|
Edinburgh IMP
Edinburgh IMP is a development of Atlas Autocode, initially developed around 1966-1969 at the University of Edinburgh, Scotland. It is a general-purpose programming language which was used heavily for systems programming. Expressively, IMP is highly similar to ALGOL and includes all the ALGOL-style block structure, reserved words (keywords), and data types such as arrays, and records. It adds to ALGOL-style languages a string type (an array of characters, although these have a predeclared size) and built-in operators for string manipulation and character handling. One significant difference from ALGOL is that IMP does not support parameters passed by name, although it does support parameters passed by reference. IMP provides significant control over the storage mapping of data, plus commands for addressing within parts of words. Most IMP compilers offer compiler-generated runtime checks and a stack trace (backtrace) facility by default, even in production code. IMP allows inli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procedural Programming
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm, derived from imperative programming, based on the concept of the ''procedure call''. Procedures (a type of routine or subroutine) simply contain a series of computational steps to be carried out. Any given procedure might be called at any point during a program's execution, including by other procedures or itself. The first major procedural programming languages appeared circa 1957–1964, including Fortran, ALGOL, COBOL, PL/I and BASIC. Pascal and C were published circa 1970–1972. Computer processors provide hardware support for procedural programming through a stack register and instructions for calling procedures and returning from them. Hardware support for other types of programming is possible, but no attempt was commercially successful (for example Lisp machines or Java processors). Procedures and modularity Modularity is generally desirable, especially in large, complicated programs. Inputs are usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stack Trace
In computing, a stack trace (also called stack backtrace or stack traceback) is a report of the active stack frames at a certain point in time during the execution of a program. When a program is run, memory is often dynamically allocated in two places; the stack and the heap. Memory is continuously allocated on a stack but not on a heap, thus reflective of their names. Stack also refers to a programming construct, thus to differentiate it, this stack is referred to as the program's function call stack. Technically, once a block of memory has been allocated on the stack, it cannot be easily removed as there can be other blocks of memory that were allocated before it. Each time a function is called in a program, a block of memory called an activation record is allocated on top of the call stack. Generally, the activation record stores the function's arguments and local variables. What exactly it contains and how it's laid out is determined by the calling convention. Programmers co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runtime (program Lifecycle Phase)
In computer science, runtime, run time, or execution time is the final phase of a computer programs life cycle, in which the code is being executed on the computer's central processing unit (CPU) as machine code. In other words, "runtime" is the running phase of a program. A runtime error is detected after or during the execution (running state) of a program, whereas a compile-time error is detected by the compiler before the program is ever executed. Type checking, register allocation, code generation, and code optimization are typically done at compile time, but may be done at runtime depending on the particular language and compiler. Many other runtime errors exist and are handled differently by different programming languages, such as division by zero errors, domain errors, array subscript out of bounds errors, arithmetic underflow errors, several types of underflow and overflow errors, and many other runtime errors generally considered as software bugs which may or may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program. Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffrey D. Ullman - Second Edition, 2007 There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A ''cross-compiler'' produces code for a different CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A ''bootstrap compiler'' is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimised compiler for a language. Related software include, a program that translates from a low-level language to a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
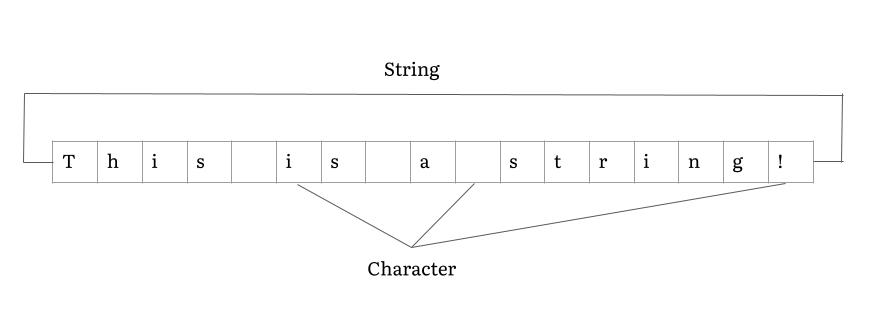
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record (computer Science)
In computer science, a record (also called a structure, struct, or compound data) is a basic data structure. Records in a database or spreadsheet are usually called "rows". A record is a collection of ''fields'', possibly of different data types, typically in a fixed number and sequence. The fields of a record may also be called ''members'', particularly in object-oriented programming; fields may also be called ''elements'', though this risks confusion with the elements of a collection. For example, a date could be stored as a record containing a numeric year field, a month field represented as a string, and a numeric day-of-month field. A personnel record might contain a name, a salary, and a rank. A Circle record might contain a center and a radius—in this instance, the center itself might be represented as a point record containing x and y coordinates. Records are distinguished from arrays by the fact that their number of fields is determined in the definition of the rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Array Data Type
In computer science, array is a data type that represents a collection of ''elements'' (value (computer science), values or variable (computer science), variables), each selected by one or more indices (identifying keys) that can be computed at Run time (program lifecycle phase), run time during program execution. Such a collection is usually called an array variable or array value.Robert W. Sebesta (2001) ''Concepts of Programming Languages''. Addison-Wesley. 4th edition (1998), 5th edition (2001), By analogy with the mathematical concepts vector (mathematics), vector and matrix (mathematics), matrix, array types with one and two indices are often called vector type and matrix type, respectively. More generally, a multidimensional array type can be called a tensor type, by anology with the physical concept, tensor. Language support for array types may include certain built-in type, built-in array data types, some syntactic constructions (''array type constructors'') that the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Type
In computer science and computer programming, a data type (or simply type) is a set of possible values and a set of allowed operations on it. A data type tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data. Most programming languages support basic data types of integer numbers (of varying sizes), floating-point numbers (which approximate real numbers), characters and Booleans. A data type constrains the possible values that an expression, such as a variable or a function, might take. This data type defines the operations that can be done on the data, the meaning of the data, and the way values of that type can be stored. Concept A data type is a collection or grouping of data values. Such a grouping may be defined for many reasons: similarity, convenience, or to focus the attention. It is frequently a matter of good organization that aids the understanding of complex definitions. Almost all programming languages explicitly include the notion of data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserved Word
In a computer language, a reserved word (also known as a reserved identifier) is a word that cannot be used as an identifier, such as the name of a variable, function, or label – it is "reserved from use". This is a syntactic definition, and a reserved word may have no user-defined meaning. A closely related and often conflated notion is a keyword, which is a word with special meaning in a particular context. This is a semantic definition. By contrast, names in a standard library but not built into the language are not considered reserved words or keywords. The terms "reserved word" and "keyword" are often used interchangeably – one may say that a reserved word is "reserved for use as a keyword" – and formal use varies from language to language; for this article we distinguish as above. In general reserved words and keywords need not coincide, but in most modern languages keywords are a subset of reserved words, as this makes parsing easier, since keywords cannot be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block (programming)
In computer programming, a block or code block or block of code is a lexical structure of source code which is grouped together. Blocks consist of one or more Declaration (computer programming), declarations and Statement (computer science), statements. A programming language that permits the creation of blocks, including blocks Nesting (computing), nested within other blocks, is called a block-structured programming language. Blocks are fundamental to structured programming, where control structures are formed from blocks. Blocks have two functions: to group statements so that they can be treated as one statement, and to define scope (computer science), scopes for name binding, names to distinguish them from the same name used elsewhere. In a block-structured programming language, the objects named in outer blocks are visible inside inner blocks, unless they are Name masking, masked by an Object (computer science), object declared with the same name. History Ideas of block st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Programming
Systems programming, or system programming, is the activity of programming computer system software. The primary distinguishing characteristic of systems programming when compared to application programming is that application programming aims to produce software which provides services to the user directly (e.g. word processor), whereas systems programming aims to produce software and software platforms which provide services to other software, are performance constrained, or both (e.g. operating systems, computational science applications, game engines, industrial automation, and software as a service applications). Systems programming requires a great degree of hardware awareness. Its goal is to achieve efficient use of available resources, either because the software itself is performance critical or because even small efficiency improvements directly transform into significant savings of time or money. Overview The following attributes characterize systems programming: * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)