|
Evaporating Cloud
The Evaporating Cloud is one of the six Thinking Processes in the Theory of Constraints. The Evaporating Cloud (EC) - also referred to in the literature as "the cloud", or as a "conflict resolution diagram" - is a logical diagram representing a problem that has no obvious satisfactory solution.Fedurko, Jelena. Behind the cloud: Enhancing logical thinking. TOC Strategic Solutions Ltd (2011) Overview The most commonly used of the TOC tools, the EC was designed to address conflict or dilemma situations (trade-off situations where there is no acceptable compromise) by diagramming the logic behind the conflict and methodically examining the assumptions behind the logic. The EC has a set format with five boxes, labelled A, B, C, D, D’, that are usually laid out as follows:Victoria J. Mabin, Steve Forgeson and Lawrence Green. Harnessing resistance: using the theory of constraints to assist change management. Journal of European Industrial Training. 25/2/3/4 001168±191 ← ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinking Processes (Theory Of Constraints)
The thinking processes in Eliyahu M. Goldratt's theory of constraints are the five methods to enable the focused improvement of any cognitive system (especially business systems). Purpose The purpose of the thinking processes is to help answer questions essential to achieving focused improvement: # ''What to change?'' # ''What to change it into?'' # ''How to cause the change?'' Sometimes two other questions are considered as well: ''Why change?'' and: ''How to maintain the process of ongoing improvement (POOGI)?'' A more thorough rationale is presented in ''What is this thing called theory of constraints and how should it be implemented''. A more thorough work, mapping the use and evolution of the Thinking Processes, was conducted by Mabin et al. Processes The primary thinking processes, as codified by Goldratt and others: * Current_reality_tree_(theory_of_constraints), Current reality tree (CRT, similar to the current state map used by many organizations) — evaluates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilemma
A dilemma ( grc-gre, δίλημμα "double proposition") is a problem offering two possibilities, neither of which is unambiguously acceptable or preferable. The possibilities are termed the ''horns'' of the dilemma, a clichéd usage, but distinguishing the dilemma from other kinds of predicament as a matter of usage. Terminology The term ''dilemma'' is attributed by Gabriel Nuchelmans to Lorenzo Valla in the 15th century, in later versions of his logic text traditionally called ''Dialectica''. Valla claimed that it was the appropriate Latin equivalent of the Greek ''dilemmaton''. Nuchelmans argued that his probable source was a logic text of c.1433 of George of Trebizond. He also concluded that Valla had reintroduced to the Latin West a type of argument that had fallen into disuse. Valla's neologism did not immediately take hold, preference being given to the established Latin term ''complexio'', used by Cicero, with ''conversio'' applied to the upsetting of dilemmatic reason ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporating Cloud - Overview
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidity affects rate of evaporation of water. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling. On average, only a fraction of the molecules in a liquid have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid. The evaporation will continue until an equilibrium is reached when the evaporation of the liquid is equal to its condensation. In an enclosed environment, a liquid will evaporate until the surrounding air is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Bach
Richard David Bach (born June 23, 1936) is an American writer. He has written numerous works of fiction and also non-fiction flight-related titles. His works include ''Jonathan Livingston Seagull'' (1970) and '' Illusions: The Adventures of a Reluctant Messiah'' (1977), both of which were among the 1970s' biggest sellers. Most of Bach's books have been semi-autobiographical, using actual or fictionalized events from his life to illustrate his philosophy. His books espouse his philosophy that our apparent physical limits and mortality are merely appearance. Bach is noted for his love of aviation and for his books related to flying in a metaphorical context. He has flown as a hobby since the age of 17. In late August 2012, Bach was severely injured when on approach to landing at Friday Harbor, Washington, his aircraft clipped some power lines and crashed upside down in a field. Early life Bach was born in Oak Park, Illinois, to Roland R. and Ruth Shaw Bach. His father was an Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illusions (Bach Novel)
''Illusions: The Adventures of a Reluctant Messiah'' is a novel by writer and pilot Richard Bach. First published in 1977, the story questions the reader's view of reality, proposing that what we call reality is merely an illusion we create for learning and enjoyment. ''Illusions'' was the author's follow-up to 1970's ''Jonathan Livingston Seagull''. Plot ''Illusions'' revolves around two barnstorming pilots who meet in a field in the Midwestern United States. The two main characters enter into a teacher-student relationship that explains the concept that the world that we inhabit is illusory, as well as the underlying reality behind it: Donald William Shimoda is a messiah who quits his job after deciding that people value the showbiz-like performance of miracles and want to be entertained by those miracles more than to understand the message behind them. He meets Richard, a fellow barnstorming pilot. Both are in the business of providing short rides—for a few dollars eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
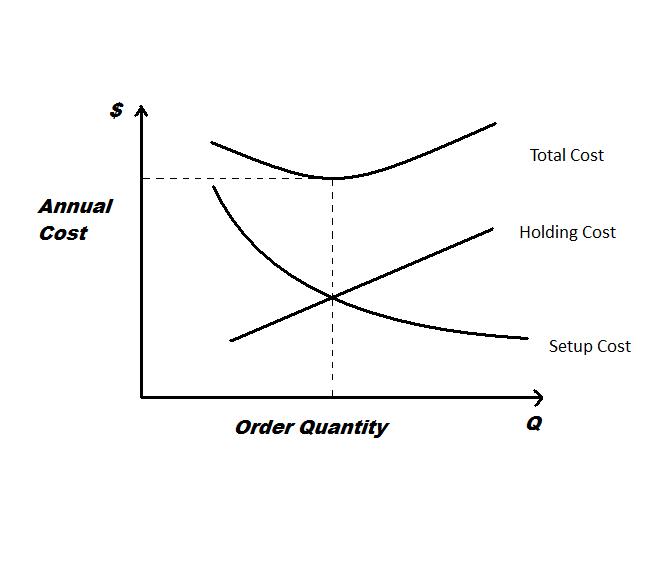
Economic Production Quantity
The economic production quantity model (also known as the EPQ model) determines the quantity a company or retailer should order to minimize the total inventory costs by balancing the inventory holding cost and average fixed ordering cost. The EPQ model was developed by E.W. Taft in 1918. This method is an extension of the economic order quantity model (also known as the EOQ model). The difference between these two methods is that the EPQ model assumes the company will produce its own quantity or the parts are going to be shipped to the company while they are being produced, therefore the orders are available or received in an incremental manner while the products are being produced. While the EOQ model assumes the order quantity arrives complete and immediately after ordering, meaning that the parts are produced by another company and are ready to be shipped when the order is placed. In some literature, "economic manufacturing quantity" model (EMQ) is used for "economic productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporating Cloud Example
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidity affects rate of evaporation of water. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling. On average, only a fraction of the molecules in a liquid have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid. The evaporation will continue until an equilibrium is reached when the evaporation of the liquid is equal to its condensation. In an enclosed environment, a liquid will evaporate until the surrounding air is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Reality Tree (Theory Of Constraints)
One of the thinking processes in the theory of constraints, a current reality tree (CRT) is a tool to analyze many systems or organizational problems at once. By identifying root causes common to most or all of the problems, a CRT can greatly aid focused improvement of the system. A current reality tree is a directed graph. Simplified explanation A CRT is a focusing procedure formulated by Eliyahu Goldratt, developer of the theory of constraints. This process is intended to help leaders gain understanding of cause and effect in a situation they want to improve. It treats multiple problems in a system as symptoms arising from one or a few ultimate root causes or systemic core problems. It describes, in a visual (cause-and-effect network) diagram, the main perceived symptoms (along with secondary or hidden ones that lead up to the perceived symptoms) of a problem scenario and ultimately the apparent root causes or core conflict. The benefit of building a CRT is that it identifies the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Decision Program Chart
Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC) is a technique designed to help prepare contingency plans. The emphasis of the PDPC is to identify the consequential impact of failure on activity plans, and create appropriate contingency plans to limit risks. Process diagrams and planning tree diagrams are extended by a couple of levels when the PDPC is applied to the bottom level tasks on those diagrams. Methodology From the bottom level of some activity box, the PDPC adds levels for: # identifying what can go wrong (failure mode or risks) # consequences of that failure (effect or consequence) # possible countermeasures (risk mitigation action plan)http://site.iugaza.edu.ps/aschokry/files/2010/02/7_Tools.pdf Similar techniques * The PDPC is similar to the failure mode and effects analysis Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA; often written with "failure modes" in plural) is the process of reviewing as many components, assemblies, and subsystems as possible to identify potential failu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)