|
Exceptional Case-marking
Exceptional case-marking (ECM), in linguistics, is a phenomenon in which the subject of an embedded infinitival verb seems to appear in a superordinate clause and, if it is a pronoun, is unexpectedly marked with object case morphology (''him'' not ''he'', ''her'' not ''she'', etc.). The unexpected object case morphology is deemed "exceptional". The term ''ECM'' itself was coined in the Government and Binding grammar framework although the phenomenon is closely related to the accusativus cum infinitivo constructions of Latin. ECM-constructions are also studied within the context of raising. The verbs that license ECM are known as ''raising-to-object'' verbs. Many languages lack ECM-predicates, and even in English, the number of ECM-verbs is small. The structural analysis of ECM-constructions varies in part according to whether one pursues a relatively flat structure or a more layered one. Examples The ECM-construction is licensed by a relatively small number of verbs in English (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the science, scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the Cognition, cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raising (linguistics)
In linguistics, raising constructions involve the movement of an argument from an embedded or subordinate clause to a matrix or main clause; in other words, a raising predicate/verb appears with a syntactic argument that is not its semantic argument, but is rather the semantic argument of an embedded predicate. For example, in ''they seem to be trying'', the predicand of ''trying'' is the subject of ''seem''. Although English has raising constructions, not all languages do. The term ''raising'' has its origins in the transformational analysis of such constructions; the constituent in question is seen as being "raised" from its initial deep structure position, as the subject of the embedded predicate, to its surface structure position in the matrix predicate/verb. Raising predicates/verbs are related to control predicates, although there are important differences between the two predicate/verb types. Examples There are at least two types of raising predicates/verbs: raising-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue (Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining trait of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation associated with dependency grammars; hence, phrase structure grammars are also known as constituency grammars. Any of several related theories for the parsing of natural language qualify as constituency grammars, and most of them have been develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control (linguistics)
In linguistics, control is a construction in which the understood subject of a given predicate is determined by some expression in context. Stereotypical instances of control involve verbs. A superordinate verb "controls" the arguments of a subordinate, nonfinite verb. Control was intensively studied in the government and binding framework in the 1980s, and much of the terminology from that era is still used today. In the days of Transformational Grammar, control phenomena were discussed in terms of ''Equi-NP deletion''. Control is often analyzed in terms of a null pronoun called ''PRO''. Control is also related to raising, although there are important differences between control and raising. Most if not all languages have control constructions and these constructions tend to occur frequently. Examples Standard instances of (obligatory) control are present in the following sentences: ::Susan promised to help us. - Subject control with the obligatory control predicate ''promise'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accusativus Cum Infinitivo
In grammar, accusative and infinitive is the name for a syntactic construction of Latin and Greek, also found in various forms in other languages such as English and Spanish. In this construction, the subject of a subordinate clause is put in the accusative case (objective case in English) and the verb appears in the infinitive form. Among other uses, information may be given in this form to indicate ''indirect speech'', also called indirect discourse. The construction is often referred to by the Latin term ''Accusativus cum infinitivo'', frequently abbreviated ''ACI''. In Latin The ''accusative and infinitive'' is the usual grammatical construction by means of which Classical Latin expressed indirect statements, that is, statements which report what someone has said, thought, felt, etc. Whereas a direct statement would say :"I am a good student," says Julia. the indirect statement might say :Julia says that she is a good student. Classical Latin tends not to use a conjunc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
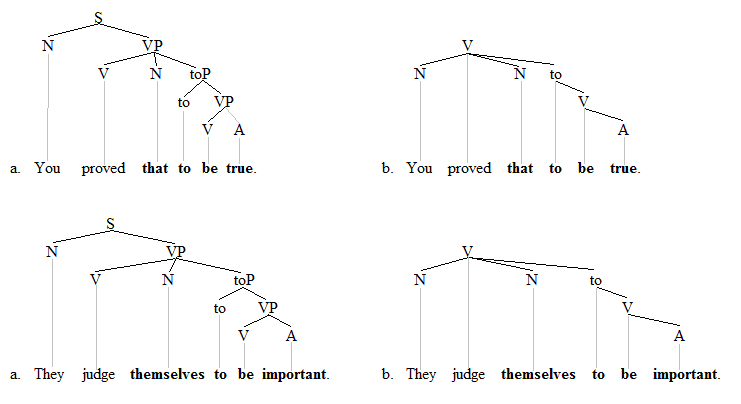
ECM Trees 2
ECM may refer to: Economics and commerce * Engineering change management * Equity capital markets * Error correction model, an econometric model * European Common Market Mathematics * Elliptic curve method * European Congress of Mathematics Science and medicine * Ectomycorrhiza * Electron cloud model * Engineered Cellular Magmatics * Erythema chronicum migrans * Extracellular matrix Sport * European Championships Management Technology * Electrochemical machining * Electronic contract manufacturing * Electronic countermeasure * Electronically commutated motor * Energy conservation measure * Engine control module * Enterprise content management * Error correction mode Other uses * Editio Critica Maior, a critical edition of the Greek New Testament * ECM Records, a record label * ECM Real Estate Investments, a defunct real estate developer based in Luxembourg * Edinburgh City Mission, a Christian organization in Scotland * Elektrani na Severna Makedonija (), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ECM Trees 1
ECM may refer to: Economics and commerce * Engineering change management * Equity capital markets * Error correction model, an econometric model * European Common Market Mathematics * Elliptic curve method * European Congress of Mathematics Science and medicine * Ectomycorrhiza * Electron cloud model * Engineered Cellular Magmatics * Erythema chronicum migrans * Extracellular matrix Sport * European Championships Management Technology * Electrochemical machining * Electronic contract manufacturing * Electronic countermeasure * Electronically commutated motor * Energy conservation measure * Engine control module * Enterprise content management * Error correction mode Other uses * Editio Critica Maior, a critical edition of the Greek New Testament * ECM Records, a record label * ECM Real Estate Investments, a defunct real estate developer based in Luxembourg * Edinburgh City Mission, a Christian organization in Scotland * Elektrani na Severna Makedonija (), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue (Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining trait of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation associated with dependency grammars; hence, phrase structure grammars are also known as constituency grammars. Any of several related theories for the parsing of natural language qualify as constituency grammars, and most of them have been develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accusativus Cum Infinitivo
In grammar, accusative and infinitive is the name for a syntactic construction of Latin and Greek, also found in various forms in other languages such as English and Spanish. In this construction, the subject of a subordinate clause is put in the accusative case (objective case in English) and the verb appears in the infinitive form. Among other uses, information may be given in this form to indicate ''indirect speech'', also called indirect discourse. The construction is often referred to by the Latin term ''Accusativus cum infinitivo'', frequently abbreviated ''ACI''. In Latin The ''accusative and infinitive'' is the usual grammatical construction by means of which Classical Latin expressed indirect statements, that is, statements which report what someone has said, thought, felt, etc. Whereas a direct statement would say :"I am a good student," says Julia. the indirect statement might say :Julia says that she is a good student. Classical Latin tends not to use a conjunc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control (linguistics)
In linguistics, control is a construction in which the understood subject of a given predicate is determined by some expression in context. Stereotypical instances of control involve verbs. A superordinate verb "controls" the arguments of a subordinate, nonfinite verb. Control was intensively studied in the government and binding framework in the 1980s, and much of the terminology from that era is still used today. In the days of Transformational Grammar, control phenomena were discussed in terms of ''Equi-NP deletion''. Control is often analyzed in terms of a null pronoun called ''PRO''. Control is also related to raising, although there are important differences between control and raising. Most if not all languages have control constructions and these constructions tend to occur frequently. Examples Standard instances of (obligatory) control are present in the following sentences: ::Susan promised to help us. - Subject control with the obligatory control predicate ''promise'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.png)
