|
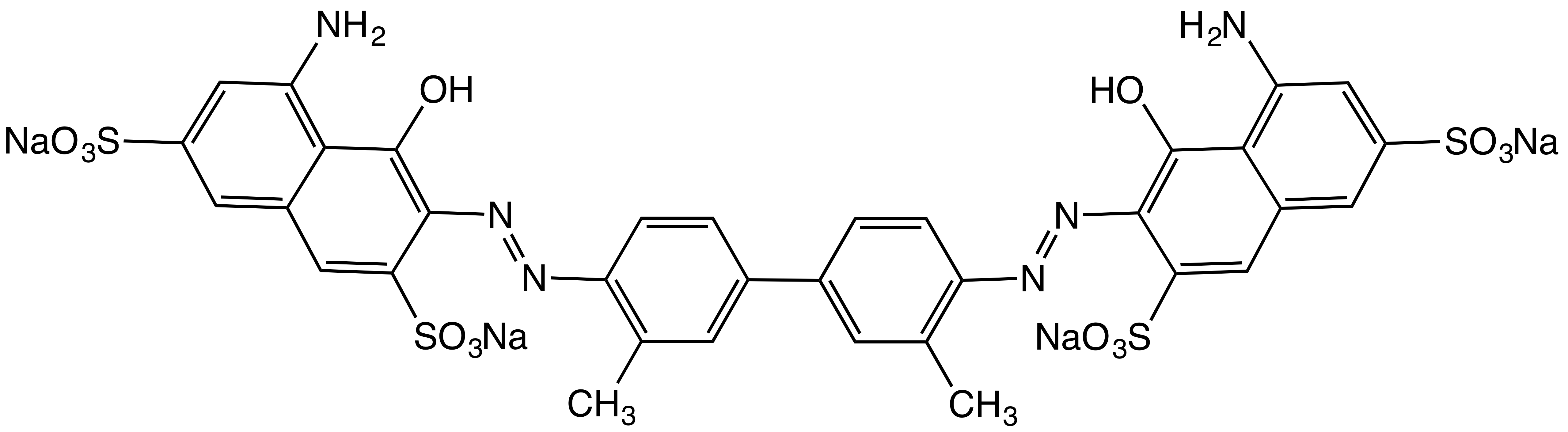
Evans Blue (dye)
T-1824 or Evans blue, often incorrectly rendered as Evan's blue, is an azo dye that has a very high affinity for serum albumin. Because of this, it can be useful in physiology in estimating the proportion of body water contained in blood plasma. It fluoresces with excitation peaks at 470 and 540 nm and an emission peak at 680 nm. Evans blue dye has been used as a viability assay on the basis of its penetration into non-viable cells, although the method is subject to error because it assumes that damaged or otherwise altered cells are not capable of repair and therefore are not viable. Evans blue is also used to assess the permeability of the blood–brain barrier to macromolecules. Because serum albumin cannot cross the barrier and virtually all Evans blue is bound to albumin, normally the neural tissue remains unstained. When the blood–brain barrier has been compromised, albumin-bound Evans blue enters the CNS. Evans blue is pharmacologically active, acting as a neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Dye
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes called "disazo dyes" contain two azo groups, some dyes called "trisazo dyes" contain three azo groups and are or more. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuptake Inhibitor
Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal (i.e., the pre-synaptic neuron at a synapse) or glial cell after it has performed its function of transmitting a neural impulse. Reuptake is necessary for normal synaptic physiology because it allows for the recycling of neurotransmitters and regulates the level of neurotransmitter present in the synapse, thereby controlling how long a signal resulting from neurotransmitter release lasts. Because neurotransmitters are too large and hydrophilic to diffuse through the membrane, specific transport proteins are necessary for the reabsorption of neurotransmitters. Much research, both biochemical and structural, has been performed to obtain clues about the mechanism of reuptake. Protein structure The first primary sequence of a reuptake protein was published in 1990. The technique for protein sequence determination relied upon the purification, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kainate Receptor Antagonists
Kainic acid, or kainate, is an acid that naturally occurs in some seaweed. Kainic acid is a potent neuroexcitatory amino acid agonist that acts by activating receptors for glutamate, the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glutamate is produced by the cell's metabolic processes and there are four major classifications of glutamate receptors: NMDA receptors, AMPA receptors, kainate receptors, and the metabotropic glutamate receptors. Kainic acid is an agonist for kainate receptors, a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. Kainate receptors likely control a sodium channel that produces excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) when glutamate binds. Kainic acid is commonly injected into laboratory animal models to study the effects of experimental ablation. Kainic acid is a direct agonist of the glutamic kainate receptors and large doses of concentrated solutions produce immediate neuronal death by overstimulating neurons to death. Such damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Dyes
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes called "disazo dyes" contain two azo groups, some dyes called "trisazo dyes" contain three azo groups and are or more. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMPA Receptor Antagonists
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid, better known as AMPA, is a compound that is a specific agonist for the AMPA receptor, where it mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter glutamate. There are several types of glutamatergic ion channels in the central nervous system including AMPA, kainic acid and ''N''-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) channels. In the synapse, these receptors serve very different purposes. AMPA can be used experimentally to distinguish the activity of one receptor from the other in order to understand their differing functions. AMPA generates fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP). AMPA activates AMPA receptors that are non-selective cationic channels allowing the passage of Na+ and K+ and therefore have an equilibrium potential near 0 mV. AMPA was first synthesized, along with several other ibotenic acid derivatives, by Krogsgaard-Larsen, Honoré, and others toward differentiating glutamate sensitive receptors from aspartate sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary
''Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary'' is an encyclopedic medical dictionary published by F.A. Davis Company since 1940 by Clarence Wilbur Taber. ''Taber's'' is a recommended medical reference book for libraries and attorneys. It is available in print, online, and in multiple mobile device A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physica ... formats. The 23rd edition, published in 2017, contains more than 65,000 entries and over 1,200 images. References Medical dictionaries {{med-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert McLean Evans
Herbert McLean Evans (September 23, 1882 – March 6, 1971) was an American anatomist and embryologist best known for co-discovering Vitamin E. Education He was born in Modesto, California. In 1908, he obtained his medical degree from Johns Hopkins University. Career Evans became associate professor of anatomy at Johns Hopkins University. Evans moved back to California in 1915 and was made professor of anatomy at the University of California, Berkeley, and held that position until his death. His medical research at Berkeley addressed problems relating to human nutrition, endocrinology, embryology, and histology. In 1918, his research into the number of human chromosomes led him to believe the number to be 48, when most people assumed the number to be much higher. It was only later discovered that the correct figure was 46. Evans had much greater success however with hormones extracted from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. He isolated Human Growth Hormone, which is ess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P2 Receptor
P2 receptor may refer to: Nucleotides if get released into the extracellular environment can lead to cell death or some other harmful cellular consequences. To avoid harm nucleotides should be neutralized, which is accomplished by P2 receptors. Almost every cell type expresses P2 receptors. Purinergic signalling also has a pathophysiological role in several immune cells including calcium mobilization, actin polymerization, chemotaxis, the release of mediators, cell maturation, cytotoxicity, and cell death etc. Depending on the nature of the receptor they are found to be of two types: *P2Y receptors (metabotropic) *P2X receptors (ionotropic) P is for purinergic, P2 refers to ATP receptors, as opposed to P1 adenosine adenosine receptors. P2X receptors are ATP activated channels that allow the passage of ions across cell membranes. P2Y receptors are ATP activated G protein-coupled receptor G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitatory Amino-acid Transporter
Glutamate transporters are a family of neurotransmitter transporter proteins that move glutamate – the principal excitatory neurotransmitter – across a membrane. The family of glutamate transporters is composed of two primary subclasses: the excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) family and vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT) family. In the brain, EAATs remove glutamate from the synaptic cleft and extrasynaptic sites via glutamate reuptake into glial cells and neurons, while VGLUTs move glutamate from the cell cytoplasm into synaptic vesicles. Glutamate transporters also transport aspartate and are present in virtually all peripheral tissues, including the heart, liver, testes, and bone. They exhibit stereoselectivity for L-glutamate but transport both L-aspartate and D-aspartate. The EAATs are membrane-bound secondary transporters that superficially resemble ion channels. These transporters play the important role of regulating concentrations of glutamate in the extracell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kainate Receptor
Kainate receptors, or kainic acid receptors (KARs), are ionotropic receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter glutamate. They were first identified as a distinct receptor type through their selective activation by the agonist kainate, a drug first isolated from the algae Digenea simplex. They have been traditionally classified as a non-NMDA-type receptor, along with the AMPA receptor. KARs are less understood than AMPA and NMDA receptors, the other ionotropic glutamate receptors. Postsynaptic kainate receptors are involved in excitatory neurotransmission. Presynaptic kainate receptors have been implicated in inhibitory neurotransmission by modulating release of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA through a presynaptic mechanism. Structure There are five types of kainate receptor subunits, GluR5 (), GluR6 (), GluR7 (), KA1 () and KA2 (), which are similar to AMPA and NMDA receptor subunits and can be arranged in different ways to form a tetramer, a four subunit rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Albumin
Serum albumin, often referred to simply as blood albumin, is an albumin (a type of globular protein) found in vertebrate blood. Human serum albumin is encoded by the ''ALB'' gene. Other mammalian forms, such as bovine serum albumin, are chemically similar. Serum albumin is produced by the liver, occurs dissolved in blood plasma and is the most abundant blood protein in mammals. Albumin is essential for maintaining the oncotic pressure needed for proper distribution of body fluids between blood vessels and body tissues; without albumin, the high pressure in the blood vessels would force more fluids out into the tissues. It also acts as a plasma carrier by non-specifically binding several hydrophobic steroid hormones and as a transport protein for hemin and fatty acids. Too much or too little circulating serum albumin may be harmful. Albumin in the urine usually denotes the presence of kidney disease. Occasionally albumin appears in the urine of normal persons following long period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMPA Receptor
The α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (also known as AMPA receptor, AMPAR, or quisqualate receptor) is an ionotropic receptor, ionotropic transmembrane receptor for glutamate (iGluR) that mediates fast synapse, synaptic transmission in the central nervous system (CNS). It has been traditionally classified as a non-NMDA_receptor, NMDA-type receptor, along with the kainate receptor. Its name is derived from its ability to be activated by the artificial glutamate analog AMPA. The receptor was first named the "quisqualate receptor" by Watkins and colleagues after a naturally occurring agonist quisqualic acid, quisqualate and was only later given the label "AMPA receptor" after the selective agonist developed by Tage Honore and colleagues at the Royal Danish School of Pharmacy in Copenhagen. The ''GRIA2''-encoded AMPA receptor ligand binding core (GluA2 LBD) was the first glutamate receptor ion channel domain to be protein crystal, crystallized. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |