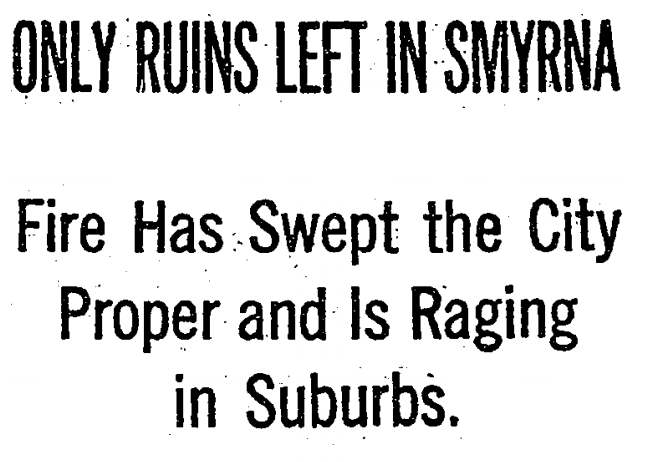|
Evangelical School Of Smyrna
The Evangelical School ( el, Ευαγγελική Σχολή) was a Greek educational institution established in 1733 in Smyrna, Ottoman Empire, now Izmir, Turkey. The school, initially an Orthodox Church-approved institution, attracted major figures of the Modern Greek Enlightenment. During the late 19th-early 20th century it became the most important Greek school in the city, possessing an archaeological museum, a natural science collection and a library, which contained some 50,000 volumes and 180 manuscripts. The Evangelical School ceased its operation in 1922 as a result of the Liberation of Izmir from Greek occupation. Early years and Greek Enlightenment The school originated as a church approved institution and was established after the efforts of the local Greek Orthodox bishop. It was originally known as ''Greek School'' ( el, Ελληνικό Φροντιστήριο), while its name changed several times during the 18th century.Augustinos (1992)p. 159/ref> Finally, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639m to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic Islands, Saronic islands and the North Aegean islands, North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Katounakiotis
Saint Daniel Katounakiotis of Smyrna ( el, Δανιήλ Κατουνακιώτης ο Σμυρναίος, also known as Daniel of Katounakia; born Dimitrios Dimitriadis, el, Δημήτριος Δημητριάδης) (Smyrna, 1846 – Mount Athos, 8 September 1929) was a Greek Orthodox monk who lived on Mount Athos. He was canonized as a saint by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople in 2020. His feast is commemorated on September 7. Today, he is known as the founder of the , which is still currently located in Katounakia at the southernmost tip of the Athos peninsula. Early years He was born in Smyrna (now İzmir in western Turkey) in 1846. He was the youngest son of a large family and graduated with honors from the Evangelical School of Smyrna, the educational institution of the Greek community of Smyrna. When he was 19, desiring to become a monk, he visited various monasteries in Peloponnesia and on the islands of Hydra, Tinos, Paros, and Ikaria, where he met variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicodemus The Hagiorite
Nicodemus the Hagiorite or Nicodemus of the Holy Mountain ( el, Ὅσιος Νικόδημος ὁ Ἁγιορείτης; 1749 – July 14, 1809) is a saint of the Eastern Orthodox Church. He was an ascetic monk, mystic, theologian, and philosopher. His life's work was a revival of traditional Christian practices and patristic literature. He wrote ascetic prayer literature and influenced the rediscovery of hesychasm, a method of contemplative prayer from the Byzantine period. He is most famous for his work with Macarius of Corinth on the anthology of monastic spiritual writings known as '' The Philokalia'', as well as for his compilation of canons known as the ''Pedalion'' (or ''The Rudder'') which he co-wrote with a hieromonk named Agapios Monachos. With Macarios of Corinth, Nicodemus was responsible for the compilation and publishing of The Evergetinos, thoroughly reviewing a vast collection of materials from a number of other collections of sayings of monastics and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambrosios Pleianthidis
Ambrosios Pleiathidis ( el, Αμβρόσιος Πλειανθίδης, 1872–1922) also known as Ambrosios of Moschonisia was the Greek Orthodox metropolitan bishop of Moschonisia, in modern Turkey, from February to September 1922. He was executed by the Turkish Army at the end of the Greco-Turkish War (1919-1922). He is commemorated by the Greek Orthodox Church as Hieromartyr ( el, ιερομάρτυρας) and his feast day is celebrated on the Sunday before the Exaltation of the Holy Cross each year (September 7–13). Life Ambrosios was born in Smyrna (modern Izmir), in the Aidin Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire, in 1872. He graduated from the Evangelical School of his home town at 1893. After his graduation Ambrosios became an archdeacon in the nearby metropolis of Heliopolis and Thyateira, based in Aydın. He continued his studies and in 1895 he attended the Theolodigal Academy of Kiev and then he became a priest in the Greek community of Feodosiya in Crimea. In 1910 Ambro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish People
The Turkish people, or simply the Turks ( tr, Türkler), are the world's largest Turkic ethnic group; they speak various dialects of the Turkish language and form a majority in Turkey and Northern Cyprus. In addition, centuries-old ethnic Turkish communities still live across other former territories of the Ottoman Empire. Article 66 of the Turkish Constitution defines a "Turk" as: "Anyone who is bound to the Turkish state through the bond of citizenship." While the legal use of the term "Turkish" as it pertains to a citizen of Turkey is different from the term's ethnic definition, the majority of the Turkish population (an estimated 70 to 75 percent) are of Turkish ethnicity. The vast majority of Turks are Muslims and follow the Sunni and Alevi faith. The ethnic Turks can therefore be distinguished by a number of cultural and regional variants, but do not function as separate ethnic groups. In particular, the culture of the Anatolian Turks in Asia Minor has underlied and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nea Smyrni
Nea Smyrni ( el, Νέα Σμύρνη, ''Néa Smýrni'', "New Smyrna") is a municipality in South Athens, Greece. At the 2011 census, it had 73,076 inhabitants. It was named after İzmir in Turkey, which Greek's called it as Smyrna, whence many refugees arrived and settled in the Nea Smyrni area following the 1922 catastrophe of Asia Minor and the Great fire of Smyrna, as a result of the Greco-Turkish war. History Although there are few details about the ancient history of the area, in 2012, during works, ancient graves were unearthed on the side of Agias Sofias Street. The specific manner of burial is known as 'burial by the roadside'. These ancient findings have already been unveiled by public authorities and are able to be visited. Nea Smyrni began to be inhabited at the beginning of the 20th century. Up until that point, it had not been inhabited in a systematic manner. At the time, it was intersected by an avenue which connected Athens and Phalerum, the ancient port of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namık Kemal High School
Namık Kemal High School ( tr, Namık Kemal Lisesi) is a public funded Anatolian high school in İzmir, Turkey. It was founded in 1853 as a rüştiye and became a lise in 1922. Located at the north of Kültürpark, it is a historic high school. History Firstly, it was decided to build the structure in 1909 by increase of number of the students of the Rum Evanjelik Mektebi and its construction plot was purchased with gathering the funds. Then, the building which is known as Namık Kemal High School was started building. However, its construction was stopped by Balkan Wars and the First World War. Afterwards, construction was started again in 1919–1922 while Greek government was in the saddle. Although retouch of building was finished 1922 summer, the school could not move to the new building because of exchange between Greece-Turkey and Küçük Asya Felaketi. After the proclamation of Turkey Republic, the building devolved on Turks. For a while, it was used as a hospit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burning Of Smyrna
The burning of Smyrna ( el, Καταστροφή της Σμύρνης, "Smyrna Catastrophe"; tr, 1922 İzmir Yangını, "1922 Izmir Fire"; hy, Զմիւռնիոյ Մեծ Հրդեհ, ''Zmyuṙno Mets Hrdeh'') destroyed much of the port city of Smyrna (modern İzmir, Turkey) in September 1922. Eyewitness reports state that the fire began on 13 September 1922Horton, George. ''The Blight of Asia''. Indianapolis: The Bobbs-Merrill Company, 1926; repr. London: Gomidas Institute, 2003, p. 96. and lasted until it was largely extinguished on 22 September. It began four days after the Turkish military captured the city on 9 September, effectively ending the Greco-Turkish War (1919–22), Greco-Turkish War, more than three years after the landing of Greek army troops at Smyrna on 15 May 1919. Estimated Ottoman Greeks, Greek and Armenians, Armenian deaths resulting from the fire range from 10,000 to 125,000.Naimark, ''Fires of Hatred'', p. 52. Approximately 80,000 to 400,000 Greek and Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenic Army
The Hellenic Army ( el, Ελληνικός Στρατός, Ellinikós Stratós, sometimes abbreviated as ΕΣ), formed in 1828, is the land force of Greece. The term ''Hellenic'' is the endogenous synonym for ''Greek''. The Hellenic Army is the largest of the three branches of the Hellenic Armed Forces, also constituted by the Hellenic Air Force (HAF) and the Hellenic Navy (HN). The army is commanded by the chief of the Hellenic Army General Staff (HAGS), which in turn is under the command of Hellenic National Defence General Staff (HNDGS). The motto of the Hellenic Army is ('Freedom stems from valour'), from Thucydides's '' History of the Peloponnesian War (2.43.4)'', a remembrance of the ancient warriors that defended Greek lands in old times. The Hellenic Army Emblem is the two-headed eagle with a Greek Cross escutcheon in the centre. The Hellenic Army is also the main contributor to, and "lead nation" of, the Balkan Battle Group, a combined-arms rapid-response force under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecumenical Patriarchate
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constantinopolitanus; tr, Rum Ortodoks Patrikhanesi, İstanbul Ekümenik Patrikhanesi, "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate") is one of the fifteen to seventeen autocephalous churches (or "jurisdictions") that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is headed by the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, currently Bartholomew, Archbishop of Constantinople. Because of its historical location as the capital of the former Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire and its role as the mother church of most modern Orthodox churches, Constantinople holds a special place of honor within Orthodoxy and serves as the seat for the Ecumenical Patriarch, who enjoys the status of '' primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the world's E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |