|
Eynsham Wood
Eynsham is an English village and civil parish in Oxfordshire, about north-west of Oxford and east of Witney. The 2011 Census recorded a parish population of 4,648. It was estimated at 5,087 in 2020. History Eynsham grew up near the historically important ford of Swinford on the River Thames flood plain. Excavations have shown that the site was used in the Bronze Age (3000–300 BCE) for a rectilinear enclosure edging a gravel terrace. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' records Eynsham as ''Egonesham'' and describes it as one of four towns that the Saxons captured from the Britons in 571 CE. Evidence has been found of 6th–7th-century Saxon buildings at New Wintles Farm, about three-quarters of a mile (1 km) from the present parish church. There is evidence that Eynsham had an early minster, probably founded in the 7th or 8th centuries. The name appears in 864 CE as ''Egenes homme'': "Ægen's enclosure or river-meadow". In 1005 Aethelmar, kinsman of Aethelred II founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnard Gate
Barnard Gate is a hamlet about east of Witney in Oxfordshire. It has a public house A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was ..., the Boot Inn. References {{Oxfordshire-geo-stub Hamlets in Oxfordshire West Oxfordshire District ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ælfric Of Eynsham
Ælfric of Eynsham ( ang, Ælfrīc; la, Alfricus, Elphricus; ) was an English abbot and a student of Æthelwold of Winchester, and a consummate, prolific writer in Old English of hagiography, homilies, biblical commentaries, and other genres. He is also known variously as ''Ælfric the Grammarian'' (''Alfricus Grammaticus''), ''Ælfric of Cerne'', and ''Ælfric the Homilist''. In the view of Peter Hunter Blair, he was "a man comparable both in the quantity of his writings and in the quality of his mind even with Bede himself." According to Claudio Leonardi, he "represented the highest pinnacle of Benedictine reform and Anglo-Saxon literature". Life and works Ælfric was educated in the Benedictine Old Minster at Winchester under Saint Æthelwold, who was bishop there from 963 to 984. Æthelwold had carried on the tradition of Dunstan in his government of the abbey of Abingdon, then in Berkshire, and at Winchester he continued his strenuous support for the English Benedictin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound Lock
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself (usually then called a caisson) that rises and falls. Locks are used to make a river more easily navigable, or to allow a canal to cross land that is not level. Later canals used more and larger locks to allow a more direct route to be taken. Pound lock A ''pound lock'' is most commonly used on canals and rivers today. A pound lock has a chamber with gates at both ends that control the level of water in the pound. In contrast, an earlier design with a single gate was known as a flash lock. Pound locks were first used in China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD), having been pioneered by the Song politician and naval eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Lock
A flash lock is a type of lock for river or canal transport. Early locks were designed with a single gate, known as a flash lock or staunch lock. The earliest European references to what were clearly flash locks were in Roman times. Development In England the "gate" was similar to a temporary needle dam: a set of boards, called ''paddles'', supported against the current by upright timbers called ''rymers'' which normally kept the level of water above it to navigable levels. Boats moving downstream would wait above the lock until the paddles (and their rymers) were removed, which would allow a "flash" of water to pass through, carrying the boats with it. Upstream boats would be winched or towed through the lock with the paddles removed. Considerable skill was involved both in removing the paddles in a timely manner and navigating the boat through the lock. Flash locks of this type have been documented since at least 1295 C.E. Flash locks were commonly built into small dams or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eynsham Lock
Eynsham Lock is a lock on the River Thames in England. It is on the southern bank near Swinford Oxfordshire. The large village of Eynsham is a little distance away on the northern bank. The lock was one of the last pound locks built on the Thames being built by the Thames Conservancy in 1928. The weir is on the other side of the island on the original course of the river. History There was previously a weir and flash lock known as Eynsham or Bolde's weir, originally owned by Eynsham Abbey. The weir was rebuilt in 1886 after there had been some proposals for removing it and around 1890 a boatslide was built for the portage of small boats.Fred. S. Thacker ''The Thames Highway: Volume II Locks and Weirs'' 1920 - republished 1968 David & Charles It was replaced by the pound lock in 1928 which was cut across the neck of a bend. The weir was reconstructed in 1950. Access to the lock The lock is close to the B4044 road where it crosses the river at Swinford Toll Bridge and is acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
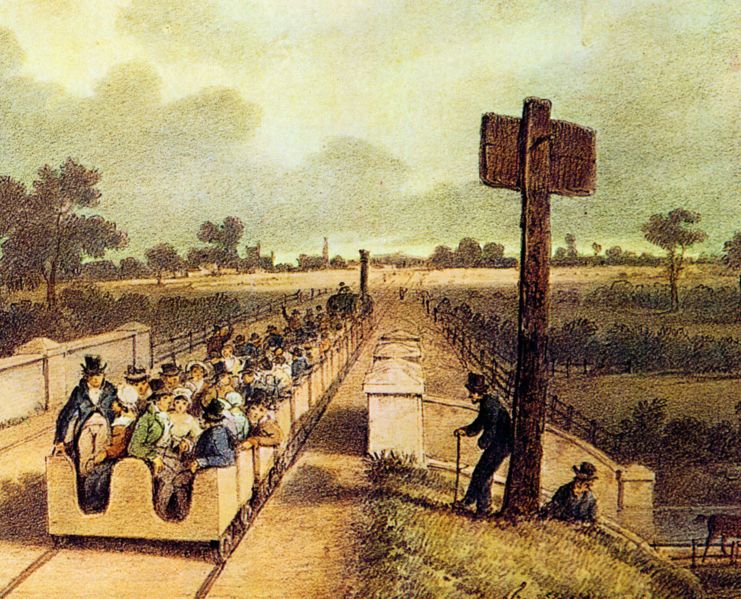
Railway Mania
Railway Mania was an instance of a stock market bubble in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in the 1840s. It followed a common pattern: as the price of railway shares increased, speculators invested more money, which further increased the price of railway shares, until the share price collapsed. The mania reached its zenith in 1846, when 263 Acts of Parliament for setting up new railway companies were passed, with the proposed routes totalling . About a third of the railways authorised were never built—the companies either collapsed due to poor financial planning, were bought out by larger competitors before they could build their line, or turned out to be fraudulent enterprises to channel investors' money into other businesses. Causes The world's first recognizably modern inter-city railway, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (the L&M), opened its railway in 1830 and proved to be successful for transporting both passengers and freight. In the late 1830s an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wharfinger
Wharfinger (pronounced ''wor-fin-jer)'' is an archaic term for a person who is the keeper or owner of a wharf. The wharfinger takes custody of and is responsible for goods delivered to the wharf, typically has an office on the wharf or dock, and is responsible for day-to-day activities including slipways, keeping tide tables and resolving disputes. The term is rarely used; today a wharfinger is usually called a "harbourmaster". Etymology The word's etymology is probably Elizabethan-era English, and possibly a corruption of ''wharfager''. An 1844 usage appears in Pigot's Directory of Dorset in which Beales and Cox are noted to be wharfingers for the Port of Weymouth. Duties In Smith v. Burnett, 173 U.S. 430 (1899), the US Supreme Court set forth the primary duties a wharfinger owes to vessels using the dock. A wharfinger does not guarantee the safety of the vessels using its dock, but must exercise reasonable diligence to determine the condition of the berth, remove dangerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries. They are split into the West Midlands and East Midlands. The region's biggest city, Birmingham often considered the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands, is the second-largest city and metropolitan area in the United Kingdom. Symbolism A saltire (diagonal cross) may have been used as a symbol of Mercia as early as the reign of Offa. By the 13th century, the saltire had become the attributed arms of the Kingdom of Mercia. The arms are blazoned ''Azure, a saltire Or'', meaning a gold (or yellow) saltire on a blue field. The saltire is used as both a flag and a coat of arms. As a flag, it is flown from Tamworth Castle, the ancient seat of the Mercian Kings, to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Canal
The Oxford Canal is a narrowboat canal in central England linking the City of Oxford with the Coventry Canal at Hawkesbury (just north of Coventry and south of Bedworth) via Banbury and Rugby. Completed in 1790, it connects to the River Thames at Oxford, and links with the Grand Union Canal, which it is combined with for between to the villages of Braunston and Napton-on-the-Hill. The canal is usually divided into the North Oxford Canal (north of Napton, via Rugby to Hawkesbury Junction near Coventry) and the South Oxford Canal, south of Napton to Banbury and Oxford. The canal was for about 15 years the main canal artery of trade between the Midlands and London, via its connection to the Thames, until the Grand Union Canal (then called the Grand Junction Canal) took most of the London-bound traffic following its opening in 1805. The North Oxford Canal (which had been straightened in the 1830s) remained an important artery of trade carrying coal and other commodities until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Reformation
The English Reformation took place in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope and the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Protestant Reformation, a religious and political movement that affected the practice of Christianity in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. Ideologically, the groundwork for the Reformation was laid by Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanists who believed that the Bible, Scriptures were the only source of Christian faith and criticized religious practices which they considered superstitious. By 1520, Martin Luther, Martin Luther's new ideas were known and debated in England, but Protestants were a religious minority and heretics under the law. The English Reformation began as more of a political affair than a theological dispute. In 1527, Henry VIII requested an annulment of his marriage, but Pope Clement VII refused. In response, the English Reformation Parliament, Refo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eynsham Abbey
Eynsham Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Eynsham, Oxfordshire, in England between 1005 and 1538. King Æthelred allowed Æthelmær the Stout to found the abbey in 1005. There is some evidence that the abbey was built on the site of an earlier minster, probably founded in the 7th or 8th centuries. The site is a Scheduled Historic Monument. History The first abbot of the abbey was the prolific writer Ælfric (c. 955–c. 1010) and the abbey was established in 1005. Eynsham Abbey was in the Diocese of Dorchester. In 1072 the recently appointed Norman Bishop of Dorchester, Remigius, moved his see from Dorchester, a few miles down the Thames from Eynsham, to Lincoln, at the other end of the diocese. In 1091 Remigius annexed Eynsham Abbey, with its revenues, to his new abbey at Stow in Lincolnshire. This may have been the opening move in an attempt to introduce monks into the Lincoln cathedral chapter, but Remigius' successor, Robert Bloet, did not follow through with the sche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talbot (dog)
The Talbot was a type of hunting hound common in England during the Middle Ages. It is depicted in art of the period as small to medium-sized, white in colour, with short legs, large powerful feet, a deep chest with a slender waist, long drooping ears, and a very long curled tail. It is shown in one well-known example at Haddon Hall with a fierce facial expression. It is now extinct, but is believed to be an ancestor of the modern Beagle and Bloodhound. It is uncertain whether it was a scenthound (bred for the quality of its nose), a sighthound (bred for the quality of sight and speed), or a dog used for digging out quarry, nor is it known what type of quarry it hunted, whether deer, fox, boar, etc. History In medieval times, "Talbot" was a common name for an individual hound, as used before 1400 in Chaucer's ''The Nun's Priest's Tale'' (line 3383), and is used as an example of a hound name in George Turberville's 1575 work ''The Noble Art of Venerie or Huntyng''. By t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)