|
Exo-Brake
Small Payload Quick Return (SPQR) is a NASA Ames Research Center concept to return small payloads from orbit. The system uses an Exo-Brake, a parachute-like drag device for use in the low-pressure exosphere of Low Earth Orbit. This is the first part of a three part return system, operating from 350 to 100 km. Exo-Brake The first test of the Exo-Brake system from orbit began with the launching of the TechEdSat-3p nano-satellite from the International Space Station The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ... on November 19, 2013.''Exo-Brake Parachute Launched From International Space Station'' by Keith Cowling, SpaceRef, Nov 201/ref> TechEdSat-4 is expected to test an Exo-Brake with variable drag in 2014. TechEdSat-3p took over 60 days to deorbit, while TechEdSat-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exo-Brake
Small Payload Quick Return (SPQR) is a NASA Ames Research Center concept to return small payloads from orbit. The system uses an Exo-Brake, a parachute-like drag device for use in the low-pressure exosphere of Low Earth Orbit. This is the first part of a three part return system, operating from 350 to 100 km. Exo-Brake The first test of the Exo-Brake system from orbit began with the launching of the TechEdSat-3p nano-satellite from the International Space Station The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ... on November 19, 2013.''Exo-Brake Parachute Launched From International Space Station'' by Keith Cowling, SpaceRef, Nov 201/ref> TechEdSat-4 is expected to test an Exo-Brake with variable drag in 2014. TechEdSat-3p took over 60 days to deorbit, while TechEdSat-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
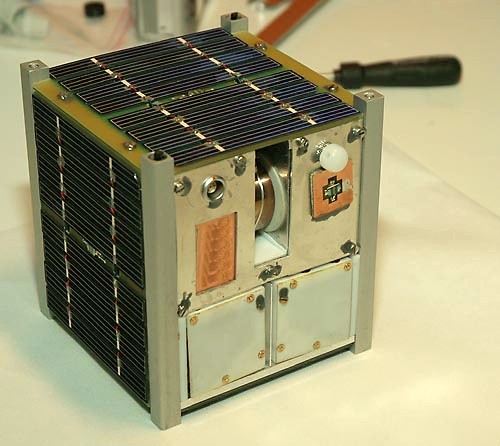
TechEdSat-3p
Technology Education Satellite (TechEdSat) is a successful nano-sat flight series conducted from the NASA Ames Research Center in collaboration with numerous universities (San Jose State University, University of Idaho, University of California, University of Minnesota, Smith College). While one of the principal aims has been to introduce young professionals and university students to the practical realm of developing space flight hardware, considerable innovations have been introduced. In addition, this evolving flight platform has tested concepts for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) sample return, as well as planetary nano-sat class mission concepts. TechEdSat-1 The first TechEdSat (later renamed "TechEdSat-1" or "TES-1") was a 1U-Cubesat designed to evaluate Space Plug-and-play Avionics (SPA) designed in Sweden by ÅAC Microtec. It was also originally intended to perform a communications experiment utilizing the Iridium and Orbcomm satellite phone network, although this functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TechEdSat-4
Technology Education Satellite (TechEdSat) is a successful nano-sat flight series conducted from the NASA Ames Research Center in collaboration with numerous universities (San Jose State University, University of Idaho, University of California, University of Minnesota, Smith College). While one of the principal aims has been to introduce young professionals and university students to the practical realm of developing space flight hardware, considerable innovations have been introduced. In addition, this evolving flight platform has tested concepts for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) sample return, as well as planetary nano-sat class mission concepts. TechEdSat-1 The first TechEdSat (later renamed "TechEdSat-1" or "TES-1") was a 1U-Cubesat designed to evaluate Space Plug-and-play Avionics (SPA) designed in Sweden by ÅAC Microtec. It was also originally intended to perform a communications experiment utilizing the Iridium and Orbcomm satellite phone network, although this functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Ames Research Center
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laboratory. That agency was dissolved and its assets and personnel transferred to the newly created National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on October 1, 1958. NASA Ames is named in honor of Joseph Sweetman Ames, a physicist and one of the founding members of NACA. At last estimate NASA Ames had over US$3 billion in capital equipment, 2,300 research personnel and a US$860 million annual budget. Ames was founded to conduct wind-tunnel research on the aerodynamics of propeller-driven aircraft; however, its role has expanded to encompass spaceflight and information technology. Ames plays a role in many NASA missions. It provides leadership in astrobiology; small satellites; robotic lunar exploration; the search for habitable planets; s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of the flight or mission, the payload of a vehicle may include cargo, passengers, flight crew, munitions, scientific instruments or experiments, or other equipment. Extra fuel, when optionally carried, is also considered part of the payload. In a commercial context (i.e., an airline or air freight carrier), payload may refer only to revenue-generating cargo or paying passengers. A payload of ordnance carried by a combat aircraft is sometimes alternatively referred to as the aircraft's warload. For a rocket, the payload can be a satellite, space probe, or spacecraft carrying humans, animals, or cargo. For a ballistic missile, the payload is one or more warheads and related systems; their total weight is referred to as the throw-weight. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosphere
The exosphere ( grc, ἔξω "outside, external, beyond", grc, σφαῖρα "sphere") is a thin, atmosphere-like volume surrounding a planet or natural satellite where molecules are gravitationally bound to that body, but where the density is so low that the molecules are essentially collisionless. In the case of bodies with substantial atmospheres, such as Earth's atmosphere, the exosphere is the uppermost layer, where the atmosphere thins out and merges with outer space. It is located directly above the thermosphere. Very little is known about it due to lack of research. Mercury, the Moon, Ceres, Europa, and Ganymede have surface boundary exospheres, which are exospheres without a denser atmosphere underneath. The Earth's exosphere is mostly hydrogen and helium, with some heavier atoms and molecules near the base. Surface boundary exosphere Mercury, Ceres and several large natural satellites, such as the Moon, Europa, and Ganymede, have exospheres without a denser a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never more than about one-third of the radius of Earth. The term ''LEO region'' is also used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. All crewed space stations to date have been within LEO. From 1968 to 1972, the Apollo program's lunar missions sent humans beyond LEO. Since the end of the Apollo program, no human spaceflights have been beyond LEO. Defining characteristics A wide variety of sources define LEO in terms of altitude. The altitude of an object in an elliptic orbit can vary significantly along the orbit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that perform a number of scientific research functions and explore new space technologies. Academia accounted for the majority of CubeSat launches until 2013, when more than half of launches were for non-academic purposes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |