|
Economic Puzzle
A puzzle in economics is a situation where the implication of theory is inconsistent with observed economic data. An example is the equity premium puzzle, which relates to the fact that over the last two hundred years, the risk premium of stocks over bonds has been around 5.5%, much larger than expected from theory. The equity premium puzzle was first documented by Mehra and Prescot (1985). List of puzzles :''See also :Economic puzzles; Financial economics #Challenges and criticism.'' *Equity premium puzzle * Home bias in trade puzzle *Equity home bias puzzle * Consumption correlations puzzle * Feldstein-Horioka puzzle *Forward premium anomaly *Real exchange rate puzzles The real exchange-rate puzzles is a common term for two much-discussed anomalies of real exchange rates: that real exchange rates are more '' volatile'' and show more ''persistence'' than what most models can account for. These two anomalies are s ... *Retirement-consumption puzzle *Missing trade puzzle, als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity Premium Puzzle
The equity premium puzzle refers to the inability of an important class of economic models to explain the average equity risk premium (ERP) provided by a diversified portfolio of U.S. equities over that of U.S. Treasury Bills, which has been observed for more than 100 years. There is significant disparity between returns produced by stocks compared to returns produced by government treasury bills. The equity premium puzzle addresses the difficulty in understanding and explaining this disparity. This disparity is calculated using the equity risk premium: The equity risk premium is equal to the difference between equity returns and returns from government bonds. It is equal to around 5% to 8% in the United States. The risk premium represents the compensation awarded to the equity holder for taking on a higher risk by investing in equities rather than government bonds. However, the 5% to 8% premium is considered to be an implausibly high difference and the equity premium puzzle ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
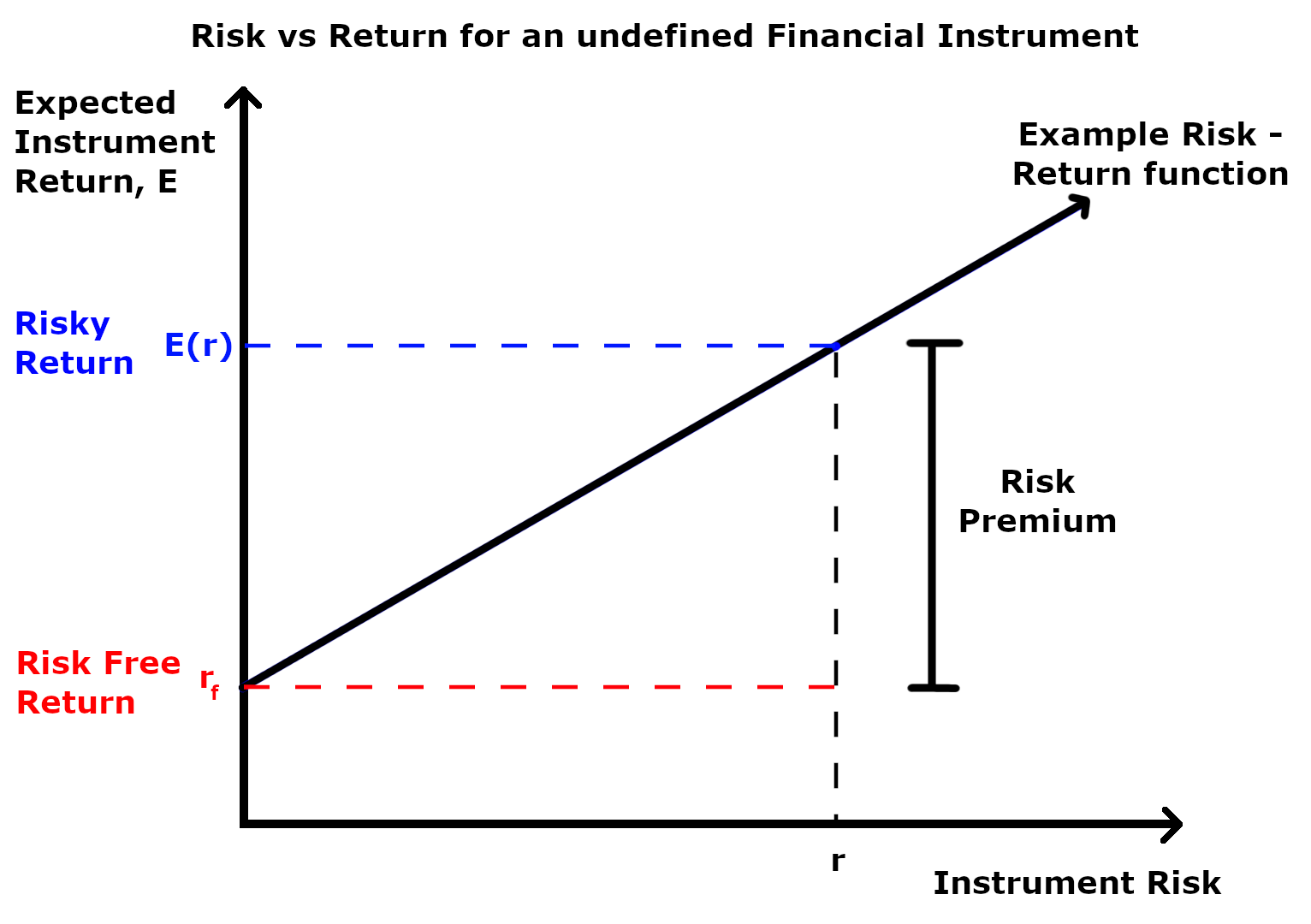
Risk Premium
A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being subjected to an increased level of risk. It is used widely in finance and economics, the general definition being the expected risky return less the risk-free return, as demonstrated by the formula below. Risk \ premium = E(r) - r_f Where E(r) is the risky expected rate of return and r_f is the risk-free return. The inputs for each of these variables and the ultimate interpretation of the risk premium value differs depending on the application as explained in the following sections. Regardless of the application, the market premium can be volatile as both comprising variables can be impacted independent of each other by both cyclical and abrupt changes. This means that the market premium is dynamic in nature and ever-changing. Additionally, a general observation regardless of application is that the risk premium is larger during economic downturns and during periods of increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock
In finance, stock (also capital stock) consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided.Longman Business English Dictionary: "stock - ''especially AmE'' one of the shares into which ownership of a company is divided, or these shares considered together" "When a company issues shares or stocks ''especially AmE'', it makes them available for people to buy for the first time." (Especially in American English, the word "stocks" is also used to refer to shares.) A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of shares. This typically entitles the shareholder (stockholder) to that fraction of the company's earnings, proceeds from liquidation of assets (after discharge of all senior claims such as secured and unsecured debt), or voting power, often dividing these up in proportion to the amount of money each stockholder has invested. Not all stock is necessarily equal, as certain classe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a type of security under which the issuer ( debtor) owes the holder ( creditor) a debt, and is obliged – depending on the terms – to repay the principal (i.e. amount borrowed) of the bond at the maturity date as well as interest (called the coupon) over a specified amount of time. The interest is usually payable at fixed intervals: semiannual, annual, and less often at other periods. Thus, a bond is a form of loan or IOU. Bonds provide the borrower with external funds to finance long-term investments or, in the case of government bonds, to finance current expenditure. Bonds and stocks are both securities, but the major difference between the two is that (capital) stockholders have an equity stake in a company (i.e. they are owners), whereas bondholders have a creditor stake in a company (i.e. they are lenders). As creditors, bondholders have priority over stockholders. This means they will be repaid in advance of stockholders, but will rank b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Economic Puzzles
{{see also cat, Paradoxes in economics Puzzles A puzzle is a game, problem, or toy that tests a person's ingenuity or knowledge. In a puzzle, the solver is expected to put pieces together ( or take them apart) in a logical way, in order to arrive at the correct or fun solution of the puzzle ... Open problems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Economics
Financial economics, also known as finance, is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on ''both sides'' of a trade". William F. Sharpe"Financial Economics", in Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus:Merton H. Miller, (1999). The History of Finance: An Eyewitness Account, ''Journal of Portfolio Management''. Summer 1999. asset pricing, commonly known as "Investments", and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance. The subject is concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment".See Fama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity Premium Puzzle
The equity premium puzzle refers to the inability of an important class of economic models to explain the average equity risk premium (ERP) provided by a diversified portfolio of U.S. equities over that of U.S. Treasury Bills, which has been observed for more than 100 years. There is significant disparity between returns produced by stocks compared to returns produced by government treasury bills. The equity premium puzzle addresses the difficulty in understanding and explaining this disparity. This disparity is calculated using the equity risk premium: The equity risk premium is equal to the difference between equity returns and returns from government bonds. It is equal to around 5% to 8% in the United States. The risk premium represents the compensation awarded to the equity holder for taking on a higher risk by investing in equities rather than government bonds. However, the 5% to 8% premium is considered to be an implausibly high difference and the equity premium puzzle ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Bias In Trade Puzzle
The Home bias in trade puzzle is a widely discussed problem in macroeconomics and international finance, first documented by John T. McCallum in an article from 1995. McCallum showed that for the United States and Canada, inter-province trade is 20 times larger than international trade, holding other determinants of trade fixed. Subsequent estimates by John F. Helliwell and others have whittled this bias down to a factor from 6 to 12. This home bias in trade has later been documented among OECD countries. The preferred explanation for this finding has been the presence of formal and informal trade barriers following national borders. Another possible solution to the fact that domestic trade is 20 times larger than international trade could be that domestically traders speak the same language. If presence of formal and informal trade barriers following national borders was the sole reason for this puzzle, home bias should not exist on the subnational level. Wolf (2000) finds, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity Home Bias Puzzle
The Home bias puzzle is the term given to describe the fact that individuals and institutions in most countries hold only modest amounts of foreign equity, and tend to strongly favor company stock from their home nation. This finding is regarded as puzzling, since observed returns on national equity portfolios suggest substantial benefits from international diversification. Maurice Obstfeld and Kenneth Rogoff identified this as one of the six major puzzles in international macroeconomics. Overview Home bias in equities is a behavioral finance phenomenon and it was first studied in an academic context by Kenneth French and James M. Poterba (1991) and Tesar and Werner (1995). Coval and Moskowitz (1999) showed that home bias is not limited to international portfolios, but that the preference for investing close to home also applies to portfolios of domestic stocks. Specifically, they showed that U.S. investment managers often exhibit a strong preference for locally headquartere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption Correlations Puzzle
{{disambiguation ...
Consumption may refer to: *Resource consumption *Tuberculosis, an infectious disease, historically * Consumption (ecology), receipt of energy by consuming other organisms * Consumption (economics), the purchasing of newly produced goods for current use also defined as the consuming of products ** Consumption function, an economic formula * Consumption (sociology) of resources, associated with social class, identity, group membership, and age See also * * Consumerism Consumerism is a social and economic order that encourages the acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing amounts. With the Industrial Revolution, but particularly in the 20th century, mass production led to overproduction—the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)