|
Extractant
Extraction in chemistry is a separation process consisting of the separation of a substance from a matrix. Common examples include '' liquid-liquid extraction'', and ''solid phase extraction''. The distribution of a solute between two phases is an equilibrium condition described by partition theory. This is based on exactly how the analyte moves from the initial solvent into the extracting solvent. The term ''washing'' may also be used to refer to an extraction in which impurities are extracted from the solvent containing the desired compound. Types of extraction * Liquid–liquid extraction * Solid-phase extraction * Acid-base extraction * Supercritical fluid extraction * Ultrasound-assisted extraction * Heat reflux extraction * Mechanochemical-assisted extraction * Maceration * Microwave-assisted extraction * Instant controlled pressure drop extraction (DIC, from the French, Détente instantanée contrôlée) * Perstraction Laboratory applications and examples Liquid- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent Impregnated Resins
Solvent impregnated resins (SIRs) are commercially available (macro)porous resins impregnated with a solvent/an extractant. In this approach, a liquid extractant is contained within the pores of (adsorption) particles. Usually, the extractant is an organic liquid. Its purpose is to extract one or more dissolved components from a surrounding aqueous environment. The basic principle combines adsorption, chromatography and liquid-liquid extraction. History The principle of Solvent Impregnated Resins was first shown in 1971 by Abraham Warshawsky. This first venture was aimed at the extraction of metals. Ever since then, SIRs have been mainly used for metal extraction, be it heavy metals or specifically radioactive metals. Much research on SIRs has been done by J.L Cortina and e.g. N. Kabay, K. Jerabek or J. Serarols. However, lately investigations also go towards using SIRs for the separation of natural compounds, and even for separation of biotechnological products. Basic principle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perstraction
Perstraction is a membrane extraction process, where two liquid phases are contacted across a membrane. The desired species in the feed, selectively crosses the membrane into the extracting solution. Perstraction was originally developed to overcome the downsides of liquid–liquid extraction, for example extractant toxicity and emulsion formation. Perstraction, or membrane extraction, has been applied to many fields including fermentation, waste water treatment and alcohol-free beverage production. Introduction Perstraction is the separation technique developed from liquid-liquid extraction. Due to the presence of the membrane a wider selection of extractants can be used, this can include the use of miscible solutions, for example the recovery of ammonia from waste water using sulphuric acid. This process is analogous to pervaporation in some ways. But the permeate is in liquid phase. Perstraction technique eliminates the problem of phase dispersion and separation altogether. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
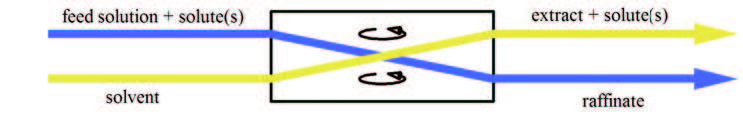
Liquid–liquid Extraction
Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE), also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes, based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water (polar) and an organic solvent (non-polar). There is a net transfer of one or more species from one liquid into another liquid phase, generally from aqueous to organic. The transfer is driven by chemical potential, i.e. once the transfer is complete, the overall system of chemical components that make up the solutes and the solvents are in a more stable configuration (lower free energy). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called the raffinate. LLE is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment called as mixer settlers. This type of process is commonly performed aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercritical Fluid Extraction
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is the process of separating one component (the extractant) from another (the matrix) using supercritical fluids as the extracting solvent. Extraction is usually from a solid matrix, but can also be from liquids. SFE can be used as a Sample preparation (analytical chemistry), sample preparation step for Analytical chemistry, analytical purposes, or on a larger scale to either strip unwanted material from a product (e.g. decaffeination) or collect a desired product (e.g. essential oils). These essential oils can include limonene and other straight solvents. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most used supercritical fluid, sometimes modified by co-solvents such as ethanol or methanol. Extraction conditions for supercritical carbon dioxide are above the critical temperature of 31 °C and critical pressure of 74 Bar (unit), bar. Addition of modifiers may slightly alter this. The discussion below will mainly refer to extraction with CO2, except where spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraction (chemistry)
Extraction in chemistry is a separation process consisting of the separation of a substance from a matrix. Common examples include '' liquid-liquid extraction'', and ''solid phase extraction''. The distribution of a solute between two phases is an equilibrium condition described by partition theory. This is based on exactly how the analyte moves from the initial solvent into the extracting solvent. The term ''washing'' may also be used to refer to an extraction in which impurities are extracted from the solvent containing the desired compound. Types of extraction * Liquid–liquid extraction * Solid-phase extraction * Acid-base extraction * Supercritical fluid extraction * Ultrasound-assisted extraction * Heat reflux extraction * Mechanochemical-assisted extraction * Maceration * Microwave-assisted extraction * Instant controlled pressure drop extraction (DIC, from the French, Détente instantanée contrôlée) * Perstraction Laboratory applications and examples Liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate ( systematically ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc, ETAC or EA) is the organic compound with the formula , simplified to . This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent. Production and synthesis Ethyl acetate was first synthesized by the Count de Lauraguais in 1759 by distilling a mixture of ethanol and acetic acid. In 2004, an estimated 1.3 million tonnes were produced worldwide. The combined annual production in 1985 of Japan, North America, and Europe was about 400,000 tonnes. The global ethyl acetate market was valued at $3.3 billion in 2018. Ethyl acetate is synthesized in industry mainly via the classic Fischer esterification reaction of ethanol and acetic acid. This mixture converts to the ester in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaching (chemistry)
Leaching is the process of a solute becoming detached or extracted from its carrier substance by way of a solvent. Leaching is a naturally occurring process which scientists have adapted for a variety of applications with a variety of methods. Specific extraction methods depend on the soluble characteristics relative to the sorbent material such as concentration, distribution, nature, and size. Leaching can occur naturally seen from plant substances (inorganic and organic), solute leaching in soil, and in the decomposition of organic materials. Leaching can also be applied affectedly to enhance water quality Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through tr ... and contaminant removal, as well as for disposal of hazardous waste products such as fly ash, or Rare-earth element, rare ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample Preparation (analytical Chemistry)
In analytical chemistry, sample preparation (working-up) refers to the ways in which a sample is treated prior to its analyses. Preparation is a very important step in most analytical techniques, because the techniques are often not responsive to the analyte in its in-situ form, or the results are distorted by interfering species. Sample preparation may involve dissolution, extraction, reaction with some chemical species, pulverizing, treatment with a chelating agent (e.g. EDTA), masking, filtering, dilution Dilution may refer to: * Reducing the concentration of a chemical * Serial dilution, a common way of going about this reduction of concentration * Homeopathic dilution * Dilution (equation), an equation to calculate the rate a gas dilutes *Tradema ..., sub-sampling or many other techniques. Treatment is done to prepare the sample into a form ready for analysis by specified analytical equipment. Sample preparation could involve: crushing and dissolution, chemical digestion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decaffeination
Decaffeination is the removal of caffeine from coffee beans, cocoa, tea leaves, and other caffeine-containing materials. Decaffeinated drinks contain typically 1–2% of the original caffeine content, and sometimes as much as 20%. Decaffeinated products are commonly termed decaf. Decaffeination of coffee Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge performed the first isolation of pure caffeine from coffee beans in 1820, after the poet Goethe heard about his work on belladonna extract, and requested he perform an analysis on coffee beans. Though Runge was able to isolate the compound, he did not learn much about the chemistry of caffeine itself, nor did he seek to use the process commercially to produce decaffeinated coffee. Decaffeination processes Various methods can be used for decaffeination of coffee. These methods take place prior to roasting and may use organic solvents such as dichloromethane or ethyl acetate, supercritical CO2, or water to extract caffeine from the beans, while leaving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soxhlet Extractor
A Soxhlet extractor is a piece of laboratory apparatus invented in 1879 by Franz von Soxhlet. It was originally designed for the extraction of a lipid from a solid material. Typically, Soxhlet extraction is used when the desired compound has a ''limited'' solubility in a solvent, and the impurity is insoluble in that solvent. It allows for unmonitored and unmanaged operation while efficiently recycling a small amount of solvent to dissolve a larger amount of material. Description A Soxhlet extractor has three main sections: a percolator (boiler and reflux) which circulates the solvent, a thimble (usually made of thick filter paper) which retains the solid to be extracted, and a siphon mechanism, which periodically empties the thimble. Assembly # The source material containing the compound to be extracted is placed inside the thimble. # The thimble is loaded into the main chamber of the Soxhlet extractor. # The extraction solvent to be used is placed in a distillation flask. # The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |