|
EIA-608
EIA-608, also known as "line 21 captions" and "CEA-608", was once the standard for closed captioning for NTSC TV broadcasts in the United States, Canada and Mexico. It was developed by the Electronic Industries Alliance and required by law to be implemented in most television receivers made in the United States. It specifies an "Extended Data Service", which is a means for including a VCR control service with an electronic program guide for NTSC transmissions that operates on the even line 21 field, similar to the TeleText based VPS that operates on line 16 which is used in PAL countries. EIA-608 captions are transmitted on either the odd or even fields of line 21 with an odd parity bit in the non-visible active video data area in NTSC broadcasts, and are also sometimes present in the picture user data in ATSC transmissions. It uses a fixed bandwidth of 480 bit/s per line 21 field for a maximum of 32 characters per line per caption (maximum four captions) for a 30 frame broadc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Captioning
Closed captioning (CC) and subtitling are both processes of displaying text on a television, video screen, or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information. Both are typically used as a transcription of the audio portion of a program as it occurs (either verbatim or in edited form), sometimes including descriptions of non-speech elements. Other uses have included providing a textual alternative language translation of a presentation's primary audio language that is usually burned-in (or "open") to the video and unselectable. HTML5 defines subtitles as a "transcription or translation of the dialogue when sound is available but not understood" by the viewer (for example, dialogue in a foreign language) and captions as a "transcription or translation of the dialogue, sound effects, relevant musical cues, and other relevant audio information when sound is unavailable or not clearly audible" (for example, when audio is muted or the viewer is deaf or hard o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIA-708
CTA-708 (formerly EIA-708 and CEA-708) is the standard for closed captioning for ATSC digital television (DTV) streams in the United States and Canada. It was developed by the Consumer Electronics sector of the Electronic Industries Alliance, which is now a standalone organization Consumer Technology Association. Unlike RLE DVB and DVD subtitles, CTA-708 captions are low bandwidth and textual like traditional EIA-608 captions and EBU Teletext subtitles. However, unlike EIA-608 byte pairs, CTA-708 captions are not able to be modulated on an ATSC receiver's NTSC VBI line 21 composite output and must be pre-rendered by the receiver with the digital video frames, they also include more of the Latin-1 character set, and include stubs to support full UTF-32 captions, and downloadable fonts. CTA-708 caption streams can also optionally encapsulate EIA-608 byte pairs internally, a fairly common usage. CTA-708 captions are injected into MPEG-2 video streams in the picture user data. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teletext
A British Ceefax football index page from October 2009, showing the three-digit page numbers for a variety of football news stories Teletext, or broadcast teletext, is a standard for displaying text and rudimentary graphics on suitably equipped television sets. Teletext sends data in the broadcast signal, hidden in the invisible vertical blanking interval area at the top and bottom of the screen. The teletext decoder in the television buffers this information as a series of "pages", each given a number. The user can display chosen pages using their remote control. In broad terms, it can be considered as Videotex, a system for the delivery of information to a user in a computer-like format, typically displayed on a television or a dumb terminal, but that designation is usually reserved for systems that provide bi-directional communication, such as Prestel or Minitel. Teletext was created in the United Kingdom in the early 1970s by John Adams, Philips' lead designer for video di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTSC
The first American standard for analog television broadcast was developed by National Television System Committee (NTSC)National Television System Committee (1951–1953), Report and Reports of Panel No. 11, 11-A, 12–19, with Some supplementary references cited in the Reports, and the Petition for adoption of transmission standards for color television before the Federal Communications Commission, n.p., 1953], 17 v. illus., diagrs., tables. 28 cm. LC Control No.:5402138Library of Congress Online Catalog/ref> in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation CCIR System M, System M. In 1953, a second NTSC standard was adopted, which allowed for color television broadcast compatible with the existing stock of black-and-white receivers. It is one of three major color formats for analog television, the others being PAL and SECAM. NTSC color is usually associated with the System M. The only other broadcast television system to use NTSC color was the System J. Since the introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Sign
The symbol is known variously in English-speaking regions as the number sign, hash, or pound sign. The symbol has historically been used for a wide range of purposes including the designation of an ordinal number and as a Typographic ligature, ligatured abbreviation for Pound (mass), pounds avoirdupois – having been derived from the now-rare . Since 2007, widespread usage of the symbol to introduce metadata tags on social media platforms has led to such tags being known as "hashtags", and from that, the symbol itself is sometimes called a hashtag. The symbol is distinguished from similar symbols by its combination of level horizontal strokes and right-tilting vertical strokes. History It is believed that the symbol traces its origins to the symbol , an abbreviation of the Roman term ''Roman pound, libra pondo'', which translates as "pound weight". This abbreviation was printed with a dedicated Ligature (writing), ligature type element, with a horizontal line across, so t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMPTE 259M
SMPTE 259M is a standard published by SMPTE which "describes a 10-bit serial digital interface operating at 143/270/360 Mb/s." The goal of SMPTE 259M is to define a serial digital interface (based on a coaxial cable), called SDI or SD-SDI. There are 4 bit rate In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time. The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction w ...s defined, which are normally used to transfer the following standard video formats: References Film and video technology SMPTE standards {{Measurement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Exchange Format
Material Exchange Format (MXF) is a container format for professional digital video and audio media defined by a set of SMPTE standards. A typical example of its use is for delivering advertisements to TV stations and tapeless archiving of broadcast TV programs. It is also used as part of the Digital Cinema Package for delivering movies to commercial theaters. Summary MXF, when used in the form of "Operational Pattern OP1A" or "OPAtom", can be used as a ''container'', ''wrapper'' or ''reference file'' format which supports a number of different streams of coded "essence", encoded in any of a variety of video and audio compression formats, together with a metadata wrapper which describes the material contained within the MXF file. Other "Operational Patterns" can contain or reference multiple materials, just like a simple timeline of a video editing program. MXF has full timecode and metadata support and is intended as a platform-agnostic stable standard for future professiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space (punctuation)
In writing, a space () is a blank area that separates words, sentences, syllables (in syllabification) and other written or printed glyphs (characters). Conventions for spacing vary among languages, and in some languages the spacing rules are complex. Inter-word spaces ease the reader's task of identifying words, and avoid outright ambiguities such as "now here" vs. "nowhere". They also provide convenient guides for where a human or program may start new lines. Typesetting can use spaces of varying widths, just as it can use graphic characters of varying widths. Unlike graphic characters, typeset spaces are commonly stretched in order to align text. The typewriter, on the other hand, typically has only one width for all characters, including spaces. Following widespread acceptance of the typewriter, some typewriter conventions influenced typography and the design of printed works. Computer representation of text facilitates getting around mechanical and physical limitations su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclamation Mark
The exclamation mark, , or exclamation point (American English), is a punctuation mark usually used after an interjection or exclamation to indicate strong feelings or to show emphasis. The exclamation mark often marks the end of a sentence, for example: "Watch out!". Similarly, a bare exclamation mark (with nothing before or after) is often used in warning signs. The exclamation mark is often used in writing to make a character seem as though they are shouting and/or excited/surprised. Other uses include: * In mathematics, it denotes the factorial operation. * Several computer languages use at the beginning of an expression to denote logical negation. For example, means "the logical negation of A", also called "not A". This usage has spread to ordinary language (e.g., "!clue" means no-clue or clueless). * Some languages use to denote a click consonant. History Graphically, the exclamation mark is represented by variations on the theme of a full stop point with a vertical l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
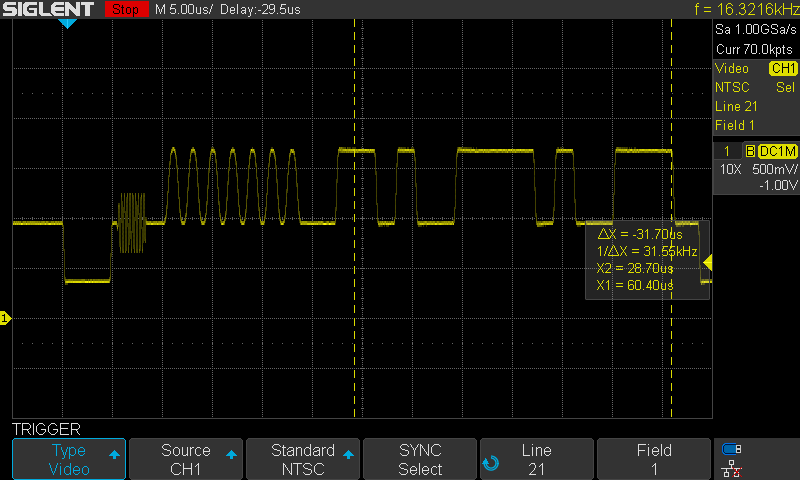
Line21ClosedCaption
Line most often refers to: * Line (geometry), object with zero thickness and curvature that stretches to infinity * Telephone line, a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system Line, lines, The Line, or LINE may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Lines'' (film), a 2016 Greek film * ''The Line'' (2017 film) * ''The Line'' (2009 film) * ''The Line'', a 2009 independent film by Nancy Schwartzman Podcasts * ''The Line'' (podcast), 2021 by Dan Taberski Literature * Line (comics), a term to describe a subset of comic book series by a publisher * ''Line'' (play), by Israel Horovitz, 1967 * Line (poetry), the fundamental unit of poetic composition * "Lines" (poem), an 1837 poem by Emily Brontë * ''The Line'' (memoir), by Arch and Martin Flanagan * ''The Line'' (play), by Timberlake Wertenbaker, 2009 Music Albums * ''Lines'' (The Walker Brothers album), 1976 * ''Lines'' (Pandelis Karayorgis album), 1995 * ''Lines'' (Unthanks album), 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampersand
The ampersand, also known as the and sign, is the logogram , representing the conjunction "and". It originated as a ligature of the letters ''et''—Latin for "and". Etymology Traditionally in English, when spelling aloud, any letter that could also be used as a word in itself ("A", "I", and, " O") was prefixed with the Latin expression ('by itself'), as in "per se A". It was also common practice to add the sign at the end of the alphabet as if it were the 27th letter, pronounced as the Latin ''et'' or later in English as ''and''. As a result, the recitation of the alphabet would end in "X, Y, Z, ''and per se and''". This last phrase was routinely slurred to "ampersand" and the term had entered common English usage by 1837. It has been falsely claimed that André-Marie Ampère used the symbol in his widely read publications and that people began calling the new shape "Ampère's and". History The ampersand can be traced back to the 1st century A.D. and the old Roman c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comma (punctuation)
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. It has the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark () in many typefaces, but it differs from them in being placed on the baseline of the text. Some typefaces render it as a small line, slightly curved or straight, but inclined from the vertical. Other fonts give it the appearance of a miniature filled-in figure on the baseline. The comma is used in many contexts and languages, mainly to separate parts of a sentence such as clauses, and items in lists mainly when there are three or more items listed. The word ''comma'' comes from the Greek (), which originally meant a cut-off piece, specifically in grammar, a short clause. A comma-shaped mark is used as a diacritic in several writing systems and is considered distinct from the cedilla. In Byzantine and modern copies of Ancient Greek, the " rough" and "smooth breathings" () appear above the letter. In Latvian, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)