|
Ewe People
The Ewe people (; , lit. "Ewe people"; or ''Mono Kple Amu (Volta) Tɔ́sisiwo Dome'', lit. "Between the Rivers Mono and Volta"; ''Eʋenyígbá'' Eweland) are a Gbe languages, Gbe-speaking ethnic group. The largest population of Ewe people is in Ghana (6.0 million), and the second largest population is in Togo (3.1 million). They speak the Ewe language () which belongs to the Gbe languages, Gbe family of languages. They are related to other speakers of Gbe languages such as the Fon people, Fon, Gen language, Gen, Phla–Pherá languages, Phla/Phera, Ogu people, Ogu/Gun, Fon language, Maxi (Mahi), and the Aja people of Togo and Benin. Demographics Ewe people are located primarily in the coastal regions of West Africa: in the region south and east of the Volta River to around the Mono River at the border of Togo and Benin; and in the southwestern part of Nigeria (close to the Atlantic Ocean, stretching from the Nigeria and Benin border to Epe). They are primarily found in the Volta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fon Language
Fon (, ) also known as Dahomean is the language of the Fon people. It belongs to the Gbe group within the larger Atlantic–Congo family. It is primarily spoken in Benin Republic, as well as in Nigeria and Togo by approximately 2.3 million speakers. Like the other Gbe languages, Fon is an isolating language with a SVO basic word order. Cultural and legal status In Benin, French is the official language, and Fon and other indigenous languages, including Yom and Yoruba, are classified as national languages. Dialects The standardized Fon language is part of the Fon cluster of languages inside the Eastern Gbe languages. Hounkpati B Christophe Capo groups Agbome, Kpase, Gun, Maxi and Weme (Ouémé) in the Fon dialect cluster, although other clusterings are suggested. Standard Fon is the primary target of language planning efforts in Benin, although separate efforts exists for Gun, Gen, and other languages of the country. Phonology Vowels Fon has seven oral vowel pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Togbe Agorkoli
Togbe Agorkoli ( Eʋegbe: Togbe Agɔ Akɔli) was a dictator and draconian ruler of Notsie, a town in modern Togo. During his rule, the Ewe people in what is now known as Ghana Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ... and Togo escaped from Notsie to their present lands. References {{reflist Legendary African people Togolese people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
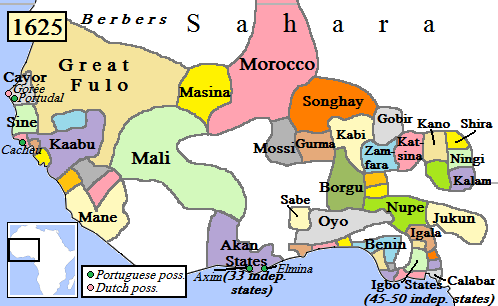
Oyo Empire
The Oyo Empire was a Yoruba people, Yoruba empire in West Africa. It was located in present-day western Nigeria (including the South West (Nigeria), South West zone, Benin Republic, and the western half of the North Central (Nigeria), North Central zone). The empire grew to become the largest Yoruba language, Yoruba-speaking state through the organizational and administrative efforts of the Yoruba people, trade, as well as the military use of cavalry. The Oyo Empire was one of the most politically important states in Western Africa from the late-16th to the early 18th century and held sway not only over most of the other kingdoms in Yorubaland, but also over nearby African states, notably the Fon people, Fon Kingdom of Dahomey in the modern Republic of Benin on its west. History Legend of origin The legendary origins of the Oyo Empire lie with Ọranyan (also known as Ọranmiyan), the last prince of the Yoruba Kingdom of Ile-Ife (Ife). According to oral traditions, Ọranmiyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amedzofe (history)
In Ewe oral history, Amedzofe (), literally 'origin/home of humanity', is one of the names for Ketu. Ketu, in present-day Benin, was a central place in the history of the Gbe peoples. The Gbe peoples originally were closer to the Yoruba Oyo people of Nigeria Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ..., but they were pressed westward by a series of wars between the 10th and the 13th century. In Ketu, the ancestors of the Gbe-speaking peoples separated themselves from other refugees and began to establish their own identity. See also * Gbe languages: History References History of Benin History of the Yoruba people {{Benin-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketu (Benin)
Ketu is the name of a Yoruba subgroup, historical kingdom and region straddling parts of what is now southeastern Republic of Benin and parts of southwest Nigeria. The chief town and traditional capital of the area was the town of Kétou (Kétu), which is considered to be one of the oldest capitals of the Yoruba-speaking people, tracing its establishment to a settlement founded by a descendant of Oduduwa (also known as; Odùduwà, Oòduà) called Sopasan or Soipasan. The Oba of the town were traditionally styled "Alákétu", and are related directly to Ile-Ife in present-day Nigeria. Other towns that were historically part of the Kétu Kingdom are; * Ilara-Ogudo Yewa – Straddling the Nigeria-Benin international border (Nigerian side) * Ilara Kanga – Straddling the Nigeria-Benin international border (Benin side) * Iwoye ketu – Imeko Afon Local Government, Ogun state, Nigeria * Ewé / Adakplamé – Plateau Department, Benin * Ijoun – Imeko Afon Local Government, O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Togoland
Togoland, officially the Togoland Protectorate (; ), was a protectorate of the German Empire in West Africa from 1884 to 1914, encompassing what is now the nation of Togo and most of what is now the Volta Region of Ghana, approximately 90,400 km2 (29,867 sq mi) in size. During the period known as the "Scramble for Africa", the colony was established in 1884 and was gradually extended inland. At the outbreak of the First World War in 1914, the colony was invaded and quickly overrun by British and French forces during the Togoland campaign and placed under military rule. In 1916 the territory was divided into separate British and French administrative zones, and this was formalised in 1922 with the creation of British Togoland and French Togoland. History The colony was established towards the end of the period of European colonisation in Africa generally known as the "Scramble for Africa". Two separate protectorates were established in 1884. In February 1884, the chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volta Region
Volta Region (or Volta) is one of Ghana's sixteen administrative regions, with Ho designated as its capital. It is located west of Republic of Togo and to the east of Lake Volta. Divided into 25 administrative districts, the region is multi-ethnic and multilingual, including groups such as the Ewe, the Guan, and the Akan people. The Guan peoples include the Lolobi, Likpe, Akpafu, Akyode, Buem, , Avatime, and Nkonya. This region was carved out of the Volta Region in December 2018 by the New Patriotic Party. The people of the Volta Region are popularly known as Voltarians (). This group includes the Ewes, Guans and other minor tribes living in the Volta Region. The people of the Volta Region are popular known for their rich cultural display and music some of which include Agbadza, Borborbor and Zigi. Background The Volta region was formed by the state union of the former British Togoland which had been part of the German protectorate of Togoland. It was admini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse colonization of North America, Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an Age of Discovery, age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, a population of more than 230 million, it is the List of African countries by population, most populous country in Africa, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in Niger–Nigeria border, the north, Chad in Chad–Nigeria border, the northeast, Cameroon in Cameroon–Nigeria border, the east, and Benin in Benin–Nigeria border, the west. Nigeria is a Federation, federal republic comprising 36 States of Nigeria, states and the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria, Federal Capital Territory, where its capital, Abuja, is located. The List of Nigerian cities by population, largest city in Nigeria by population is Lagos, one of the largest List of largest cities, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mono River
The Mono River is the major river of eastern Togo. Approximately long, and draining a basin of about , it rises between the town of Sokodé and the border with Benin, and flows south. Along the southern portion of the river towards its mouth, it forms the Benin-Togo border, international boundary between Togo and Benin. The river drains into the Bight of Benin through an extensive system of brackish water lagoons and lakes, including Lake Togo. Only the part of the river nearest its mouth is navigable. Most of the river's basin on the upper tableland is Tillage, cultivated for maize, yam (vegetable), yams, rice, cotton and cassava. The river is dammed from its mouth by the Nangbeto Dam, a partnership between Benin and Togo completed in 1987. Studies have reported economic benefits from the dam, including tourism and fishing in the lake behind it. The dam's construction displaced between 7,600 and 10,000 people, however, and studies indicate that it has substantially modified th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volta River
The Volta River (, , ) is the main Drainage system (geomorphology), river system in the West African country of Ghana. It flows south into Ghana from the Bobo-Dioulasso Department, Bobo-Dioulasso highlands of Burkina Faso. The three main parts of the river are the Black Volta, the White Volta, and the Red Volta. In the northwest, the Black Volta forms the international borders of the Ivory Coast, Ghana, and Burkina Faso. The Volta flows southward along the Akwapim-Togoland highlands, and empties into the Atlantic Ocean at the Gulf of Guinea at Ada Foah. One of its smaller tributaries, the Oti River, Oti River, enters Ghana from Togo in the east. The Volta River has been dammed at Akosombo for generating hydroelectricity. The reservoir named Lake Volta stretches from Akosombo Dam in the south to the northern part of the country, and is the largest man-made reservoir by area in the world. The country of Burkina Faso was formerly called Republic of Upper Volta, Upper Volta, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |