|
East Suffolk (county)
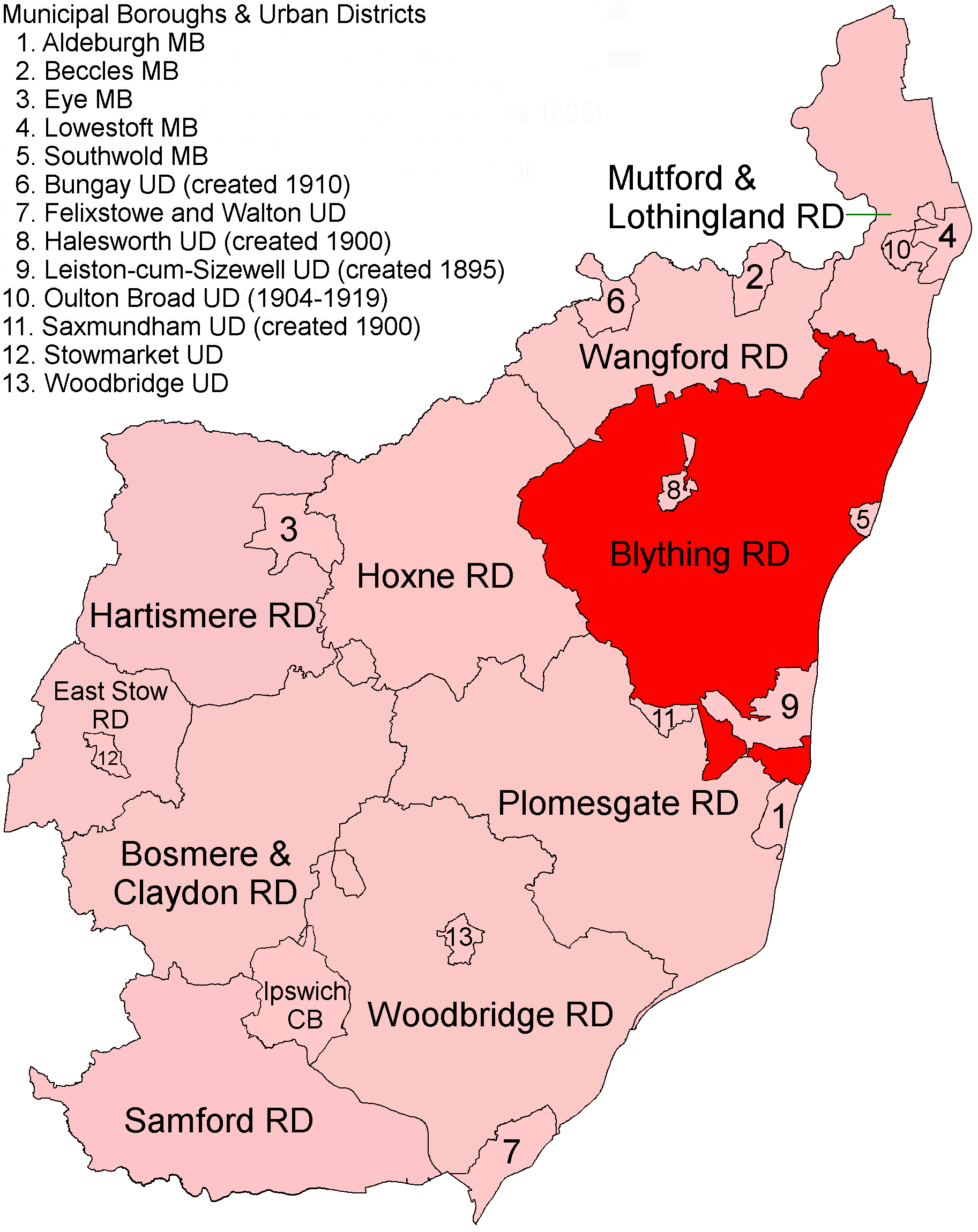
East Suffolk, along with West Suffolk, was created in 1888 as an administrative county of England. The administrative county was based on the eastern quarter sessions division of Suffolk. East Suffolk County Council's headquarters were at East Suffolk County Hall in Ipswich. In 1974, most of the county reunified with West Suffolk and the county borough of Ipswich to form the non-metropolitan county of Suffolk. Subdivisions From 1894 the administrative county was divided into municipal boroughs, urban districts and rural districts: *Boroughs: Aldeburgh, Beccles, Eye, Lowestoft, Southwold *Urban districts: Bungay (created 1910), Felixstowe and Walton, (renamed Felixstowe 1914), Halesworth (created 1900), Leiston-cum-Sizewell (created 1895), Oulton Broad (created 1904, abolished 1919), Saxmundham (created 1900), Stowmarket, Woodbridge *Rural districts created in 1894: Blything, Bosmere and Claydon, East Stow, Hartismere, Hoxne, Mutford and Lothingland, Plomesgate, Samford, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldeburgh
Aldeburgh ( ) is a coastal town in the English county, county of Suffolk, England. Located to the north of the River Alde. Its estimated population was 2,276 in 2019. It was home to the composer Benjamin Britten and remains the centre of the international Aldeburgh Festival of arts at nearby Snape Maltings, which was founded by Britten in 1948.Aldeburgh Town Council Retrieved 9 January 2016.Archives Hub Retrieved 7 March 2019. It also hosts an annual poetry festival and several food festivals and other events. Aldeburgh, as a port, gained borough status in 1529 under Henry VIII. Its historic buildings include a 16th-centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blything Rural District
Blything Rural District was a rural district within the administrative county of East Suffolk between 1894 and 1934. Evolution The district had its origins in the Blything Hundred Incorporation, set up in 1764 to administer the poor laws in the hundred of Blything. A workhouse to serve the area was built at Bulcamp in the parish of Blythburgh, opening in 1766. Following the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, the old incorporation was dissolved and replaced by the Blything Poor Law Union in 1835. In 1872, sanitary districts were established, with responsibility for public health and local government given to the boards of guardians of poor law unions for areas without urban authorities. The Blything Rural Sanitary District therefore covered the area of the Blything Poor Law Union except for the parish of Southwold, which was a municipal borough and so formed its own urban sanitary district. Under the Local Government Act 1894, rural sanitary districts became rural districts on 28 Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodbridge Urban District
Woodbridge may refer to: Places Australia *Woodbridge, Western Australia formerly called ''West Midland'' *Woodbridge, Tasmania Canada *Woodbridge, Ontario England *Woodbridge, Suffolk, the location of **Woodbridge (UK Parliament constituency), 1885–1950 **Woodbridge School **RAF Woodbridge * Woodbridge High School, Redbridge *Woodbridge, Devon * Woodbridge, Dorset * Woodbridge, Gloucestershire, a location * Woodbridge, Northumberland, a location United States *Woodbridge, California *Woodbridge, Irvine, California *Woodbridge, Connecticut *Woodbridge Township, New Jersey *Woodbridge (CDP), New Jersey *Woodbridge, Virginia *Woodbridge, Dallas, Texas, a neighborhood *Woodbridge, Detroit Other uses *Woodbridge (plantation), formerly in Prince William County, Virginia, US *Woodbridge (surname) *The Woodbridge Company *Woodbridge's Regiment of Militia, a Massachusetts regiment in the American Revolutionary War *Woodbridge wine, made by Robert Mondavi (now part of Constellation B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stowmarket
Stowmarket ( ) is a market town in Suffolk, England,OS Explorer map 211: Bury St.Edmunds and Stowmarket Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton A2 edition. Publishing Date:2008. on the busy A14 road (Great Britain), A14 trunk road between Bury St Edmunds to the west and Ipswich to the southeast. The town is on the main railway line between London and Norwich, and lies on the River Gipping, which is joined by its tributary, the River Rat, to the south of the town. The town takes its name from the Old English language, Old English word ''stōw'' meaning "principal place", and was granted a market charter in 1347 by Edward III of England, Edward III. A bi-weekly market is still held there today on Thursday and Saturday. The population of the town has increased from around 6,000 in 1981 to its current level of around 19,000, with considerable further development planned for the town and surrounding villages as part of an area action plan. It is the largest town in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxmundham
Saxmundham ( ) is a market town in Suffolk, England, set in the valley of the River Fromus about north-east of Ipswich and west of the coast at Sizewell. The town is bypassed by the main A12 road between London and Lowestoft. The town is served by Saxmundham railway station on the East Suffolk Line between Ipswich and Lowestoft. Governance Saxmundham Town Council comes under East Suffolk District. It was previously in Suffolk Coastal District before April 2019. The district electoral ward also has the name Saxmundham. Its population at the 2011 census was 4,913. As of December 2022, Saxmundham Town Council consisted of ten councillors. Heritage The place-name Saxmundham is first attested in the Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Sasmunde(s)ham''. It appears as ''Saxmundham'' in the Feet of Fines of 1213. The name denotes "Seaxmund's village or estate". The Parish Church of St John the Baptist dates back to the 11th century. Some features remain from the medieval period, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oulton Broad
Oulton Broad refers to both the lake and the suburb of Lowestoft in the English county of Suffolk. The suburb is located west of the centre of Lowestoft. It became a civil parish in 2017. It had an estimated population of 10,338 at the 2011 United Kingdom census. Oulton Broad Oulton Broad is an expanse of water and marsh which forms part of the network of man-made bodies of water known as The Broads. It is believed to be the remnant of medieval peat cutting. To the east it is linked by Mutford Lock to the saltwater Lake Lothing which passes through the centre of Lowestoft and opens into the North Sea. To the west it is linked by Oulton Dyke to the River Waveney. The Broad is the most southern area of open water in the Broads system, and is a busy tourist and sporting centre. It is used for a variety of watersports, including powerboat racing, and as the base for boat hire. Facilities include a yacht station and moorings as well as a 'village' of holiday chalets. Nicholas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiston-cum-Sizewell
Leiston ( ) is an English town in the East Suffolk non-metropolitan district of Suffolk, near Saxmundham and Aldeburgh, about from the North Sea coast, north-east of Ipswich and north-east of London. The town had a population of 5,508 at the 2011 Census. History The 14th-century remains of Leiston Abbey lie north-west of the town.Leiston Abbey English Heritage. Retrieved 30 March 2011. Leiston thrived in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a manufacturing town, dominated by , owners of Leiston Works, which boasted the world's first flow assembly line, for the manufacture of |
Halesworth
