|
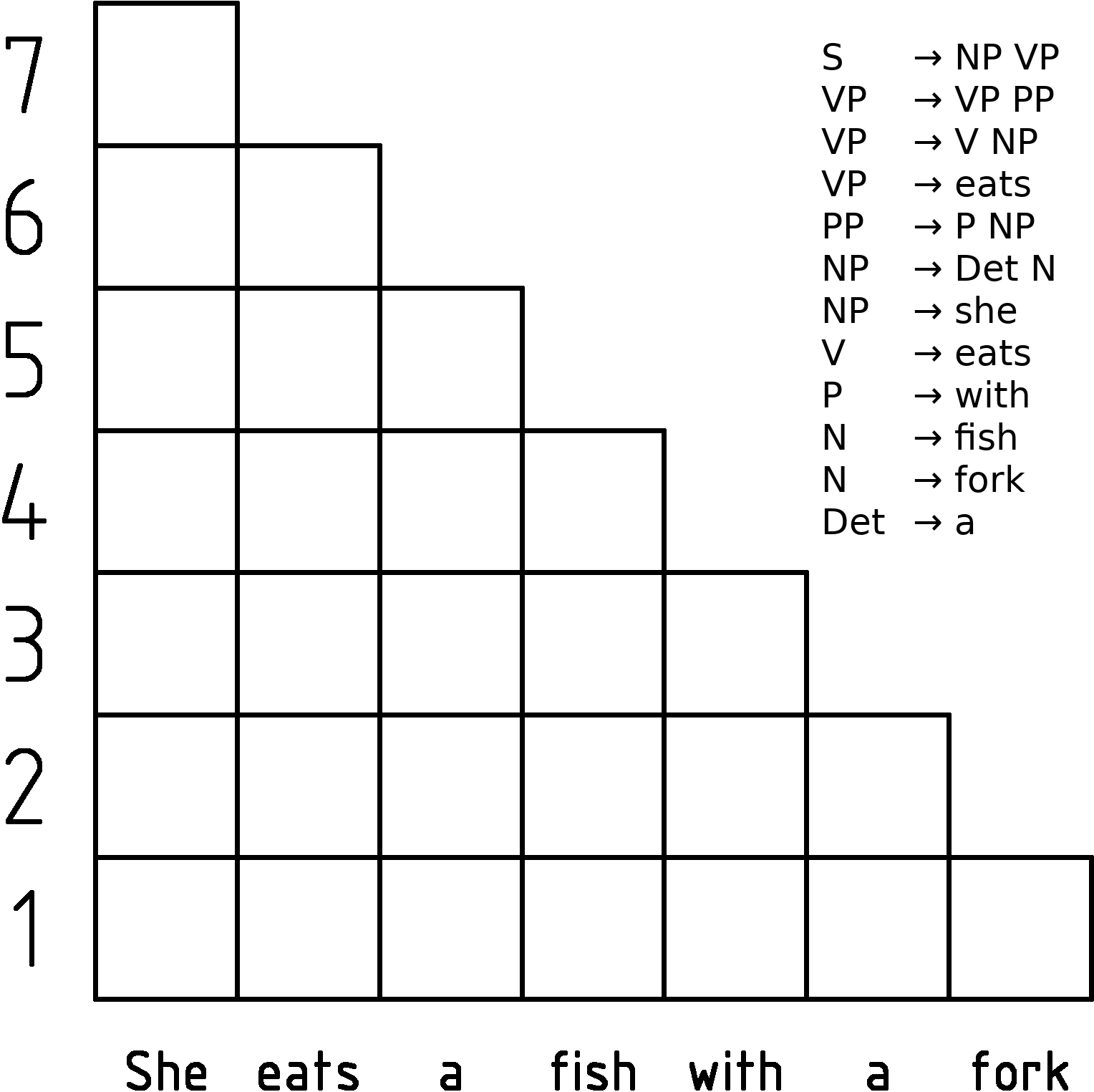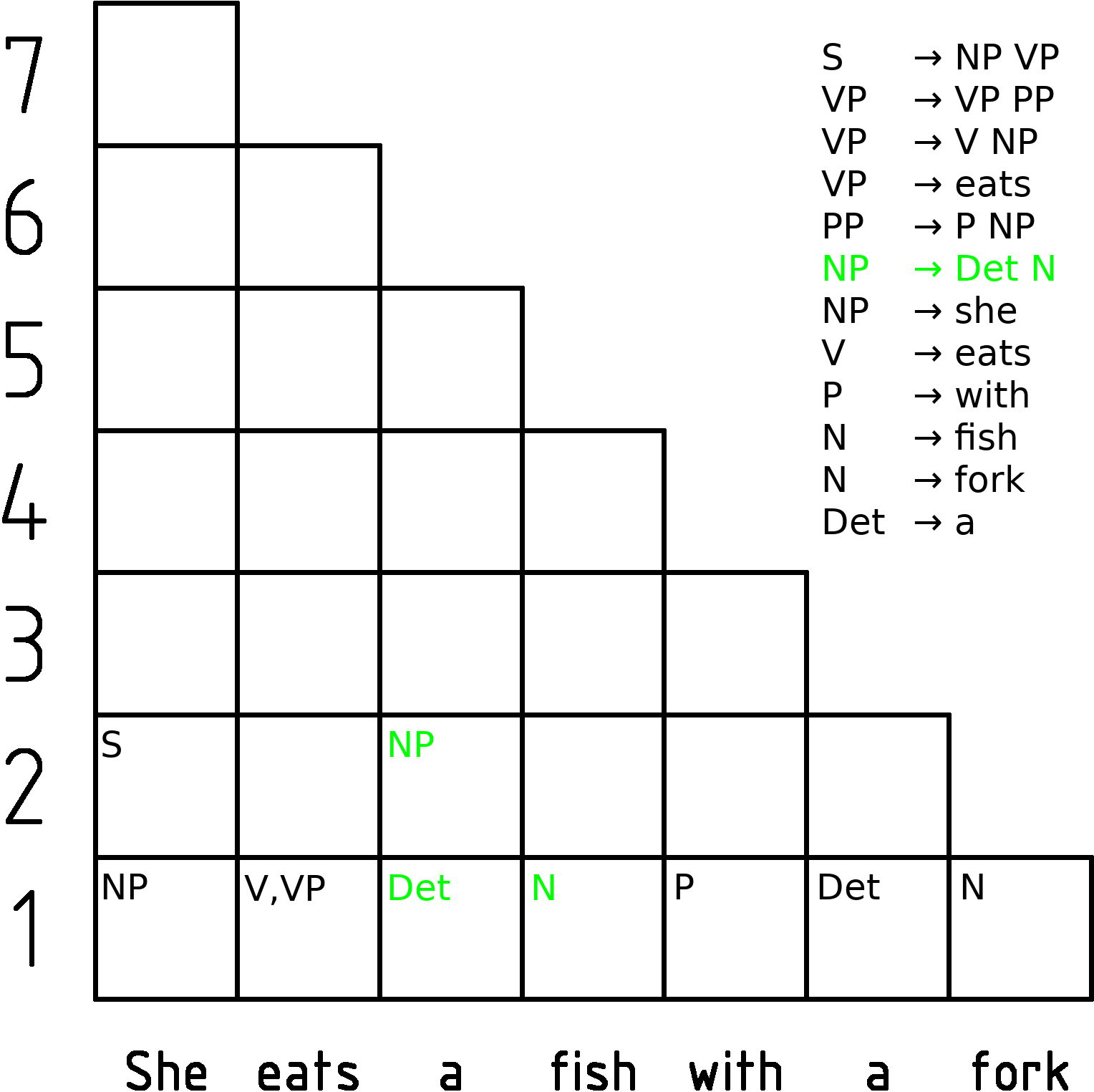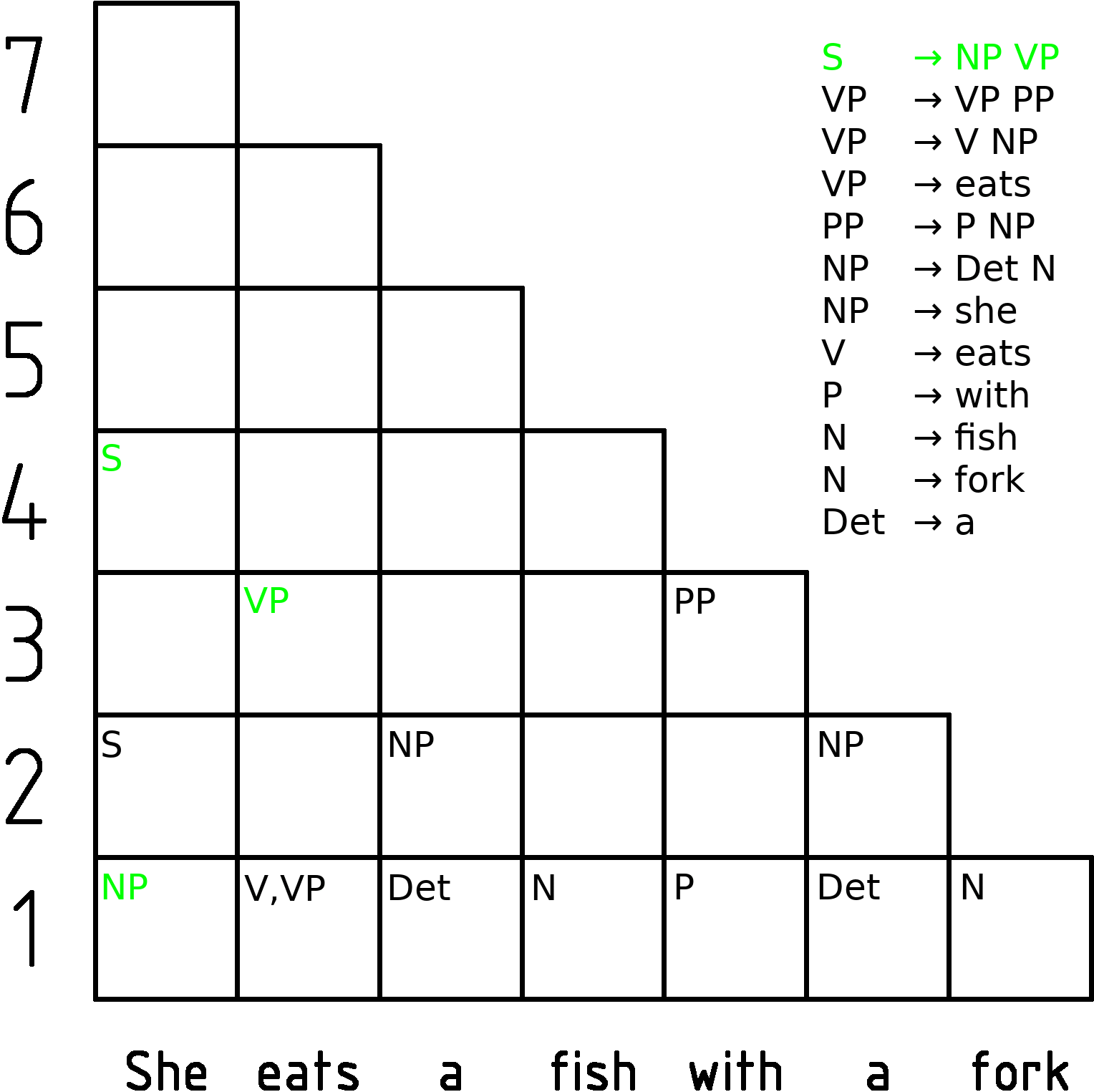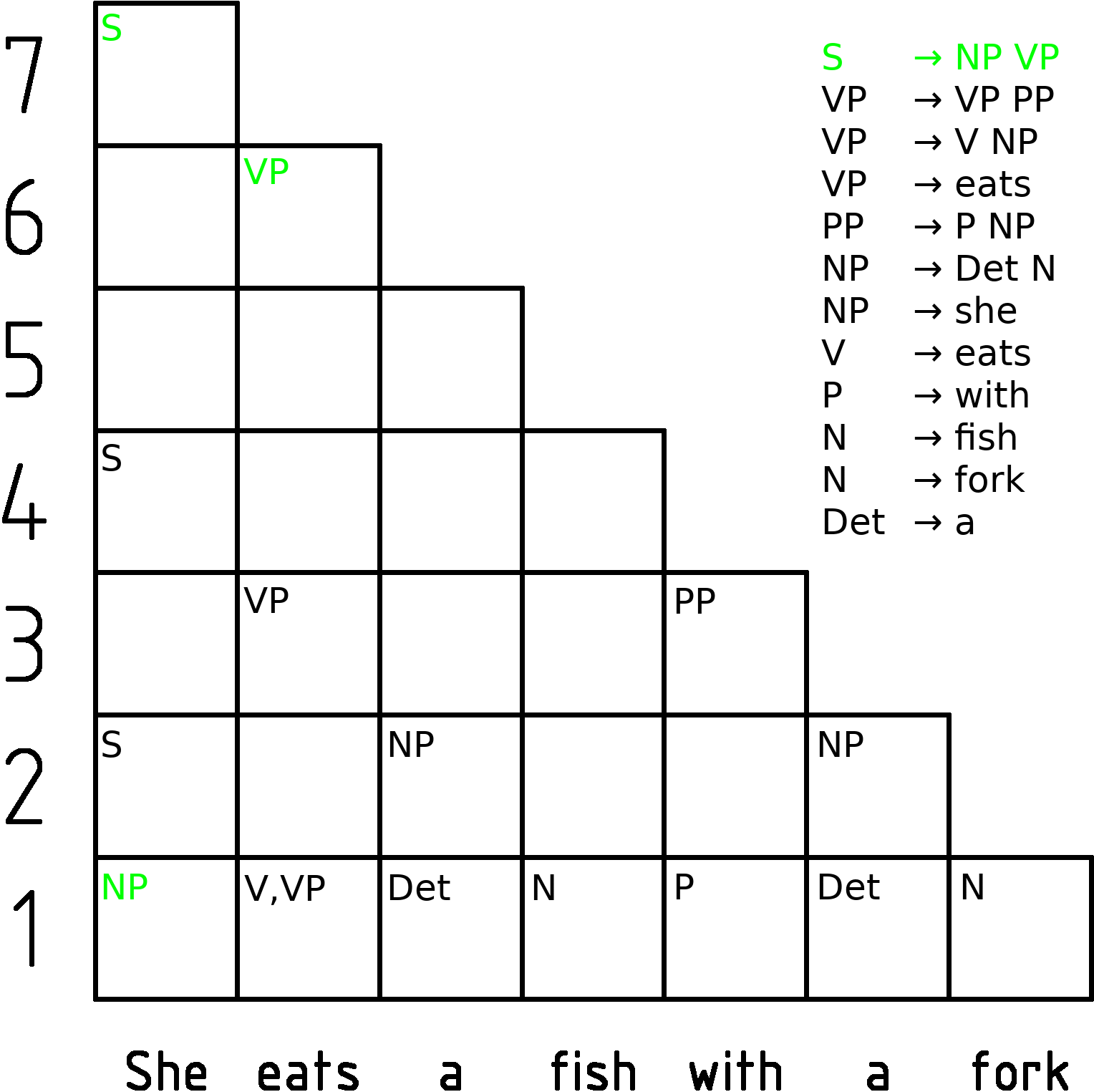
Earley Parser
In computer science, the Earley parser is an algorithm for parsing strings that belong to a given context-free language, though (depending on the variant) it may suffer problems with certain nullable grammars. The algorithm, named after its inventor Jay Earley, is a chart parser that uses dynamic programming; it is mainly used for parsing in computational linguistics. It was first introduced in his dissertation in 1968 (and later appeared in abbreviated, more legible form in a journal). Earley parsers are appealing because they can parse all context-free languages, unlike LR parsers and LL parsers, which are more typically used in compilers but which can only handle restricted classes of languages. The Earley parser executes in cubic time in the general case (n^3), where ''n'' is the length of the parsed string, quadratic time for unambiguous grammars (n^2), and linear time for all deterministic context-free grammars. It performs particularly well when the rules are written l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a String (computer science), string of Symbol (formal), symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning Part of speech, part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional Sentence (linguistics), sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject (grammar), subject and predicate (grammar), predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unambiguous Grammar
In computer science, an ambiguous grammar is a context-free grammar for which there exists a string that can have more than one leftmost derivation or parse tree. Every non-empty context-free language admits an ambiguous grammar by introducing e.g. a duplicate rule. A language that only admits ambiguous grammars is called an inherently ambiguous language. Deterministic context-free grammars are always unambiguous, and are an important subclass of unambiguous grammars; there are non-deterministic unambiguous grammars, however. For computer programming languages, the reference grammar is often ambiguous, due to issues such as the dangling else problem. If present, these ambiguities are generally resolved by adding precedence rules or other context-sensitive parsing rules, so the overall phrase grammar is unambiguous. Some parsing algorithms (such as Earley or GLR parsers) can generate sets of parse trees (or "parse forests") from strings that are syntactically ambiguous. Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Computer Journal
''The Computer Journal'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering computer science and information systems. Established in 1958, it is one of the oldest computer science research journals. It is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT. The authors of the best paper in each annual volume receive the Wilkes Award from BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT. Editors-in-chief The following people have been editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ...: * 1958–1969 Eric N. Mutch * 1969–1992 Peter Hammersley * 1993–2000 C. J. van Rijsbergen * 2000–2008 Fionn Murtagh * 2008–2012 Erol Gelenbe * 2012–2016 Fionn Murtagh * 2016–2020 Steve Furber * 2021–present Tom Crick References External links Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Algorithms
An algorithm is fundamentally a set of rules or defined procedures that is typically designed and used to solve a specific problem or a broad set of problems. Broadly, algorithms define process(es), sets of rules, or methodologies that are to be followed in calculations, data processing, data mining, pattern recognition, automated reasoning or other problem-solving operations. With the increasing automation of services, more and more decisions are being made by algorithms. Some general examples are; risk assessments, anticipatory policing, and pattern recognition technology. The following is a list of well-known algorithms. Automated planning Combinatorial algorithms General combinatorial algorithms * Brent's algorithm: finds a cycle in function value iterations using only two iterators * Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm: finds a cycle in function value iterations * Gale–Shapley algorithm: solves the stable matching problem * Pseudorandom number generators (uniformly dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CYK Algorithm
In computer science, the Cocke–Younger–Kasami algorithm (alternatively called CYK, or CKY) is a parsing algorithm for context-free grammars published by Itiroo Sakai in 1961. The algorithm is named after some of its rediscoverers: John Cocke, Daniel Younger, Tadao Kasami, and Jacob T. Schwartz. It employs bottom-up parsing and dynamic programming. The standard version of CYK operates only on context-free grammars given in Chomsky normal form (CNF). However any context-free grammar may be algorithmically transformed into a CNF grammar expressing the same language . The importance of the CYK algorithm stems from its high efficiency in certain situations. Using big ''O'' notation, the worst case running time of CYK is \mathcal\left( n^3 \cdot \left, G \ \right), where n is the length of the parsed string and \left, G \ is the size of the CNF grammar G . This makes it one of the most efficient parsing algorithms in terms of worst-case asymptotic complexity, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Syntactic Ambiguity
Syntactic ambiguity, also known as structural ambiguity, amphiboly, or amphibology, is characterized by the potential for a sentence to yield multiple interpretations due to its ambiguous syntax. This form of ambiguity is not derived from the varied meanings of individual words but rather from the relationships among words and clauses within a sentence, concealing interpretations beneath the word order. Consequently, a sentence presents as syntactically ambiguous when it permits reasonable derivation of several possible grammatical structures by an observer. In jurisprudence, the interpretation of syntactically ambiguous phrases in statutory texts or contracts may be done by courts. Occasionally, claims based on highly improbable interpretations of such ambiguities are dismissed as being frivolous litigation and without merit. The term ''parse forest'' refers to the collection of all possible syntactic structures, known as '' parse trees'', that can represent the ambiguous sente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Masaru Tomita
is a Japanese scientist in the fields of systems biology and computer science, best known as the founder of the E-Cell simulation system and/or the inventor of GLR parser algorithm. He served a professor of Keio University, Director of the Institute for Advanced Biosciences, and the founder and board member of various spinout companies, including Human Metabolome Technologies, Inc. and Spiber Inc. He is also the co-founder and on the board of directors of The Metabolomics Society. His father was the composer and synthesiser player Isao Tomita. From Oct. 2005 to Sep. 2007, he served as Dean of Faculty of Environment and Information Studies, Keio University. He received an M.S. (1983) and a Ph.D. (1985) in computer science from Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) under Jaime Carbonell, and three other doctoral degrees in electronic engineering (Kyoto University, 1994), molecular biology (Keio University, 1998), and media and governance (Keio University, 2019). At CMU, starting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Daniel Jurafsky
Daniel Jurafsky is a professor of linguistics and computer science at Stanford University, and also an author. With Daniel Gildea, he is known for developing the first automatic system for semantic role labeling (SRL). He is the author of ''The Language of Food: A Linguist Reads the Menu'' (2014) and a textbook on speech and language processing (2000). For the former, Jurafsky was named a finalist for the James Beard Award. Jurafsky was given a MacArthur Fellowship in 2002. Education Jurafsky received his B.A in linguistics (1983) and Ph.D. in computer science (1992), both at University of California, Berkeley; and then a postdoc at International Computer Science Institute, Berkeley (1992–1995). Academic life He is the author of ''The Language of Food: A Linguist Reads the Menu'' (W. W. Norton & Company, 2014). With James H. Martin, he wrote the textbook ''Speech and Language Processing: An Introduction to Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics, and Speech Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tuple
In mathematics, a tuple is a finite sequence or ''ordered list'' of numbers or, more generally, mathematical objects, which are called the ''elements'' of the tuple. An -tuple is a tuple of elements, where is a non-negative integer. There is only one 0-tuple, called the ''empty tuple''. A 1-tuple and a 2-tuple are commonly called a singleton and an ordered pair, respectively. The term ''"infinite tuple"'' is occasionally used for ''"infinite sequences"''. Tuples are usually written by listing the elements within parentheses "" and separated by commas; for example, denotes a 5-tuple. Other types of brackets are sometimes used, although they may have a different meaning. An -tuple can be formally defined as the image of a function that has the set of the first natural numbers as its domain. Tuples may be also defined from ordered pairs by a recurrence starting from an ordered pair; indeed, an -tuple can be identified with the ordered pair of its first elements and its t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lexical Analysis
Lexical tokenization is conversion of a text into (semantically or syntactically) meaningful ''lexical tokens'' belonging to categories defined by a "lexer" program. In case of a natural language, those categories include nouns, verbs, adjectives, punctuations etc. In case of a programming language, the categories include identifiers, operators, grouping symbols, data types and language keywords. Lexical tokenization is related to the type of tokenization used in large language models (LLMs) but with two differences. First, lexical tokenization is usually based on a lexical grammar, whereas LLM tokenizers are usually probability-based. Second, LLM tokenizers perform a second step that converts the tokens into numerical values. Rule-based programs A rule-based program, performing lexical tokenization, is called ''tokenizer'', or ''scanner'', although ''scanner'' is also a term for the first stage of a lexer. A lexer forms the first phase of a compiler frontend in processing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Formal Grammar
A formal grammar is a set of Terminal and nonterminal symbols, symbols and the Production (computer science), production rules for rewriting some of them into every possible string of a formal language over an Alphabet (formal languages), alphabet. A grammar does not describe the semantics, meaning of the strings — only their form. In applied mathematics, formal language theory is the discipline that studies formal grammars and languages. Its applications are found in theoretical computer science, theoretical linguistics, Formal semantics (logic), formal semantics, mathematical logic, and other areas. A formal grammar is a Set_(mathematics), set of rules for rewriting strings, along with a "start symbol" from which rewriting starts. Therefore, a grammar is usually thought of as a language generator. However, it can also sometimes be used as the basis for a "recognizer"—a function in computing that determines whether a given string belongs to the language or is grammatical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Empty String
In formal language theory, the empty string, or empty word, is the unique String (computer science), string of length zero. Formal theory Formally, a string is a finite, ordered sequence of character (symbol), characters such as letters, digits or spaces. The empty string is the special case where the sequence has length zero, so there are no symbols in the string. There is only one empty string, because two strings are only different if they have different lengths or a different sequence of symbols. In formal treatments, the empty string is denoted with ε or sometimes Λ or λ. The empty string should not be confused with the empty language ∅, which is a formal language (i.e. a set of strings) that contains no strings, not even the empty string. The empty string has several properties: * , ε, = 0. Its string (computer science)#Formal theory, string length is zero. * ε ⋅ s = s ⋅ ε = s. The empty string is the identity element of the concatenation operation. The set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |