|
Evolutionary Image Processing
Evolutionary image processing (EIP) is a sub-area of digital image processing. Evolutionary algorithms (EA) are used to optimize and solve various image processing problems. Evolutionary image processing thus represents the combination of evolutionary optimization and digital image processing. EAs have been used for several decades in computer science to optimize various problems. The application in image processing, on the other hand, is still a relatively new field of research. This is primarily due to the technological development of computer systems, as EIP is a relatively computationally intensive process. Evolutionary computer vision (ECV) is an application of EIP for computer vision. It has been shown that genetic programming (GP) as a subclass of EAs is particularly useful for image processing. Genetic programming for image processing In evolutionary image processing, genetic programming optimizes the arrangement of different image-processing operators for specific outputs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Image Processing
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It allows a much wider range of algorithms to be applied to the input data and can avoid problems such as the build-up of Noise (signal processing), noise and distortion during processing. Since images are defined over two dimensions (perhaps more), digital image processing may be modeled in the form of Multidimensional system, multidimensional systems. The generation and development of digital image processing are mainly affected by three factors: first, the development of computers; second, the development of mathematics (especially the creation and improvement of discrete mathematics, discrete mathematics theory); and third, the demand for a wide range of applications in environment, agriculture, military, industry and medical science has incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Algorithms
Evolutionary algorithms (EA) reproduce essential elements of the biological evolution in a computer algorithm in order to solve "difficult" problems, at least Approximation, approximately, for which no exact or satisfactory solution methods are known. They belong to the class of Metaheuristic, metaheuristics and are a subset of Population Based Bio-Inspired Algorithms, population based bio-inspired algorithms and evolutionary computation, which itself are part of the field of computational intelligence. The mechanisms of biological evolution that an EA mainly imitates are reproduction, mutation, genetic recombination, recombination and natural selection, selection. Candidate solutions to the optimization problem play the role of individuals in a population, and the fitness function determines the quality of the solutions (see also loss function). Evolution of the population then takes place after the repeated application of the above operators. Evolutionary algorithms often perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Programming
Genetic programming (GP) is an evolutionary algorithm, an artificial intelligence technique mimicking natural evolution, which operates on a population of programs. It applies the genetic operators selection (evolutionary algorithm), selection according to a predefined fitness function, fitness measure, mutation (evolutionary algorithm), mutation and crossover (evolutionary algorithm), crossover. The crossover operation involves swapping specified parts of selected pairs (parents) to produce new and different offspring that become part of the new generation of programs. Some programs not selected for reproduction are copied from the current generation to the new generation. Mutation involves substitution of some random part of a program with some other random part of a program. Then the selection and other operations are recursively applied to the new generation of programs. Typically, members of each new generation are on average more fit than the members of the previous gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolutional Neural Network
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of feedforward neural network that learns features via filter (or kernel) optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different types of data including text, images and audio. Convolution-based networks are the de-facto standard in deep learning-based approaches to computer vision and image processing, and have only recently been replaced—in some cases—by newer deep learning architectures such as the transformer. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by the regularization that comes from using shared weights over fewer connections. For example, for ''each'' neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded ''convolution'' (or cross-correlation) kernels, only 25 weights for each convolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
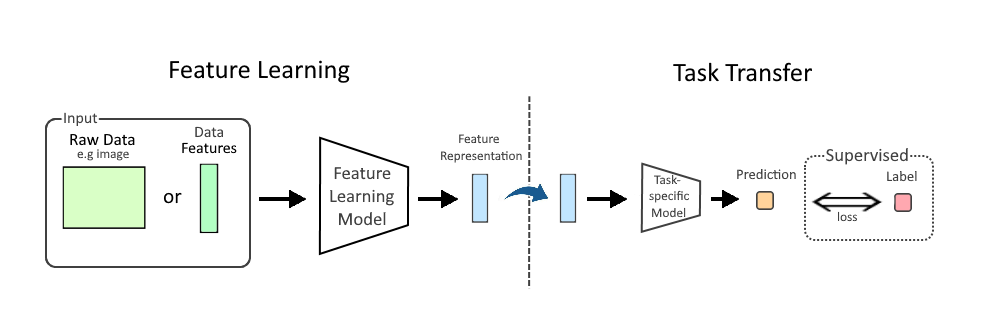
Feature Learning
In machine learning (ML), feature learning or representation learning is a set of techniques that allow a system to automatically discover the representations needed for feature detection or classification from raw data. This replaces manual feature engineering and allows a machine to both learn the features and use them to perform a specific task. Feature learning is motivated by the fact that ML tasks such as classification often require input that is mathematically and computationally convenient to process. However, real-world data, such as image, video, and sensor data, have not yielded to attempts to algorithmically define specific features. An alternative is to discover such features or representations through examination, without relying on explicit algorithms. Feature learning can be either supervised, unsupervised, or self-supervised: * In supervised feature learning, features are learned using labeled input data. Labeled data includes input-label pairs where the inp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Detection
Object detection is a computer technology related to computer vision and image processing that deals with detecting instances of semantic objects of a certain class (such as humans, buildings, or cars) in digital images and videos. Well-researched domains of object detection include face detection and pedestrian detection. Object detection has applications in many areas of computer vision, including image retrieval and video surveillance. Uses It is widely used in computer vision tasks such as image annotation, vehicle counting, activity recognition, face detection, face recognition, video object co-segmentation. It is also used in tracking objects, for example tracking a ball during a football match, tracking movement of a cricket bat, or tracking a person in a video. Often, the test images are sampled from a different data distribution, making the object detection task significantly more difficult. To address the challenges caused by the domain gap between training and test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Genetic Algorithm Applications
This is a list of genetic algorithm (GA) applications. Natural Sciences, Mathematics and Computer Science * Bayesian inference links to particle methods in Bayesian statistics and hidden Markov chain models * Computational creativity, Artificial creativity * Chemical kineticsgasansolidphases) * Calculation of bound states and local-density approximations * Code-breaking, using the GA to search large solution spaces of ciphers for the one correct decryption. * Computer architecture: using GA to find out weak links in approximate computing such as Combinatorial search#Lookahead, lookahead. * Configuration applications, particularly physics applications of optimal molecule configurations for particular systems like C60 (Fullerene, buckyballs) * Construction of facial composites of suspects by Witness, eyewitnesses in forensic science. * Data Center/Server Farm. * Distributed computer network topologies * Electronic circuit design, known as evolvable hardware * Evolutionary image proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applications Of Evolutionary Algorithms
Application may refer to: Mathematics and computing * Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks ** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a communications network * Function application, in mathematics and computer science Processes and documents * Application for employment, a form or forms that an individual seeking employment must fill out * College application, the process by which prospective students apply for entry into a college or university * Patent application, a document filed at a patent office to support the grant of a patent Other uses * Application (virtue), a characteristic encapsulated in diligence * Topical application, the spreading or putting of medication to body surfaces See also * * Apply In mathematics and computer science, apply is a function that applies a function to arguments. It is central to programming languages derived from lambda calcul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |