|
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor carpi ulnaris is a skeletal muscle located on the ulnar side of the forearm. The extensor carpi ulnaris acts to extend and adduct at the carpus/wrist from anatomical position. Being an extensor muscle, extensor carpi ulnaris is located on the posterior side of the forearm. Origin and insertion It originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the posterior border of the ulna, and crosses the forearm to the ulnar (medial) side to insert at the base of the 5th metacarpal. Action The extensor carpi ulnaris extends the wrist, but when acting alone inclines the hand toward the ulnar side; by its continued action it extends the elbow-joint. The muscle is a minor extensor of the carpus in carnivores, but has become a flexor in ungulates. In this case it would be described as ''ulnaris lateralis''. Innervation Despite its name, the extensor carpi ulnaris is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve (C7 and C8), the continuation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony process on the proximal, posterior end of the ulna. It forms the protruding part of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit (trochlear notch). The olecranon serves as a lever for the extensor muscles that straighten the elbow joint. Structure The olecranon is situated at the proximal end of the ulna, one of the two bones in the forearm. When the hand faces forward ( supination) the olecranon faces towards the back (posteriorly). It is bent forward at the summit so as to present a prominent lip which is received into the olecranon fossa of the humerus during extension of the forearm. Its base is contracted where it joins the body and the narrowest part of the upper end of the ulna. Its posterior surface, directed backward, is triangular, smooth, subcutaneous, and covered by a bursa. Its superior surface is of quadrilateral form, marked behind by a rough impression for the insertion of the triceps brachi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow ( brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis is an enthesopathy (attachment point disease) of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis on the lateral epicondyle. It causes pain and tenderness over the bony part of the lateral epicondyle. Symptoms range from mild tenderness to severe, persistent pain. The pain may also extend into the back of the forearm. It usually has a gradual onset, but it can seem sudden and be misinterpreted as an injury. Tennis elbow is often idiopathic. Its cause and pathogenesis are unknown. It likely involves tendinosis, a degeneration of the local tendon. It is thought this condition is caused by excessive use of the muscles of the back of the forearm, but this is not supported by evidence. It may be associated with work or sports, classically racquet sports (including paddle sports), but most people with the condition are not exposed to these activities. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and examination. Medical imaging is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachial Plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves (nerve plexus) formed by the anterior rami of the lower four Spinal nerve#Cervical nerves, cervical nerves and first Spinal nerve#Thoracic nerves, thoracic nerve (cervical spinal nerve 5, C5, Cervical spinal nerve 6, C6, cervical spinal nerve 7, C7, cervical spinal nerve 8, C8, and thoracic spinal nerve 1, T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the axilla, armpit, it supplies Afferent nerve fiber, afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand. Structure The brachial plexus is divided into five ''roots'', three ''trunks'', six ''divisions'' (three anterior and three posterior), three ''cords'', and five ''branches''. There are five "terminal" branches and numerous other "pre-terminal" or "collateral" branches, such as the subscapular nerve, the thoracodorsal nerve, and the long thoracic nerve, that leave the plexus at vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Branch Of The Radial Nerve
The radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the supinator In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius (bone), radius. Its function is to supination, supinate the forearm. Structure The supinator consists of tw ..., and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm. The deep branch provides motor function to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm, which is mostly the extensor muscles of the hand. The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The posterior cord takes nerves from the upper, lower, and middle trunk, so ultimately the radial nerve is formed from the anterior rami of C5 through T1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Interosseous Nerve
The posterior interosseous nerve (or dorsal interosseous nerve/deep radial nerve) is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve. The nerve fibers originate from cervical segments C7 and C8 in the spinal column. Structure Course It descends along the interosseous membrane, anterior to the extensor pollicis longus muscle, to the back of the carpus, where it presents a gangliform enlargement from which filaments are distributed to the ligaments and articulations of the carpus. Supply The posterior interosseous nerve supplies all the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm, except anconeus muscle, brachioradialis muscle, and extensor carpi radialis longus muscle. In other words, it supplies the following muscles: * Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle — deep branch of radial nerve * Ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined to be a polyphyletic and thereby invalid clade based on molecular data. As a result, true ungulates had since been reclassified to the newer clade Euungulata in 2001 within the clade Laurasiatheria while Paenungulata has been reclassified to a distant clade Afrotheria. Living ungulates are divided into two orders: Perissodactyla including Equidae, equines, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and Artiodactyla including Bos, cattle, antelope, Sus (genus), pigs, giraffes, camels, Ovis, sheep, deer, and Hippopotamidae, hippopotamuses, among others. Cetaceans such as Whale, whales, Dolphin, dolphins, and Porpoise, porpoises are also classified as artiodactyls, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Epicondyle Of The Humerus
The lateral epicondyle of the humerus is a large, tuberculated eminence, curved a little forward, and giving attachment to the radial collateral ligament of the elbow joint, and to a tendon common to the origin of the supinator and some of the extensor muscles. Specifically, these extensor muscles include the anconeus muscle, the supinator, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and extensor carpi ulnaris. In birds, where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods, it is termed dorsal epicondyle of the humerus. In comparative anatomy, the term ''ectepicondyle'' is sometimes used. A common injury associated with the lateral epicondyle of the humerus is lateral epicondylitis also known as tennis elbow. Repetitive overuse of the forearm, as seen in tennis or other sports, can result in inflammation of "the tendons that join the forearm muscles on the outside of the elbow. The forearm muscles and tendons become damaged from overu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Anatomical Position
The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism. In medical disciplines, all references to a location on or in the body are made based upon the standard anatomical position. A straight position is assumed when describing a proximo- distal axis (towards or away from a point of attachment). This helps avoid confusion in terminology when referring to the same organism in different postures. For example, if the elbow is flexed, the hand remains distal to the shoulder even if it approaches the shoulder. Human anatomy In standard anatomical position, the human body is standing erect and at rest. Unlike the situation in other vertebrates, the limbs are placed in positions reminiscent of the supine position imposed on cadavers during autopsy. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin wikt:carpus#Latin, carpus and the Greek language, Greek wikt:καρπός#Ancient Greek, καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to joint, articulate with the radius (bone), radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint (i.e. wrist joint),Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior compartment of the forearm, anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers. In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius (bone), radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
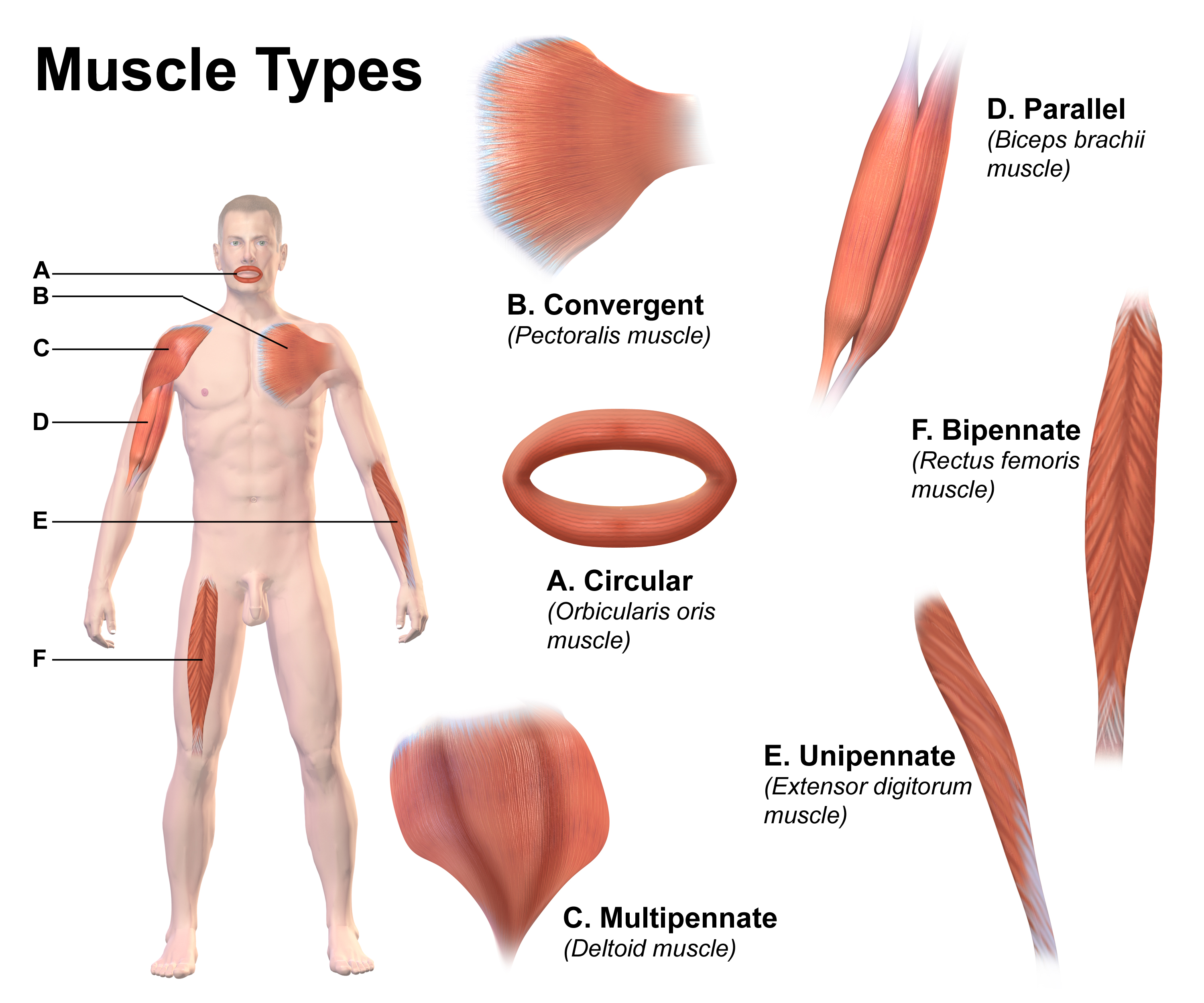
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
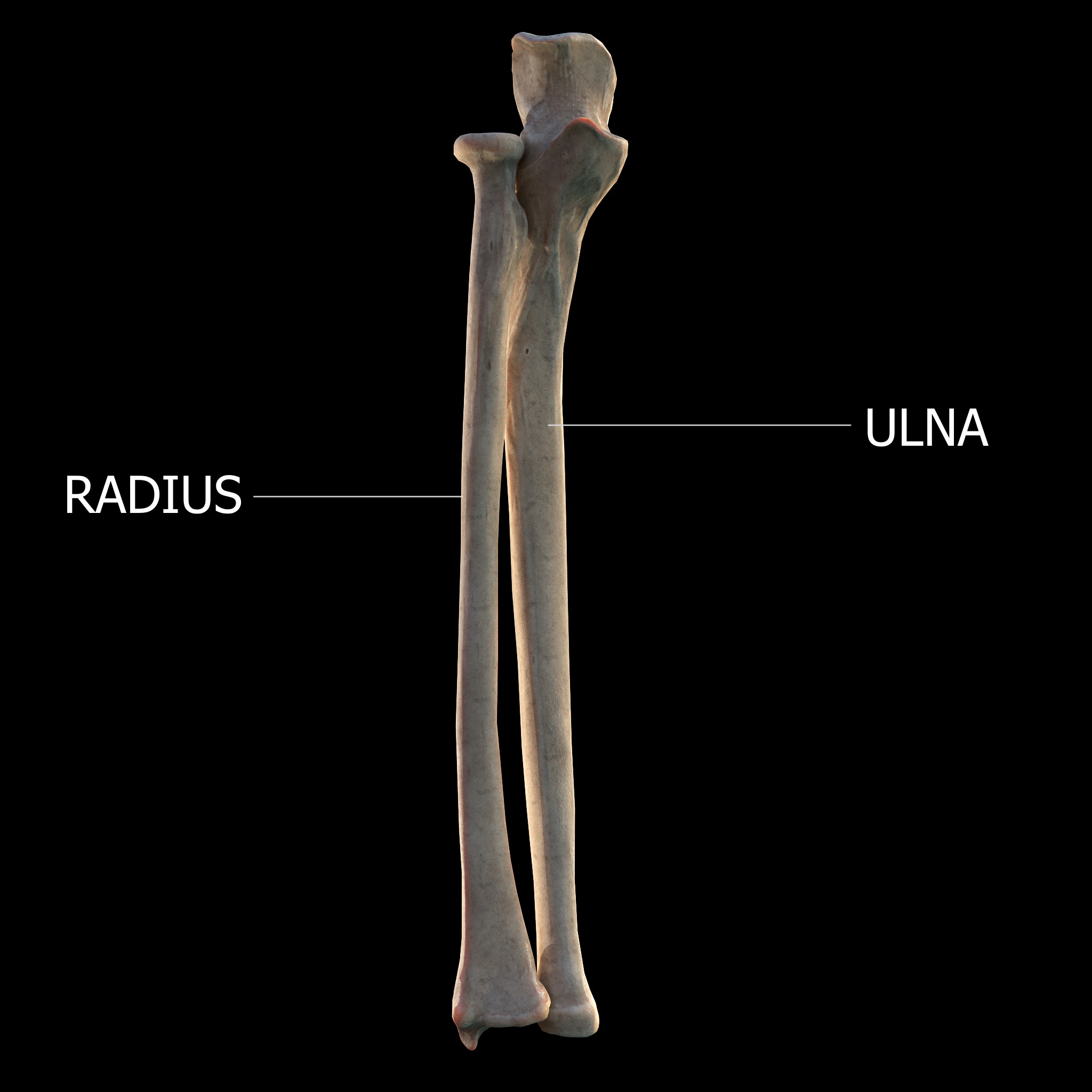
Ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long bone. Longer and thinner than the radius, the ulna is considered to be the smaller long bone of the lower arm. The corresponding bone in the Human leg#Structure, lower leg is the fibula. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the wrist, and when in standard anatomical position, is found on the Medial (anatomy), medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony Process (anatomy), process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is also a radial notch for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |