|
Exercise Grand Slam
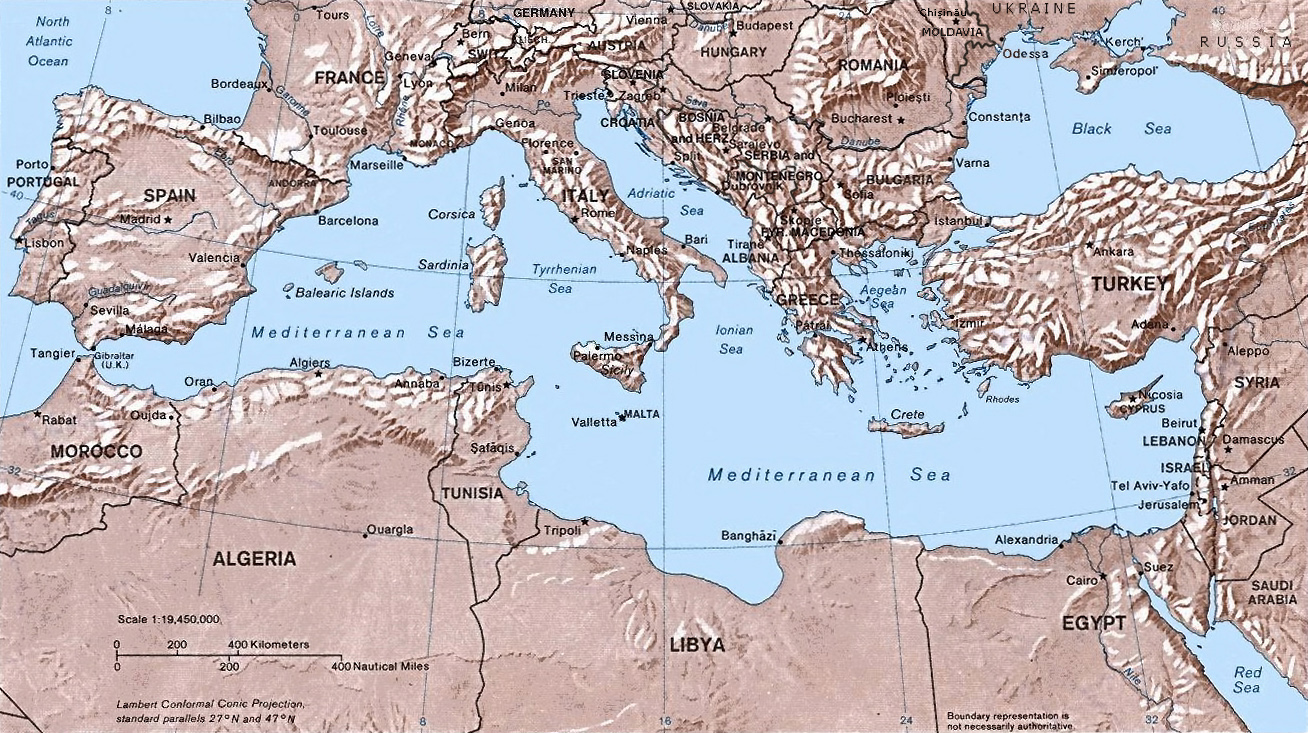
Exercise Grand Slam was an early major naval exercise of the newly formed North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). This 1952 combined naval exercise took place in the Mediterranean Sea, and it included a naval force that was described as being "the largest armada to be assembled in that area since the end of World War II." Exercise Grand Slam was an early test for NATO's Allied Forces Southern Europe. With Exercise Longstep, this exercise served as the prototype for future NATO maritime exercises in the Mediterranean Sea during the Cold War. Background In January 1950, the North Atlantic Council approved NATO's military strategy of Containment, deterring Soviet aggression. NATO military planning took on a renewed urgency following the outbreak of the Korean War in mid-1950, prompting NATO to establish a "force under a centralised command, adequate to deter aggression and to ensure the defence of Western Europe". Allied Command Europe was established under General of the Army (U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War (1947–1953)
The Cold War was a period of global geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. The term ''cold war'' is used because there was no direct fighting between the two superpowers, though each supported opposing sides in regional conflicts known as proxy wars. In addition to the struggle for ideological and economic influence and an arms race in both conventional and nuclear weapons, the Cold War was expressed through technological rivalries such as the Space Race, espionage, propaganda campaigns, embargoes, and sports diplomacy. After the end of World War II in 1945, during which the US and USSR had been allies, the USSR installed satellite governments in its occupied territories in Eastern Europe and North Korea by 1949, resulting in the political division of Europe (and Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
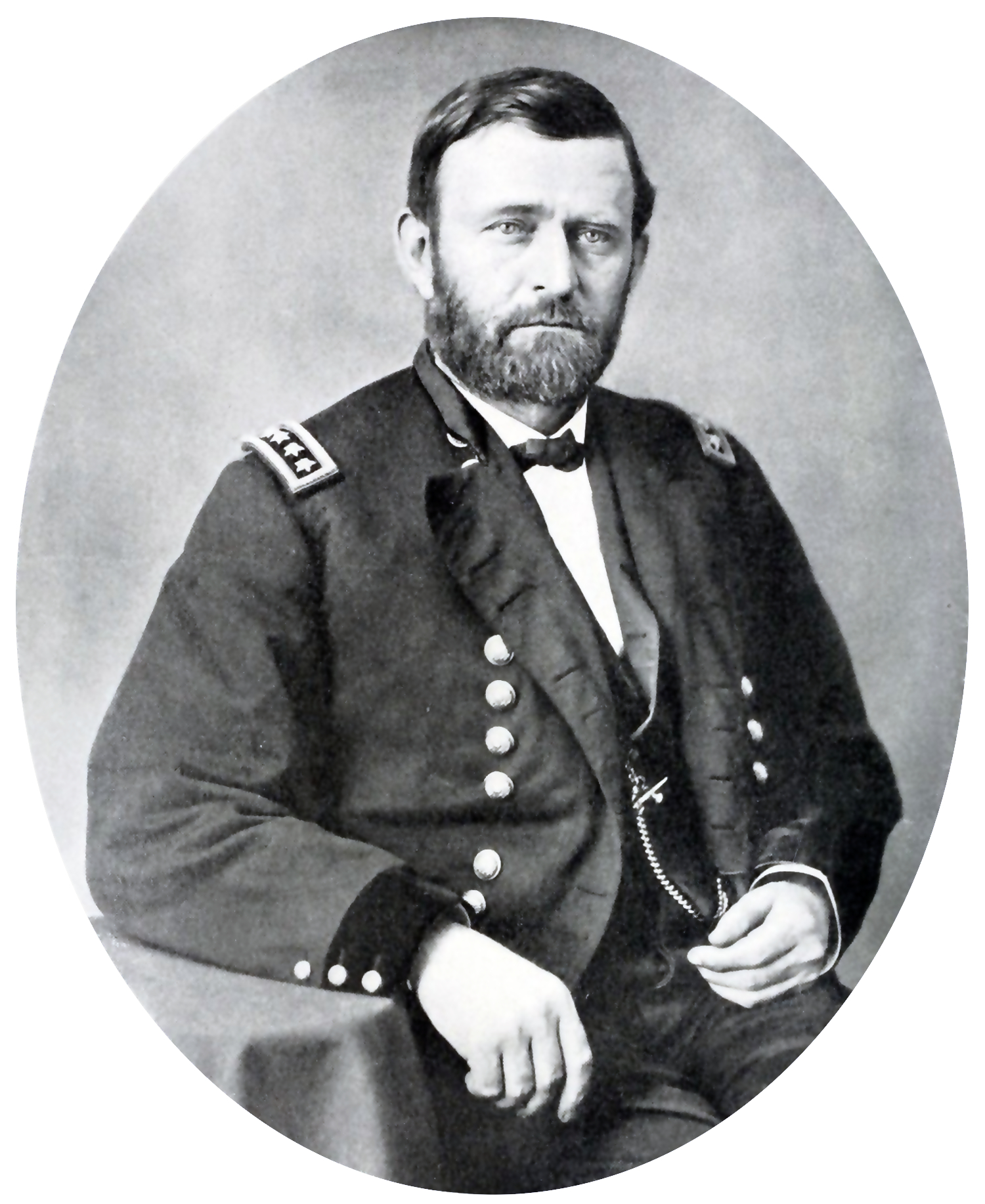
General Of The Army (United States)
General of the Army (abbreviated as GA) is a five-star rank, five-star general officer rank in the United States Army. It is generally equivalent to the rank of field marshal in other countries. In the United States, a General of the Army ranks above General (United States), generals and is equivalent to a Fleet admiral (United States), fleet admiral and a general of the Air Force. The General of the Army insignia consisted of five stars in a pentagonal pattern, with touching points. The insignia was paired with the gold and enameled United States coat of arms on service coat shoulder loops. The silver colored five-star chain has major insignia alone would be worn for use as a collar insignia of grade and on the garrison cap. Soft shoulder epaulets with five stars in silver thread and gold-threaded United States coat of arms on green cloth were worn with shirts and sweaters. The rank of "General of the Army" (the highest rank in the army) has had two incarnations. The first w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Fayette (R96)
''La Fayette'' was an 11,000-ton that served the French Navy from 1951 to 1963. She was the first French vessel named after the 18th century general Marquis de Lafayette. She was initially USS ''Langley'' (CVL-27) serving the United States Navy from 1943 to 1947 before transferring to the French Navy. History Built at Camden, New Jersey, ''Langley'' was originally ordered as the light cruiser USS ''Fargo'' (CL-85), but by the time her keel was laid in April 1942, she had been redesigned as an aircraft carrier, using the original cruiser hull and machinery. Commissioned in August 1943, ''Langley'' served in the Pacific theatre during World War II. The carrier was decommissioned at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in February 1947. ''Langley'' was taken out of "mothballs" early in 1951, refurbished and transferred to France under the Mutual Defense Assistance Program. Based in Toulon, ''La Fayette'' carried out many missions in the Far East until June 1953. During this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Navy
The Italian Navy (; abbreviated as MM) is one of the four branches of Italian Armed Forces and was formed in 1946 from what remained of the ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) after World War II. , the Italian Navy had a strength of 30,923 active personnel, with approximately 184 vessels in service, including minor auxiliary vessels. It is considered a multiregional and a blue-water navy. History Before and during World War II The ''Regia Marina'' was formed on 17 March 1861, after the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy. The Italian Navy assumed its present name after the Italian monarchy was abolished following a popular referendum held on 2 June 1946. After World War II At the end of its five years involvement in World War II, Italy was a devastated nation. After the end of hostilities, the ''Regia Marina'' – which at the beginning of the war was the fourth largest navy in the world, with a mix of modernised and new battleships – started a long and complex rebuilding proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean (France)
The French Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean, also known as CECMED (French for ''Commandant en chef pour la Méditerranée'') is a French Armed Forces regional commander. He commands the zone, the region and the Mediterranean maritime ''arrondissements''. He is usually an admiral of the French Navy, and is under the direct authority of the French Chief of the Defence Staff. the position was held by Admiral Yann Tainguy. CECMED today is simultaneously: * Commander of the région and the Mediterranean maritime ''arrondissement'', * Maritime Zone commander, * Maritime Prefect for the Méditerranean. Today the main French naval combat force in the Mediterranean is the Force d'action navale (FAN) headquartered at Toulon. The Admiral commanding the Naval Action Force (ALFAN) is responsible to the Chief of Staff of the French Navy at the rue Royale in Paris. History Mediterranean Squadron Vice-amiral François Fournier was Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Squadron (''Commandant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Mediterranean Fleet
The British Mediterranean Fleet, also known as the Mediterranean Station, was a formation of the Royal Navy. The Fleet was one of the most prestigious commands in the navy for the majority of its history, defending the vital sea link between the United Kingdom and the majority of the British Empire in the Eastern Hemisphere. The first Commander-in-Chief for the Mediterranean Fleet was the appointment of General at Sea Robert Blake in September 1654 (styled as Commander of the Mediterranean Fleet). The Fleet was in existence until 1967. Pre-Second World War The Royal Navy gained a foothold in the Mediterranean Sea when Gibraltar was captured by the British in 1704 during the War of Spanish Succession, and formally allocated to Britain in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht. Though the British had maintained a naval presence in the Mediterranean before, the capture of Gibraltar allowed the British to establish their first naval base there. The British also used Port Mahon, on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bostwick Carney
Robert Bostwick Carney (March 26, 1895 – June 25, 1990) was an admiral in the United States Navy who served as commander-in-chief of the NATO forces in Southern Europe (1951–1953) and then as Chief of Naval Operations (1953–1954) during the Eisenhower administration. He was the father in law of Joseph K. Taussig Jr. Early years Born in Vallejo, California, Carney graduated from the United States Naval Academy in 1916. He served in World War I, seeing combat against German U-boats. Between wars Carney served as Flag Secretary to Admiral Louis R. de Steiguer during the mid-1920s during de Steiguer's time in command of various battleship forces. Their relationship was not happy, mainly due to de Steiguer's imperious manner described by Carney as "constant pressure, irascibility, criticism, and unpleasantness". Famously, Carney eventually marched into de Steiguer's cabin, snapped, "Admiral, I just want to tell you I think you are a goddamn rotten son of a bitch," and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Army
The Italian Army ( []) is the Army, land force branch of the Italian Armed Forces. The army's history dates back to the Italian unification in the 1850s and 1860s. The army fought in colonial engagements in China and Italo-Turkish War, Libya. It fought in Northern Italy against the Austro-Hungarian Empire during World War I, Abyssinia before World War II and in World War II in Albania, Balkans, North Africa, the Soviet Union, and Italy itself. During the Cold War, the army prepared itself to defend against a Warsaw Pact invasion from the east. Since the end of the Cold War, the army has seen extensive peacekeeping service and combat in Afghanistan and Iraq. Its best-known combat vehicles are the Dardo IFV, Dardo infantry fighting vehicle, the Centauro (Tank destroyer), Centauro tank destroyer and the Ariete tank and among its aircraft the Agusta A129 Mangusta, Mangusta attack helicopter, recently deployed in UN missions. The headquarters of the Army General Staff are located in Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Land Forces Southern Europe
Allied Land Forces Southern Europe (LANDSOUTH) was a military command of NATO's Allied Forces Southern Europe (AFSOUTH) command. Based in Verona in Northern Italy LANDSOUTH was tasked with defending Italy north of the Apennine Mountains against a Warsaw Pact or Yugoslavian invasion. Activated in 1951 under an Italian Army four-star general, the command was disbanded in 2004. Commander, Allied Land Forces Southern Europe was a NATO Principal Subordinate Commander. History Following the creation of NATO in 1949, the Italian military was integrated into NATO's Allied Forces Southern Europe (AFSOUTH) and prepared for a feared Soviet invasion from the east, possibly via Yugoslavia. Allied Land Forces Southern Europe (LANDSOUTH), was activated on 10 July 1951 to defend northeastern Italy and headquartered in the Carli Palace in Verona. Three infantry divisions and three brigades were the only forces initially available to this command to defend Northern Italy. The divisions in qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise Verity
Exercise Verity was the only major training exercise of the Western Union (WU). Undertaken in July 1949, it involved 60 warships from the British, French, Belgian and Dutch navies. A contemporary newsreel described this exercise as involving "the greatest assembly of warships since the Battle of Jutland." Command structure The command authority for Exercise Verity was the Western Union. Field Marshal the Viscount Montgomery of Alamein was WUDO's senior officer as Chairman of the Commanders-in-Chief Committee. Admiral of the Fleet Sir Rhoderick McGrigor, RN, was in overall command of Exercise Verity. At the time of the exercise, Admiral McGrigor was serving as Commander-in-Chief of the British Royal Navy's Home Fleet. Operation The 60-ship fleet gathered in Mount's Bay, near Penzance, prior to setting sail for the Bay of Biscay for the week-long exercise. Field Marshal Montgomery held a reception on board the flagship, the aircraft carrier . Prince Bernhard of the Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Union Defence Organization
From April 1948, the member states of the Western Union (WU), decided to create a military agency under the name of the Western Union Defence Organisation (WUDO). WUDO was formally established on September 27–28, 1948. Objective The objective of WUDO was to provide for the coordination of defence between the five powers in the military and supply fields and for the study of the tactical problems of the defence of Western Europe; in addition, to provide a framework on which, in the event of any emergency, a command organization could be built up. The Treaty of Brussels contained a mutual defence clause as set forth in Article IV: :If any of the High Contracting Parties should be the object of an armed attack in Europe, the other High Contracting Parties will, in accordance with the provisions of Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations, afford the Party so attacked all the military and other aid and assistance in their power. Article V set forth the obligations of Bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |