|
EASA CS-VLA
EASA CS-VLA is the European Aviation Safety Agency Certification Specification for Very Light Aircraft. The Very Light Aircraft (VLA) aircraft certification category introduced in 2003 by the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) is intended to make it easier and less costly to get full European certification, operation and maintenance of a general aviation aircraft.EASA"Easy Access Rules for Very Light Aeroplanes (CS-VLA) (Amendment 1)" January 24, 2021. The somewhat relaxed certification procedure is available for aircraft satisfying the following criteria: *Maximum take-off weight (MTOW) of not more than 750 kg *One or two seats maximum *Maximum Stall speed in the landing configuration ( VS0) of no more than 83 km/h (45 knots) *Approved only for day-VFR visual flight rules conditions *Certified in the Normal Category only, all aerobatics Aerobatics is the practice of flying maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in conventional passenger-carryi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Aviation Safety Agency
The European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) with responsibility for civil aviation safety. It carries out certification, regulation and standardisation and also performs investigation and monitoring. It collects and analyses safety data, drafts and advises on safety legislation and co-ordinates with similar organisations in other parts of the world. The idea of a European-level aviation safety authority goes back to 1996, but the agency was legally established only in 2002; it began its work in 2003. History Based in Cologne, Germany, the agency was created on 15 July 2002 as the "European Aviation Safety Agency", and reached full functionality in 2008, taking over functions of the Joint Aviation Authorities. It was renamed the "European Union Aviation Safety Agency" in 2018. European Free Trade Association countries participate in the agency. The United Kingdom was a member until the end of the Brexit transition period on 31 Decem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services for other purposes. However, for statistical purposes ICAO uses a definition of general aviation which includes aerial work. General aviation thus represents the "private transport" and recreational components of aviation. Definition The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines civil aviation aircraft operations in three categories: General Aviation (GA), Aerial Work (AW) and Commercial Air Transport (CAT). Aerial work operations are separated from general aviation by ICAO by this definition. Aerial work is when an aircraft is used for specialized services such as agriculture, construction, photography, surveying, observation and patrol, search and rescue, and aerial advertisement. However, for statistical purposes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Take-off Weight
The maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) or maximum gross takeoff weight (MGTOW) or maximum takeoff mass (MTOM) of an aircraft is the maximum weight at which the pilot is allowed to attempt to takeoff, take off, due to structural or other limits. The analogous term for rockets is gross lift-off mass, or GLOW. MTOW is usually specified in units of kilograms or pounds. MTOW is the heaviest weight at which the aircraft has been shown to meet all the airworthiness requirements applicable to it. MTOW of an aircraft is fixed and does not vary with altitude, air temperature, or the length of the runway to be used for takeoff or landing. Maximum permissible takeoff weight or "regulated takeoff weight", varies according to flap setting, altitude, air temperature, length of runway and other factors. It is different from one takeoff to the next, but can never be higher than the MTOW. Certification standards Certification standards applicable to the airworthiness of an aircraft contain many requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stall Speed
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack increases.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 486. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. This occurs when the critical angle of attack of the foil is exceeded. The critical angle of attack is typically about 15°, but it may vary significantly depending on the fluid, foil, and Reynolds number. Stalls in fixed-wing flight are often experienced as a sudden reduction in lift as the pilot increases the wing's angle of attack and exceeds its critical angle of attack (which may be due to slowing down below stall speed in level flight). A stall does not mean that the engine(s) have stopped working, or that the aircraft has stopped moving—the effect is the same even in an unpowered glider aircraft. Vectored thrust in aircraft is used to maintain altitude or controlled flight with wings stalled by replacing lost wing lift with engine or propeller thru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
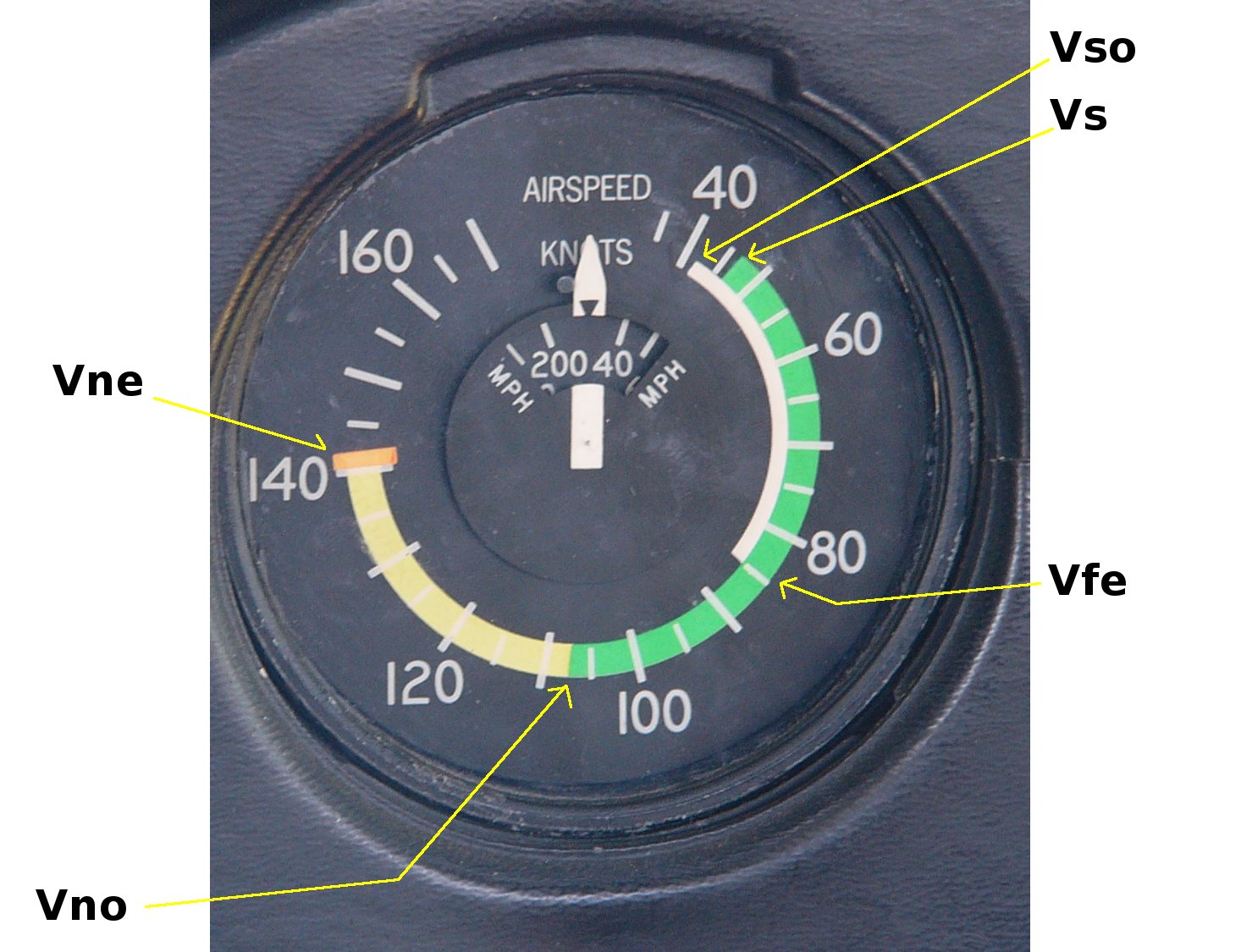
VS Speed
In aviation, V-speeds are standard terms used to define airspeeds important or useful to the operation of all aircraft. These speeds are derived from data obtained by aircraft designers and manufacturers during flight testing for aircraft type-certification. Using them is considered a best practice to maximize aviation safety, aircraft performance, or both. The actual speeds represented by these designators are specific to a particular model of aircraft. They are expressed by the aircraft's indicated airspeed (and not by, for example, the ground speed), so that pilots may use them directly, without having to apply correction factors, as aircraft instruments also show indicated airspeed. In general aviation aircraft, the most commonly used and most safety-critical airspeeds are displayed as color-coded arcs and lines located on the face of an aircraft's airspeed indicator. The lower ends of the white arc and the green arc are the stalling speed with wing flaps in landing conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile definition in 1970, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Flight Rules
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e. in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft. If the weather is less than VMC, pilots are required to use instrument flight rules, and operation of the aircraft will be primarily through referencing the instruments rather than visual reference. In a control zone, a VFR flight may obtain a clearance from air traffic control to operate as Special VFR. Requirements VFR require a pilot to be able to see outside the cockpit, to control the aircraft's altitude, navigate, and avoid obstacles and other aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobatics
Aerobatics is the practice of flying maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in conventional passenger-carrying flights. The term is a portmanteau of "aerial" and "acrobatics". Aerobatics are performed in aeroplanes and gliders for training, recreation, entertainment, and sport. Additionally, some helicopters, such as the MBB Bo 105, are capable of limited aerobatic manoeuvres. An example of a fully aerobatic helicopter, capable of performing loops and rolls, is the Westland Lynx. Most aerobatic manoeuvres involve rotation of the aircraft about its longitudinal (roll) axis or lateral (pitch) axis. Other maneuvers, such as a spin, displace the aircraft about its vertical (yaw) axis. Manoeuvres are often combined to form a complete aerobatic sequence for entertainment or competition. Aerobatic flying requires a broader set of piloting skills and exposes the aircraft to greater structural stress than for normal flight. In some countries, the pilot must wear a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin (aerodynamics)
In flight dynamics a spin is a special category of stall resulting in autorotation (uncommanded roll) about the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a shallow, rotating, downward path approximately centred on a vertical axis. Spins can be entered intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude if the aircraft has sufficient yaw while at the stall point. In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different. Either situation causes the aircraft to autorotate toward the stalled wing due to its higher drag and loss of lift. Spins are characterized by high angle of attack, an airspeed below the stall on at least one wing and a shallow descent. Recovery and avoiding a crash may require a specific and counter-intuitive set of actions. A spin differs from a spiral dive, in which neither wing is stalled an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EASA CS-23
EASA CS-23 is the European Aviation Safety Agency Certification Specification for Normal, Utility, Aerobatic, and Commuter Category Aeroplanes. This certification procedure is available for aircraft satisfying the following criteria: * Single-engine aeroplanes in the normal, utility and aerobatic categories that have a seating configuration, excluding the pilot seat(s), of 9 or fewer and a maximum certificated take-off weight MTOW of 5670 kg (12 500 lb) or less (these aircraft are also known as class B under EU-OPS 1), * Twin-engined propeller-driven aeroplanes in the commuter category that have a seating configuration, excluding the pilot seat(s), of 19 or fewer and a maximum certificated take-off weight of 8618 kg (19 000 lb) or less (some of these aircraft are also known as class C under EU-OPS 1), * Aeroplanes in this category can be used for flying in VFR, SVFR, NVFR and IFR conditions day and night and also in known icing conditions if they are equipped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Flight Rules
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR). The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) ''Instrument Flying Handbook'' defines IFR as: "Rules and regulations established by the FAA to govern flight under conditions in which flight by outside visual reference is not safe. IFR flight depends upon flying by reference to instruments in the flight deck, and navigation is accomplished by reference to electronic signals." It is also a term used by pilots and controllers to indicate the type of flight plan an aircraft is flying, such as an IFR or VFR flight plan. Basic information Comparison to visual flight rules It is possible and fairly straightforward, in relatively clear weather conditions, to fly an aircraft solely by reference to outside visual cues, such as the horizon to maintain orientation, nearby buildings and terrain features for n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Visual Flight Rules
Night visual flight rules (NVFR) are the visual flight rules under which a flight may be performed at night primarily by visual reference. The alternative is flight by instrument flight rules (IFR), under which visual reference to terrain and traffic is not required. In EASA countries the requirements for a NVFR rating (at an approved training organisation) are: * total of 5 hours of VFR flying at night (NVFR), * including 3 hours ''dual'' flying (with an instructor), * including 5 take-offs and landings at night, * including 1 dual navigational flight by visual flight rules at night, at least 50 km and 1 hour. In many countries, NVFR is not permitted, in which case night flying is by IFR which requires an instrument rating Instrument rating refers to the qualifications that a pilot must have in order to fly under instrument flight rules (IFR). It requires specific training and instruction beyond what is required for a private pilot certificate or commercial pilot .... Coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)