|
Ecoenergy
{{Infobox organization , name = Ecoenergy , logo = Ecoenergy.JPG , location = Canada , website NRCan Natural Resources Canada's (NRCan's) ecoENERGY retrofit program provides financial support to homeowners, small and medium-sized businesses, public institutions and industrial facilities to help them implement energy saving projects that reduce energy-related greenhouse gases (GHGs) and air pollution. There was originally a residential program, and a business program. Natural Resources Canada's Office of Energy Efficiency is no longer offering the ecoENERGY Retrofit Incentive for Buildings, the commercial/institutional component of the ecoENERGY Retrofit financial incentives for existing homes, buildings and industrial processes. The business program ended on June 6, 2012. See also *EnerGuide for New Houses *EnerGuide *EnerGuide for Houses External linksecoENERGY Initiative [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Resources Canada
Natural Resources Canada (NRCan; french: Ressources naturelles Canada; french: RNCan, label=none)Natural Resources Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Natural Resources (). is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for natural resources, energy, minerals and metals, forests, earth sciences, mapping, and remote sensing. It was formed in 1994 by amalgamating the Department of Energy, Mines and Resources with the Department of Forestry. Under the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', primary responsibility for natural resources falls to provincial governments, however, the federal government has jurisdiction over off-shore resources, trade and commerce in natural resources, statistics, international relations, and boundaries. The department administers federal legislation relating to natural resources, including energy, forests, minerals and metals. The department also collaborates with American and Mexican governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
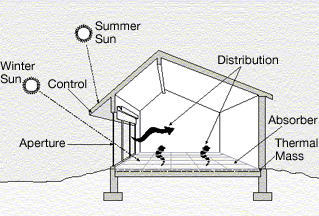
Retrofit
Retrofitting is the addition of new technology or features to older systems. Retrofits can happen for a number of reasons, for example with big capital expenditures like naval vessels, military equipment or manufacturing plants, businesses or governments may retrofit in order to reduce the need to replace a system entirely. Other retrofits may be due to changing codes or requirements, such as seismic retrofit which are designed strengthening older buildings in order to make them earthquake-resistant. Retrofitting is also an important part of climate change mitigation and climate change adaptation: because society invested in built infrastructure, housing and other systems before the magnitude of changes anticipated by climate change. Retrofits to increase building efficiency, for example, both help reduce the overall negative impacts of climate change by reducing building emissions and environmental impacts while also allowing the building to be more healthy during extreme wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Saving
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane (), nitrous oxide (), and ozone (). Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of . The atmospheres of atmosphere of Venus, Venus, atmosphere of Mars, Mars and atmosphere of Titan, Titan also contain greenhouse gases. Human activities since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (around 1750) have increased the Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide by over 50%, from 280 parts per million, ppm in 1750 to 421 ppm in 2022. The last time the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide was this high was over 3&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, heart disease, COPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EnerGuide For New Houses
EnerGuide is the official Government of Canada mark associated with the labelling and rating of the energy consumption or energy efficiency of specific products. The EnerGuide's efficiency percent is calculated by dividing the power output by power input. EnerGuide labelling exists for appliances, heating and cooling equipment, houses and vehicles. EnerGuide includes a house energy evaluation, including tests to find air leakage and the energy efficiency of its heating. It was designed to help Canadians reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and to save energy. To accomplish the same goals for new home construction the EnerGuide for New Houses program was initiated in 2006. The new Saskatchewan EnerGuide for Houses program is active from April 1, 2011 to October 31, 2013. EnerGuide for New Houses The EnerGuide for New Houses program, a sister program of EnerGuide for Houses, helps Canadians plan and build new homes that are cost-effective and energy efficient, that lower greenhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EnerGuide
EnerGuide is the official Government of Canada mark associated with the labelling and rating of the energy consumption or energy efficiency of specific products. The EnerGuide's efficiency percent is calculated by dividing the power output by power input. EnerGuide labelling exists for appliances, heating and cooling equipment, houses and vehicles. EnerGuide includes a house energy evaluation, including tests to find air leakage and the energy efficiency of its heating. It was designed to help Canadians reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and to save energy. To accomplish the same goals for new home construction the EnerGuide for New Houses program was initiated in 2006. The new Saskatchewan EnerGuide for Houses program is active from April 1, 2011 to October 31, 2013. EnerGuide for New Houses The EnerGuide for New Houses program, a sister program of EnerGuide for Houses, helps Canadians plan and build new homes that are cost-effective and energy efficient, that lower greenhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EnerGuide For Houses
EnerGuide is the official Government of Canada mark associated with the labelling and rating of the energy consumption or energy efficiency of specific products. The EnerGuide's efficiency percent is calculated by dividing the power output by power input. EnerGuide labelling exists for appliances, heating and cooling equipment, houses and vehicles. EnerGuide includes a house energy evaluation, including tests to find air leakage and the energy efficiency of its heating. It was designed to help Canadians reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and to save energy. To accomplish the same goals for new home construction the EnerGuide for New Houses program was initiated in 2006. The new Saskatchewan EnerGuide for Houses program is active from April 1, 2011 to October 31, 2013. EnerGuide for New Houses The EnerGuide for New Houses program, a sister program of EnerGuide for Houses, helps Canadians plan and build new homes that are cost-effective and energy efficient, that lower greenhous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |