|
EROS B
The Earth Remote Observation System-B (EROS-B) is the second satellite launched in a series of the EROS family of Israeli commercial Earth observation satellites, designed and manufactured by Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI). It is owned and operated by ImageSat International N.V. (ISI), in the Netherlands Antilles, Cayman Islands, with offices in Limassol, Cyprus, and in Tel Aviv, Israel. ImageSat International announced that it had begun construction of "EROS B", a day before the launch of "EROS A". According to the plan, the launch of the "EROS B" was to take place in 2001, after which another 6 satellites in the series were planned. In July 2000, the company announced the completion of a capital raising of more than $90 million. A year later, it signed a $70 million credit agreement with Bank Leumi to finance the further development of the satellite series, and announced that the launch of the second satellite had been postponed to 2003. On July 28, 2001, IAI official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Observation Satellite
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others. The most common type are Earth imaging satellites, that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs; some EO satellites may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation. The first occurrence of satellite remote sensing can be dated to the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. Sputnik 1 sent back radio signals, which scientists used to study the ionosphere. The United States Army Ballistic Missile Agency launched the first American satellite, Explorer 1, for NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on January 31, 1958. The information sent back from its radiation detector led to the discovery of the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territory—the largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the south of Cuba and northeast of Honduras, between Jamaica and Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. The capital city is George Town on Grand Cayman, which is the most populous of the three islands. The Cayman Islands is considered to be part of the geographic Western Caribbean Zone as well as the Greater Antilles. The territory is a major world offshore financial centre for international businesses and wealthy individuals, largely as a result of the state not charging taxes on any income earned or stored. With a GDP per capita of $91,392, the Cayman Islands has the highest standard of living in the Caribbean. Immigrants from over 130 countries and territories reside in the Cayman Islands. History No archaeological evidence for an indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscopes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
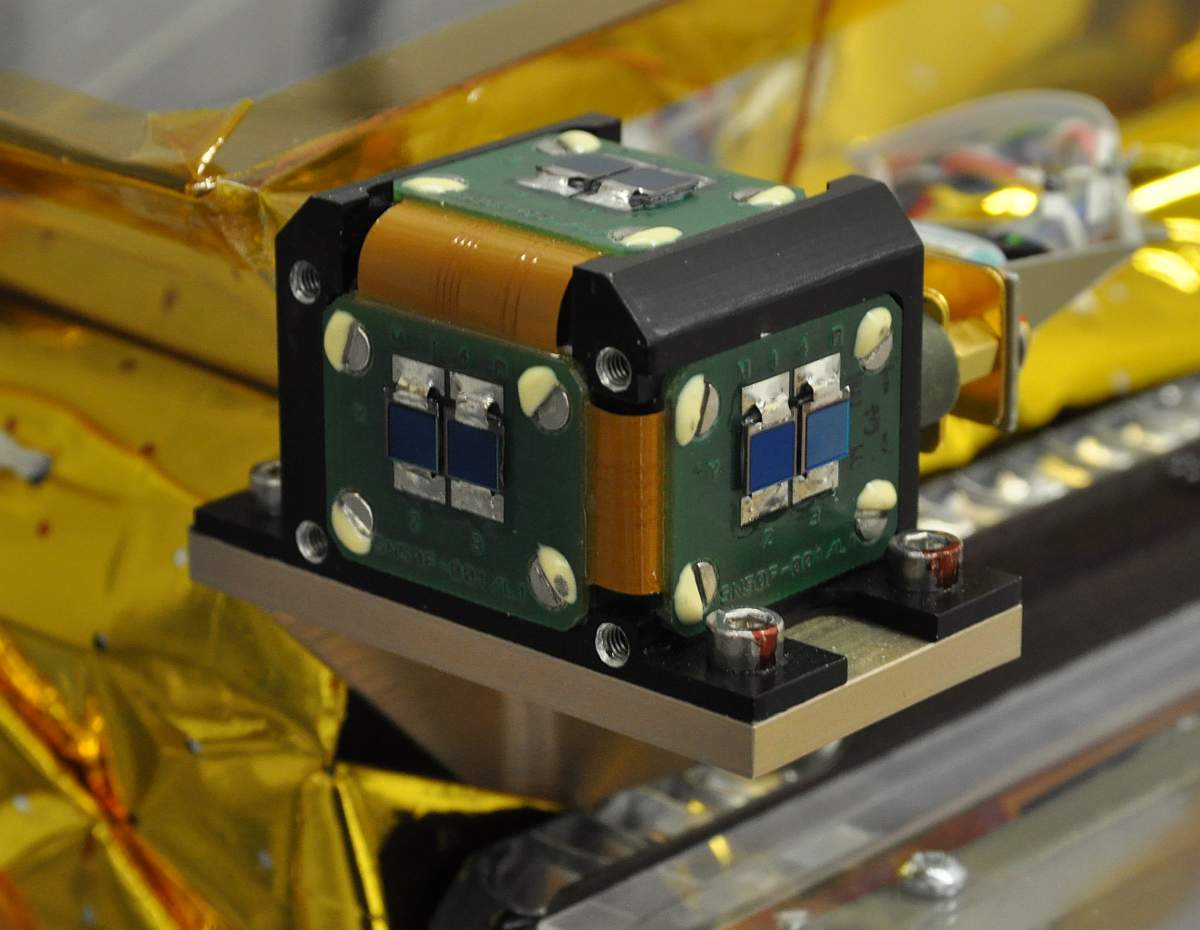
Sun Sensor
A sun sensor is a navigational instrument used by spacecraft to detect the position of the sun. Sun sensors are used for attitude control, solar array pointing, gyro updating, and fail-safe recovery. In addition to spacecraft, sun sensors find use in ground-based weather stations and sun-tracking systems, and aerial vehicles including balloons and UAVs. Mechanism There are various types of sun sensors, which differ in their technology and performance characteristics. Sun presence sensors provide a binary output, indicating when the sun is within the sensor's field of view. Analog and digital sun sensors, in contrast, indicate the angle of the sun by continuous and discrete signal outputs, respectively. In typical sun sensors, a thin slit at the top of a rectangular chamber allows a line of light to fall on an array of photodetector cells at the bottom of the chamber. A voltage is induced in these cells, which is registered electronically. By orienting two sensors perpendicular to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Tracker
A star tracker is an optical device that measures the positions of stars using photocells or a camera. As the positions of many stars have been measured by astronomers to a high degree of accuracy, a star tracker on a satellite or spacecraft may be used to determine the orientation (or attitude) of the spacecraft with respect to the stars. In order to do this, the star tracker must obtain an image of the stars, measure their apparent position in the reference frame of the spacecraft, and identify the stars so their position can be compared with their known absolute position from a star catalog. A star tracker may include a processor to identify stars by comparing the pattern of observed stars with the known pattern of stars in the sky. History In the 1950s and early 1960s, star trackers were an important part of early long-range ballistic missiles and cruise missiles, in the era when inertial navigation systems (INS) were not sufficiently accurate for intercontinental ranges. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
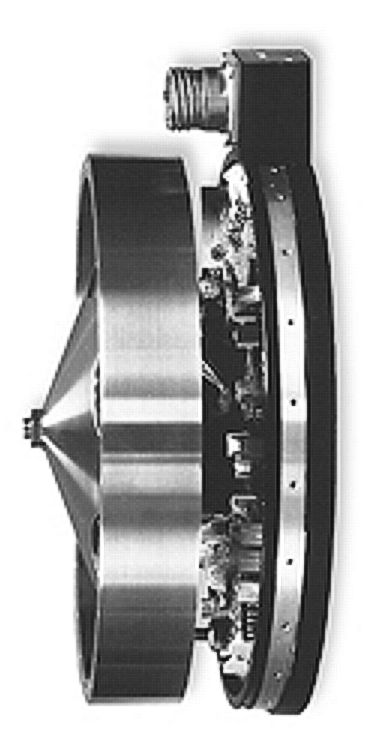
Reaction Wheels
A reaction wheel (RW) is used primarily by spacecraft for three-axis attitude control, and does not require rockets or external applicators of torque. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be rotated by very small amounts, such as keeping a telescope pointed at a star. A reaction wheel is sometimes operated as (and referred to as) a momentum wheel, by operating it at a constant (or near-constant) rotation speed, to provide a satellite with a large amount of stored angular momentum. Doing so alters the spacecraft's rotational dynamics so that disturbance torques perpendicular to one axis of the satellite (the axis parallel to the wheel's spin axis) do not result directly in spacecraft angular motion about the same axis as the disturbance torque; instead, they result in (generally smaller) angular motion (precession) of that spacecraft axis about a perpendicular axis. This has the effect of tending to stabilize that spacecraft ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-axis Stabilization
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle/satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires sensors to measure vehicle orientation, actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on (1) sensor measurements of the current attitude and (2) specification of a desired attitude. The integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called guidance, navigation and control (GNC). Overview A spacecraft's attitude must typically be stabilized and controlled for a variety of reasons. It is often needed so that the spacecraft high-gain antenna may be accurately pointed to Earth for communications, so that onboard experiments may accomplish precise pointing for accurate collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globes (newspaper)
''Globes'' ( he, גלובס) is a Hebrew-language daily evening financial newspaper in Israel. Globes was founded in the early 1980s and published in Tel Aviv, Israel. It deals with economic issues and news from the Israeli and international business worlds. The paper is printed on salmon-colored paper, inspired by the British ''Financial Times''. ''Globes'' was one of the first Israeli dailies to publish its contents on the World Wide Web, dating back to April 1995. Its web version publishes in Hebrew and English. According to TGI 2022 media survey, ''Globes'' market share is 4.1% among Israeli financial newspapers. Its main competitors as Israeli financial newspapers in printed media are ''TheMarker'', of the ''Haaretz'' group, and ''Calcalist'', published by the ''Yedioth Ahronoth'' Group. History The daily paper founded by Haim Bar-On, the publisher of the newspaper, on the basis of a small, Haifa-based financial newspaper, in partnership with businessman Eliezer Fishman. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Leumi
Bank Leumi ( he, בנק לאומי, lit. ''National Bank''; ar, بنك لئومي) is an Israeli bank. It was founded on February 27, 1902, in Jaffa as the ''Anglo Palestine Company'' as subsidiary of the Jewish Colonial Trust (Jüdische Kolonialbank) Limited formed before in London by members of the Zionist movement to promote the industry, construction, agriculture, and infrastructure of the land hoped to ultimately become Israel. Today, Bank Leumi is Israel's largest bank (by total assets as of 2015), with overseas offices in Luxembourg, US, Switzerland, the UK, Mexico, Uruguay, Romania, Jersey, and China. Though nationalized in 1981, now Bank Leumi is mainly in private hands, with the government as the largest single shareholder, with 14.8% of the stock (as of June 2006). The other major shareholders are Shlomo Eliyahu and Branea Invest, which each hold 10% of the stock, constituting the control core of the bank. Sixty percent of the bank's stocks are held by the public and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haaretz
''Haaretz'' ( , originally ''Ḥadshot Haaretz'' – , ) is an Israeli newspaper. It was founded in 1918, making it the longest running newspaper currently in print in Israel, and is now published in both Hebrew and English in the Berliner format. The English edition is published and sold together with the ''International New York Times''. Both Hebrew and English editions can be read on the internet. In North America, it is published as a weekly newspaper, combining articles from the Friday edition with a roundup from the rest of the week. It is considered Israel's newspaper of record. It is known for its left-wing and liberal stances on domestic and foreign issues. As of 2022, ''Haaretz'' has the third-largest circulation in Israel. It is widely read by international observers, especially in its English edition, and discussed in the international press. According to the Center for Research Libraries, among Israel's daily newspapers, "''Haaretz'' is considered the most infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_DAILY_OF_THE_EARLY_20S.jpg)