|
Eve's Footprint
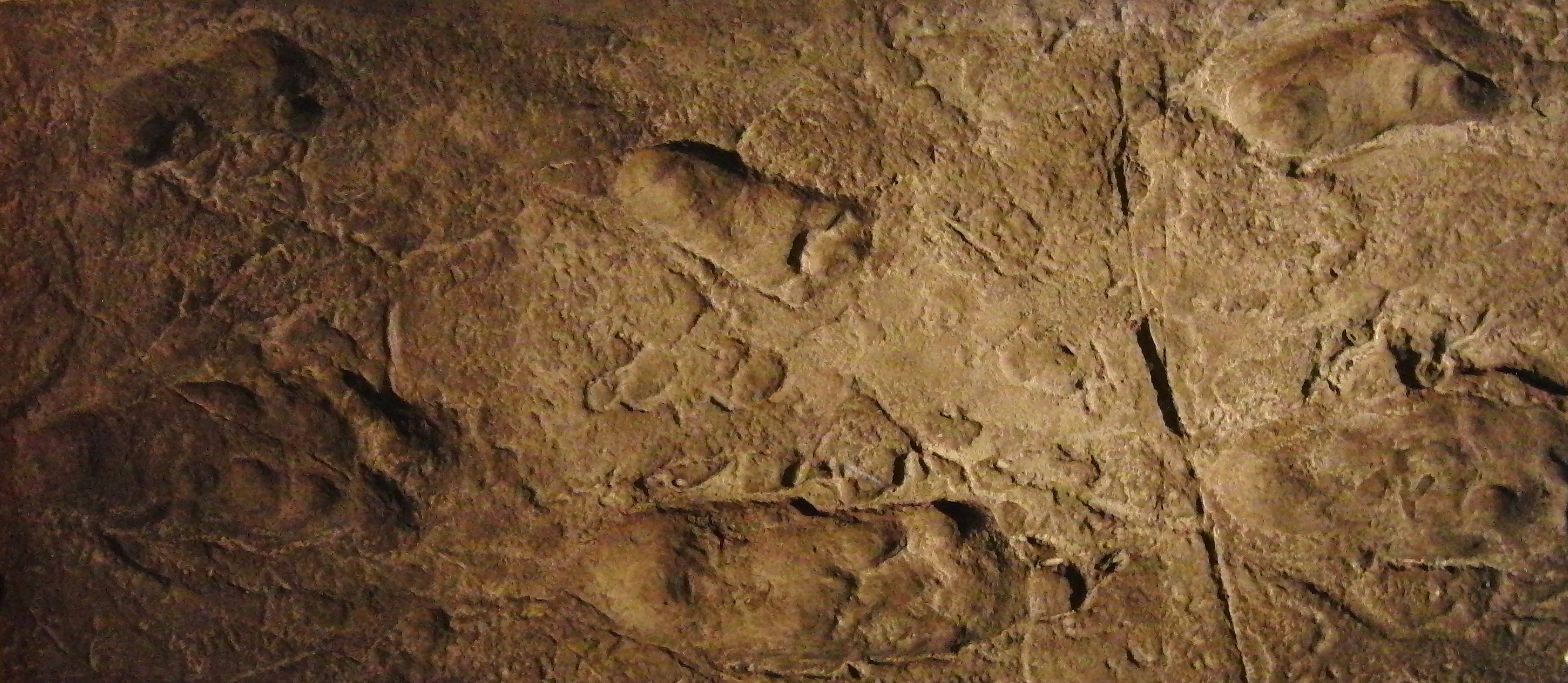
Eve's footprint is the popular name for a set of fossilized footprints discovered on the shore of Langebaan Lagoon, South Africa in 1995. They are thought to be those of a female human and have been dated to approximately 117,000 years ago. This makes them the oldest known footprints of an anatomically-modern human. The estimated age of Eve's footprint means that the individual who left the tracks in the soil, thought to be female, would have lived within the current wide range of estimates for the date of Mitochondrial Eve. History The three footprints were found in 1995 by geologist David Roberts from the Council for Geoscience and announced at a press conference with paleoanthropologist Lee R. Berger of the University of the Witwatersrand at Johannesburg, South Africa, at the National Geographic Society in Washington, D.C. The discovery was documented in the August, 1997, issue of the '' South African Journal of Science''. Berger and Roberts say the prints were made on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eve Footprints Replica
Eve (; ; ar, حَوَّاء, Ḥawwāʾ; el, Εὕα, Heúa; la, Eva, Heva; Syriac language, Syriac: romanized: ) is a figure in the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible. According to the origin story, "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop through oral traditions and therefore typically have multiple versions." of the Abrahamic religions, she was the Protoplast (religion), first woman, yet some debate within Judaism has also given that position to Lilith. Eve is known also as Adam's wife. According to the second chapter of Genesis, Eve was created by God in Abrahamic religions, God (Yahweh) by taking her from the rib of Adam, to be Adam's companion. Adam is charged with guarding and keeping the garden before her creation; she is not present when God commands Adam Taboo#In religion and mythology, not to eat the forbidden fruit – although it is clear that she was aware of the command. She decide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
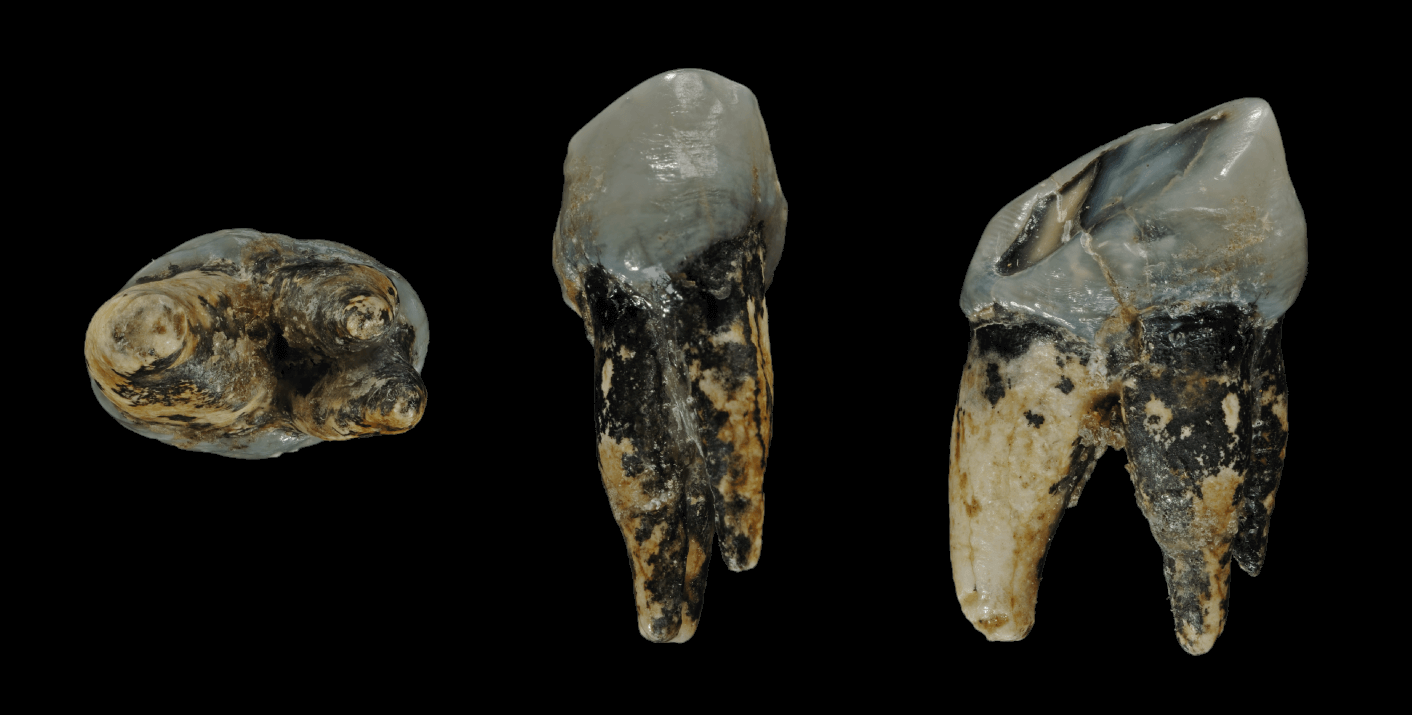
List Of Human Evolution Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of Hominini, hominin fossils and Skeleton, remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the Chimpanzee–human last common ancestor, human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hominidae
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the eastern and western gorilla); '' Pan'' (the chimpanzee and the bonobo); and ''Homo'', of which only modern humans remain. Several revisions in classifying the great apes have caused the use of the term ''"hominid"'' to vary over time. The original meaning of "hominid" referred only to humans (''Homo'') and their closest extinct relatives. However, by the 1990s humans, apes, and their ancestors were considered to be "hominids". The earlier restrictive meaning has now been largely assumed by the term ''"hominin"'', which comprises all members of the human clade after the split from the chimpanzees (''Pan''). The current meaning of "hominid" includes all the great apes including humans. Usage still varies, however, and some scientists and la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laetoli
Laetoli is a pre-historic site located in Enduleni ward of Ngorongoro District in Arusha Region, Tanzania. The site is dated to the Plio-Pleistocene and famous for its Hominina footprints, preserved in volcanic ash. The site of the Laetoli footprints (Site G) is located 45 km south of Olduvai gorge. The location and tracks were discovered by archaeologist Mary Leakey and her team in 1976, and were excavated by 1978. Based on analysis of the footfall impressions "The Laetoli Footprints" provided convincing evidence for the theory of bipedalism in Pliocene Hominina and received significant recognition by scientists and the public. Since 1998, paleontological expeditions have continued under the leadership of Amandus Kwekason of the National Museum of Tanzania and Terry Harrison of New York University, leading to the recovery of more than a dozen new Hominina finds, as well as a comprehensive reconstruction of the paleoecology. The site is a registered National Historic Sites of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
) , national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"() , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Nairobi , coordinates = , largest_city = Nairobi , official_languages = Constitution (2009) Art. 7 ational, official and other languages"(1) The national language of the Republic is Swahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are Swahili and English. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities." , languages_type = National language , languages = Swahili , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2019 census , religion = , religion_year = 2019 census , demonym = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor'' — with the former generally considered to have been the ancestor to Neanderthals, Denisovans, and modern humans — appear to have evolved from ''H. erectus''. Its specimens are among the first recognizable members of the genus ''Homo''. ''H. erectus'' was the first human ancestor to spread throughout Eurasia, with a continental range extending from the Iberian Peninsula to Java. Asian populations of ''H. erectus'' may be ancestral to '' H. floresiensis'' and possibly to '' H. luzonensis''. The last known population of ''H. erectus'' is '' H. e. soloensis'' from Java, around 117,000–108,000 years ago. ''H. erectus'' had a more modern gait and body proportions, and was the first human species to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileret
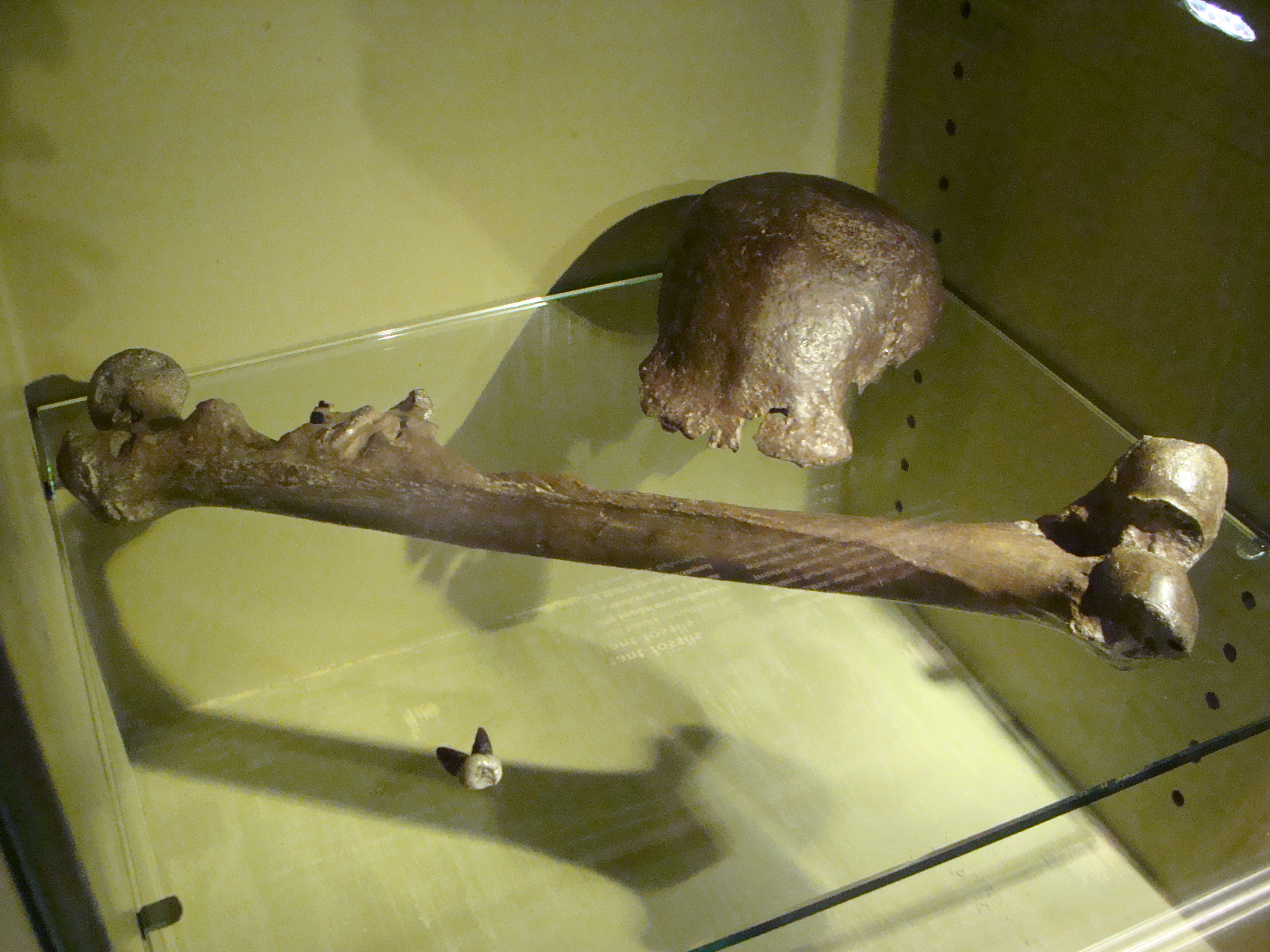
Ileret (also spelled Illeret) is a village in Marsabit County, Kenya. It is located in Northern Kenya, on the eastern shore of Lake Turkana, north of Sibiloi National Park and near the Ethiopian border. Numerous hominin fossils have been found near Ileret, including ''Homo erectus'' footprints dating back to about 1.5 million years ago, making them the second oldest hominin footprints ever found after those at Laetoli, Tanzania. Hominin fossils found near Ileret Besides the ''Homo erectus'' footprints, numerous other fossils have been found near the Ileret site. In 2012–2013, a team of researchers from Stony Brook University found new hominin fossils near Ileret, in two sites within the Kolom Odiet area. The fossils were representative of three different individuals, composing of two partial skeletons – KNM-ER ( Kenya National Museum – East Rudolf) 64061 and KNM-ER 64062 – and an almost entirely completed mandible, KNM-ER 64060. KNM-ER 64060 and KNM-ER 64061 date b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happisburgh Footprints
The Happisburgh footprints were a set of fossilized hominid footprints that date to the early Pleistocene, over 800,000 years ago. They were discovered in May 2013 in a newly uncovered sediment layer of the Cromer Forest Bed on a beach at Happisburgh in Norfolk, England, and carefully photographed in 3D before being destroyed by the tide shortly afterwards. Results of research on the footprints were announced on 7 February 2014 and identified them as the oldest known hominid footprints outside Africa.Ashton N, Lewis SG, De Groote I, Duffy SM, Bates M, et al. (201"Hominin Footprints from Early Pleistocene Deposits at Happisburgh, UK" ''PLoS ONE'' 9(2): e88329. Before the Happisburgh discovery, the oldest known footprints in Britain were at Uskmouth in South Wales, from the Mesolithic and carbon-dated to 4,600 BCE. The oldest known hominin footprints in Europe were the Ciampate del Diavolo tracks found at the Roccamonfina volcano in Italy, dated to around 350,000 years ago. Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. , it was estimated to be the second largest city in Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English. Originally inhabited by various indigenous cultures since ancient times, the region was conquered by the Spanish Empire in the 16th century. Nicaragua gained independence from Spain in 1821. The Mosquito Coast followed a different historical path, being colonized by the English in the 17th century and later coming under British rule. It became an autonomous territory of Nicaragua in 1860 and its northernmost part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Managua
Lake Managua ( es, Lago de Managua, ), also known as Lake Xolotlán (), is a lake in Nicaragua. At 1,042 km², it is approximately long and wide. Similarly to the name of Lake Nicaragua, its other name comes from the Nahuatl language, possibly from the Spanish Tlaxcalan and Mexica allies or the Nawat Nicarao that were already there in today Rivas Department. The city of Managua, the capital of Nicaragua, lies on its southwestern shore. Islands There are two uninhabited lake islands: * , a volcanic island. There is another nearby volcano, on the mainland: Momotombo. * Isla Rosa, an islet Floodings The level of Lake Managua raises significantly during the periods of heavy rain. The highest water level was recorded during the flooding of 1933. The lake rose 3 metres (10 ft) in five days during Hurricane Mitch in 1998, destroying the homes of many who lived on its edge. An even higher flooding occurred in September/October 2010. Since then, the city has prohibited re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Footprints Of Acahualinca
The Ancient footprints of Acahualinca (; es, Huellas de Acahualinca) exist in Managua, Nicaragua near the southern shore of Lake Managua. The region was once called "El Cauce". The tracks are fossil Late Holocene human footprints left behind in volcanic ash and mud, which solidified about 2,120±120 years ago, shortly after the group of up to 15 people passed by. It is sometimes reported that the people were running to escape from a volcanic explosion, but the distance between the footprints indicates a walking gait. Fossilized footprints of several animals are also present, but the fact that they intersect the human footprints shows they were not traveling with the people. Scientific analysis of the footprints In 1874, construction workers discovered the footprints. The United States medical doctor and archaeological collector, Earl Flint, brought the footprints to the attention of the international science community and media in 1884. The Carnegie Institution of Washington b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as "red ochre" (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. * Yellow ochre, , is a hydrated iron hydroxide (limonite) also called gold ochre. * Red ochre, , takes its reddish colour from the mineral hematite, which is an anhydrous iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |