'Flaherties. Ó Caollaidhe became a student at the College of Navarre in Paris, and there graduated with a Doctorate of Divinity. He was professor of philosophy at the Sorbonne for a time. He returned to Ireland and was appointed the vicar-apostolic of Killaloe by a papal brief on 30 August 1619. Following the death of Florence Conroy, he was appointed the archbishop of Tuam on 28 June 1630 and consecrated at Galway on 10 October 1630 by Thomas Walsh, archbishop of Cashel, with Richard Arthur, bishop of Limerick, and Boetius Egan, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barry Edward O'Meara
Barry Edward O'Meara (1786–1836), born in Newtown House, Newtown-on-Sea (now known as Blackrock), Dublin, was an Irish surgeon and founding member of the Reform Club, who accompanied Napoleon to Saint Helena and became his physician, having been surgeon on board the Bellerophon when the emperor surrendered himself. He was a medical graduate of Trinity College Dublin. Life O'Meara is remembered as the author of ''Napoleon in Exile, or A Voice From St. Helena'' (1822) a book which charged Sir Hudson Lowe with mistreating the former emperor and created no small sensation on its appearance. Less known are his secret letters he sent clandestinely from Saint Helena to a clerk at the Admiralty in London. These letters shed a unique light on Napoleon's state of mind as a captive and the causes of his complaints against Lowe and the British government. O'Meara was also the physician to have performed the very first medical operation on Napoleon: by extracting a wisdom tooth in the autum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathleen O'Meara (writer)
Kathleen O'Meara, also known under her pen name Grace Ramsay (1839 – 10 November 1888), was an Irish-French Catholic writer and biographer during the late Victorian era. She was the Paris correspondent of ''The Tablet'', a leading British Catholic magazine. ''Irish Monthly'' also published many of her serialized and biographical works. O'Meara also wrote works of fiction where she explored a variety of topics from women's suffrage to eastern European revolutions. The majority of her novels contained Catholic themes and social reform issues. Life O'Meara was born in Dublin in 1839.Cooper, Thompson, and Maria Luddy. "O'Meara, Kathleen seud. Grace Ramsay(1839-1888), Writer." Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (2004): Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Web. Her father was Dennis O'Meara of Tipperary, while her grandfather, Barry Edward O'Meara, had been Napoleon's physician on St. Helena from the years 1815–1818. He later denounced Britain's treatment of the ex-empero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the University of Oxford, the oldest university in the English-speaking world; it has buildings in every style of English architecture since late Anglo-Saxon. Oxford's industries include motor manufacturing, education, publishing, information technology and science. History The history of Oxford in England dates back to its original settlement in the Saxon period. Originally of strategic significance due to its controlling location on the upper reaches of the River Thames at its junction with the River Cherwell, the town grew in national importance during the early Norman period, and in the late 12th century became home to the fledgling University of Oxford. The city was besieged during The Anarchy in 1142. The university rose to dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Irish Medical Doctors
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Veloso_Salgado.png)
_Venenbild.jpg)