Halesworth is a market town, civil parish and electoral ward in north-eastern Suffolk, England. The population stood at 4,726 in the 2011 Census. It lies south-west of Lowestoft, on a tributary of the River Blyth, upstream from Southwold. The town is served by Halesworth railway station on the Ipswich–Lowestoft East Suffolk Line. It is twinned with Bouchain in France and Eitorf in Germany. Nearby villages include Cratfield, Wissett, Chediston, Walpole, Blyford, Linstead Parva, Wenhaston, Thorington, Spexhall, Bramfield, Huntingfield, Cookley and Holton. History A Roman settlement, Halesworth has a medieval church; St Mary's with Victorian additions and a variety of houses, from early timber-framed buildings to the remnants of Victorian prosperity. Former almshouses used to house the Halesworth & District Museum (open from May to September) but this has now been moved to Halesworth railway station. There is a Town Trail walk. The place-name 'Halesworth' is fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felixstowe
Felixstowe ( ) is a port town in Suffolk, England. The estimated population in 2017 was 24,521. The Port of Felixstowe is the largest container port in the United Kingdom. Felixstowe is approximately 116km (72 miles) northeast of London. History The town is named after Felix of Burgundy, a saint and the first bishop of the East Angles in the seventh century. The old Felixstowe hamlet was centred on a pub and church, having stood on the site since long before the Norman conquest of England. The early history of Felixstowe, including its Roman, Anglo-Saxon, Norman and medieval defences, is told under the name of Walton, because the name Felixstowe was given retrospectively, during the 13th century, to a place which had expanded to a form beyond the boundaries of Walton alone. In the Doomsday book, for instance, only Walton is shown, and not Felixstowe, which at the time held little more than a few houses scattered over the cliff tops. Walton was a settlement on the River Orwell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bungay, Suffolk
Bungay () is a market town, civil parish and electoral ward in the English county of Suffolk.OS Explorer Map OL40: The Broads: (1:25 000) : . It lies in the Waveney Valley, west of Beccles on the edge of The Broads, and at the neck of a meander of the River Waveney. History The origin of the name of Bungay is thought to derive from the Anglo-Saxon title ''Bunincga-haye'', signifying the land belonging to the tribe of Bonna, a Saxon chieftain. Due to its high position, protected by the River Waveney and marshes, the site was in a good defensive position and attracted settlers from early times. Roman artefacts have been found in the region. Bungay Castle, which is shown on Bungay's town sign, was built by the Normans but was later rebuilt by Roger Bigod, 5th Earl of Norfolk and his family, who also owned Framlingham Castle. The castle contains a unique surviving example of mining galleries, dating to the siege of the castle in 1174. They were intended to undermine and thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwold
Southwold is a seaside town and civil parish on the English North Sea coast in the East Suffolk district of Suffolk. It lies at the mouth of the River Blyth within the Suffolk Coast and Heaths Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The town is about south of Lowestoft, north-east of Ipswich and north-east of London, within the parliamentary constituency of Suffolk Coastal. The "All Usual Residents" 2011 Census figure gives a total of 1,098 persons for the town. The 2012 Housing Report by the Southwold and Reydon Society concluded that 49 per cent of the dwellings are used as second homes or let to holiday-makers. History Southwold was mentioned in ''Domesday Book'' (1086) as a fishing port, and after the "capricious River Blyth withdrew from Dunwich in 1328, bringing trade to Southwold in the 15th century", it received its town charter from Henry VII in 1489. The grant of the charter is marked by the annual Trinity Fair, when it is read out by the Town Clerk. Over following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

