|
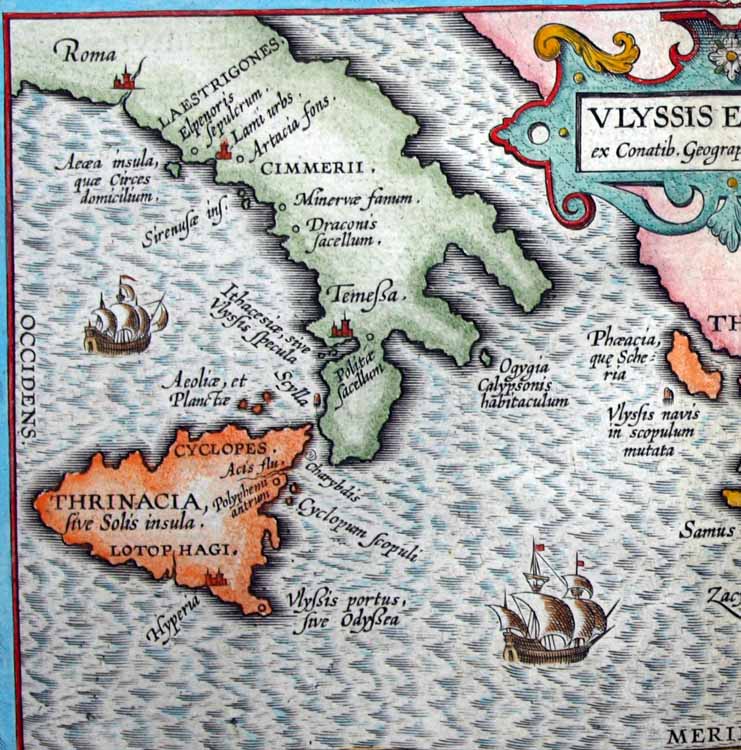
Eëa
__NOTOC__ Aeaea, Ææa or Eëä ( or ; grc, Αἰαία, Aiaíā ) was a mythological island said to be the home of the goddess-sorceress Circe. In Homer's ''Odyssey'', Odysseus tells Alcinous that he stayed here for one year on his way home to Ithaca. He says that he could not resist the need to be on this island, not so much for Circe but so that he does not resist the pull. Before leaving Aeaea, Odysseus was given instructions by Circe about how to cross the ocean and assisted by the North Wind to reach the underworld: Description Homer describes Aeaea as covered with a mixture of pasture and dense woodland of oak and beech. There were high hills or bluffs from which the sea could be seen encircling the island in all directions. Circe's stone house was located in a "dense forest of trees" "in a place that could be seen from far." Location The somewhat inconsistent geography of Homer's ''Odyssey'' is often considered more mythic than literal, but the geography of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helius
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyperion ("the one above") and Phaethon ("the shining"). Helios is often depicted in art with a radiant crown and driving a horse-drawn chariot through the sky. He was a guardian of oaths and also the god of sight. Though Helios was a relatively minor deity in Classical Greece, his worship grew more prominent in late antiquity thanks to his identification with several major solar divinities of the Roman period, particularly Apollo and Sol. The Roman Emperor Julian made Helios the central divinity of his short-lived revival of traditional Roman religious practices in the 4th century AD. Helios figures prominently in several works of Greek mythology, poetry, and literature, in which he is often described as the son of the Titans Hyperion and Theia and brother of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Kvarner Gulf. It is shared by three countries: Croatia, Slovenia, and Italy.Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer''History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th And 20th Centuries'' John Benjamins Publishing Co. (2006), Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas''A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe'' Routledge, 1sr ed. (2002), Croatia encapsulates most of the Istrian peninsula with its Istria County. Geography The geographical features of Istria include the Učka/Monte Maggiore mountain range, which is the highest portion of the Ćićarija/Cicceria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
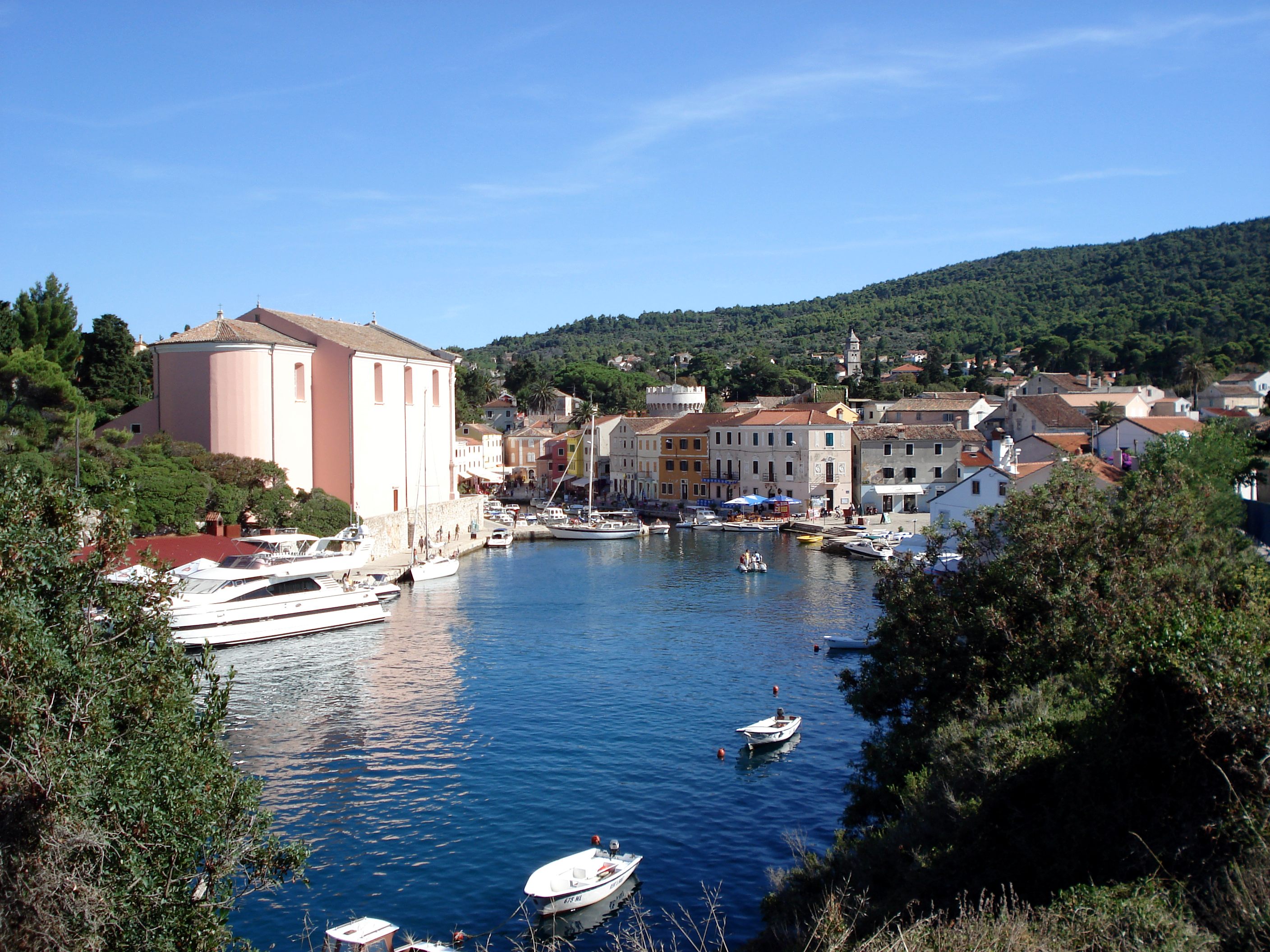
Lošinj
Lošinj (; it, Lussino; vec, Lusin, earlier ''Osero''; german: Lötzing; la, Apsorrus; grc, Ἄψορρος) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, in the Kvarner Gulf. It is almost due south of the city of Rijeka and part of the Primorje-Gorski Kotar County. The settlements on Lošinj include Nerezine, Sveti Jakov, Ćunski, Artatore, Mali Lošinj and Veli Lošinj. A regional road runs the length of the island; ferry connections (via the island of Cres) include Brestova - Porozina, Merag - Valbiska, Mali Lošinj - Zadar, Mali Lošinj - Pula. There is also an airport on the island of Lošinj. Geography Lošinj is part of the Cres-Lošinj archipelago. The Cres-Lošinj archipelago includes the two major islands Cres and Lošinj, some minor islands Unije, Ilovik, Susak, Vele Srakane, Male Srakane and a number of uninhabited small islets and outcrops. Cres is the largest by area, followed by Lošinj. Cres and Lošinj are connected by a small bridge at the town o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Graves
Captain Robert von Ranke Graves (24 July 1895 – 7 December 1985) was a British poet, historical novelist and critic. His father was Alfred Perceval Graves, a celebrated Irish poet and figure in the Gaelic revival; they were both Celticists and students of Irish mythology. Graves produced more than 140 works in his lifetime. His poems, his translations and innovative analysis of the Greek myths, his memoir of his early life—including his role in World War I—''Good-Bye to All That'', and his speculative study of poetic inspiration ''The White Goddess'' have never been out of print. He is also a renowned short story writer, with stories such as "The Tenement" still being popular today. He earned his living from writing, particularly popular historical novels such as ''I, Claudius''; '' King Jesus''; ''The Golden Fleece''; and ''Count Belisarius''. He also was a prominent translator of Classical Latin and Ancient Greek texts; his versions of ''The Twelve Caesars'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeëtes
Aeëtes (; , ; , ), or Aeeta, was a king of Colchis in Greek mythology. The name comes from the ancient Greek word (, "eagle"). Family Aeëtes was the son of Sun god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis, brother of Circe, Perses and Pasiphaë, and father of Medea, Chalciope and Absyrtus. His consort was either (1) Idyia, the youngest daughter of Oceanus, (2) Asterodeia, a Caucasian Oceanid, (3) the Nereid Neaera, (4) Clytia, (5) Ipsia or Eurylyte. According to others, he was the brother of Perses, a king of Tauris, husband of his niece Hecate, and father of Medea, Chalciope and Absyrtus. Yet other versions make Aeëtes a native of Corinth and son of Ephyra, an Oceanid, or else of a certain Antiope. Asterope was also one of the possible mothers of Aeëtes. Mythology Foundation of Colchis Pausanias states that, according to the poet Eumelos, Aeëtes was the son of Helios (from northern Peloponnesus) and brother of Aloeus. Helios divided the land he ruled, and he gave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia (country), Georgia. Its population, the Colchians are generally thought to have been an early Kartvelian languages, Kartvelian-speaking tribe ancestral to the contemporary western Georgians, namely Svans and Zans. According to David Marshall Lang: "one of the most important elements in the modern Georgian nation, the Colchians were probably established in the Caucasus by the Middle Bronze Age."''The Cambridge Ancient History'', John Anthony Crook, Elizabeth Rawson, p. 255 It has been described in modern scholarship as "the earliest Georgian formation", which, along with the Kingdom of Iberia, would later contribute significantly to the development of the Kingdom of Georgia and the Georgians, Georgian nation.Cyril Toumanoff, ''Studies in Christian Caucasian History'', pp. 69, 84Christopher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioannis Kakridis
Ioannis Kakridis ( el, Ιωάννης Κακριδής) (17 November 1901 – 20 March 1992) was a Greek classical scholar and was one of the leading scholars of Homeric Poetry in the twentieth century. He was born in Athens in 1901 and received his PhD at the University of Athens. He went on to become a professor at the universities of Athens, Thessaloniki, Tübingen, Stockholm, Lund and Uppsala. Kakridis was a Homer scholar and one of the most important classicists of twentieth-century Greece. He was also an early and staunch advocate of the adoption of the monotonic system in the Greek language. In 1941, he was denounced by the faculty of the University of Athens for republishing a lecture in the monotonic system, which led to the so-called "Trial of Accents" and his suspension and later dismissal from the university.Demaras, K. Th., ''A History of Modern Greek Literature'', trans. by Mary Gianos (London 1974) ii. 193–97, cited in The list of his written work is quite exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponza
Ponza (Italian: ''isola di Ponza'' ) is the largest island of the Italian Pontine Islands archipelago, located south of Cape Circeo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is also the name of the commune of the island, a part of the province of Latina in the Lazio region. History The island was inhabited from neolithic through Roman times. According to local legends, Ponza was named after Pontius Pilate, Roman governor of Judea who tried Jesus of Nazareth for sedition against Roman rule. Pontius Pilate's family owned a grotto on Ponza, which is still named after him. The Pontius Pilate legend of Ponza's name has recently come into dispute amongst historians, because the name "Pontia" appears in Strabo's ''Geography''. This pre-dates the birth of Pilate. It is not known if this is the same name as Ponza or a similar name. Also, ''Pontia'' means "Land of Bridges" in Latin, a name which could have been applied for Ponza's many naturally occurring arches and bridge-like landforms. Another theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lido
Lido may refer to: Geography Africa * Lido, a district in the city of Fez, Morocco Asia * Lido, an area in Chaoyang District, Beijing * Lido, a cinema theater in Siam Square shopping area in Bangkok * Lido City, a resort in West Java owned by MNC Corporation Europe * Lido (Belgrade), a river beach on the Danube in Belgrade, Serbia * Lidö, an island in the Stockholm Archipelago, Sweden * Lido di Venezia, an 11-kilometre-long sandbar near Venice, Italy * , a restaurant chain in Latvia founded by Gunārs Ķirsons * Ruislip Lido, a reservoir and artificial beach in Ruislip, London, UK. North America * Di Lido Island, a neighborhood of the South Beach district of Miami Beach, Florida * Lido Isle, Newport Beach, a man-made island, located in the harbor of Newport Beach, California * Lido Key, a barrier island off the coast of Sarasota, Florida Oceania * Lido, Papua New Guinea, a village Music * Lido (musician), Norwegian producer * ''Lido'' (Clearlake album), 2001 * ''Lido'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysius Of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς, ; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime. Dionysius' opinion of the necessity of a promotion of paideia within education, from true knowledge of classical sources, endured for centuries in a form integral to the identity of the Greek elite. Life He was a Halicarnassian. At some time after the end of the civil wars he moved to Rome, and spent twenty-two years studying Latin and literature and preparing materials for his history. During this period, he gave lessons in rhetoric, and enjoyed the society of many distinguished men. The date of his death is unknown. In the 19th century, it was commonly supposed that he was the ancestor of Aelius Dionysius of Halicarnassus. Works His major work, entitled ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all continents. The size of a peninsula can range from tiny to very large. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula. Peninsulas form due to a variety of causes. Etymology Peninsula derives , which is translated as 'peninsula'. itself was derived , or together, 'almost an island'. The word entered English in the 16th century. Definitions A peninsula is usually defined as a piece of land surrounded on most, but not all sides, but is sometimes instead defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. A peninsula may be bordered by more than one body of water, and the body of water does not have to be an ocean or a sea. A piece of land on a very tight river bend or one between two rivers is sometimes s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |