|
European Space Operations Center
The European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) serves as the main mission control centre for the European Space Agency (ESA) and is located in Darmstadt, Germany. ESOC's primary function is the operation of unmanned spacecraft on behalf of ESA and the launch and early orbit phases (LEOP) of ESA and third-party missions. The Centre is also responsible for a range of operations-related activities within ESA and in cooperation with ESA's industry and international partners, including ground systems engineering, software development, flight dynamics and navigation, development of mission control tools and techniques and space debris studies. ESOC's current major activities comprise operating planetary and solar missions, such as Mars Express and the Trace Gas Orbiter, astronomy & fundamental physics missions, such as Gaia (spacecraft) and XMM Newton, and Earth observation missions such as CryoSat2 and Swarm (spacecraft). ESOC is responsible for developing, operating and maintaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Organization
Globalization is social change associated with increased connectivity among societies and their elements and the explosive evolution of transportation and telecommunication Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that fe ... technologies to facilitate international cultural and economic exchange. The term is applied in various social, cultural, commercial and economic contexts. ''To browse the category, you may prefer to use the Globalization Category Tree.'' {{cmbox , text =''Note: Pages in this category should be moved to subcategories where applicable. This category may require frequent maintenance to avoid becoming too large. It should directly contain very few, if any, articles and should mainly contain subcategories.'' Global civilization Linear theories Politics by is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Orbiter
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) is a Sun-observing satellite developed by the European Space Agency (ESA). SolO, designed to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the nascent solar wind, will also perform close observations of the polar regions of the Sun which is difficult to do from Earth. These observations are important in investigating how the Sun creates and controls its heliosphere. SolO makes observations of the Sun from an eccentric orbit moving as close as ≈60 solar radii (RS), or 0.284 astronomical units (au), placing it inside Mercury's perihelion of 0.3075 au. During the mission the orbital inclination will be raised to about 24°. The total mission cost is US$1.5 billion, counting both ESA and NASA contributions. SolO was launched on 10 February 2020. The mission is planned to last seven years. Spacecraft The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is a Sun-pointed, three-axis stabilised platform with a dedicated heat shield to provide protection from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ExoMars
ExoMars (Exobiology on Mars) is an astrobiology programme of the European Space Agency (ESA). The goals of ExoMars are to search for signs of past life on Mars, investigate how the Martian water and geochemical environment varies, investigate atmospheric trace gases and their sources and by doing so demonstrate the technologies for a future Mars sample-return mission. The first part of the programme is a mission launched in 2016 that placed the Trace Gas Orbiter into Mars orbit and released the ''Schiaparelli'' EDM lander. The orbiter is operational but the lander crashed on the planet's surface. The second part of the programme was planned to launch in July 2020, when the ''Kazachok'' lander would have delivered the ''Rosalind Franklin'' rover on the surface, supporting a science mission that was expected to last into 2022 or beyond. On 12 March 2020, it was announced that the second mission was being delayed to 2022 as a result of problems with the parachutes, which could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
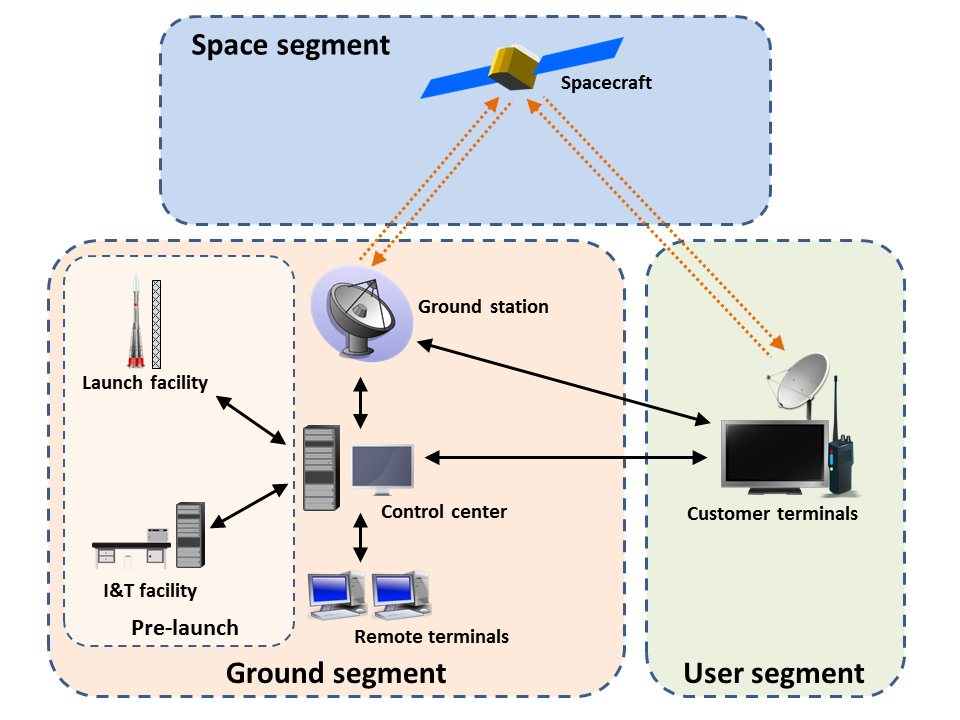
Ground Segment
A ground segment consists of all the ground-based elements of a space system used by operators and support personnel, as opposed to the space segment and user segment. The ground segment enables management of a spacecraft, and distribution of payload data and telemetry among interested parties on the ground. The primary elements of a ground segment are: * Ground (or Earth) stations, which provide radio interfaces with spacecraft * Mission control (or operations) centers, from which spacecraft are managed * Remote terminals, used by support personnel * Spacecraft integration and test facilities * Launch facilities * Ground networks, which allow for communication between the other ground elements These elements are present in nearly all space missions, whether commercial, military, or scientific. They may be located together or separated geographically, and they may be operated by different parties. Some elements may support multiple spacecraft simultaneously. Elements Groun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADM-Aeolus
Aeolus, or, in full, Atmospheric Dynamics Mission-Aeolus (ADM-Aeolus), is an Earth observation satellite operated by the European Space Agency (ESA). It was built by Airbus Defence and Space and launched on 22 August 2018. ADM-Aeolus is the first satellite with equipment capable of performing global wind-component-profile observation and will provide much-needed information to improve weather forecasting. Aeolus is the first satellite capable of observing what the winds are doing on Earth, from the surface of the planet and into the stratosphere 30 km high. The satellite was named after Aeolus, a god from the Greek mythology, the ruler of the winds. Program The program was initially approved in 1999 for a 2007 launch but technological obstacles caused 11 years of delay, as it was launched on 22 August 2018. For an estimated €481 million (US$568 million) program cost, it should provide 64,000 daily profiles from March or April 2019. Its altitude is a low for enough back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel-5 Precursor
Sentinel-5 Precursor (Sentinel-5P) is an Earth observation satellite developed by ESA as part of the Copernicus Programme to close the gap in continuity of observations between Envisat and Sentinel-5. Overview Sentinel-5 Precursor is the first mission of the Copernicus Programme dedicated to monitoring air pollution. Its instrument is an ultraviolet, visible, near and short-wavelength infrared spectrometer called Tropomi. The satellite is built on a hexagonal Astrobus L 250 satellite bus equipped with S- and X-band communication antennas, three foldable solar panels generating 1500 watts and hydrazine thrusters for station-keeping. The satellite operates in an 824 km Sun-synchronous orbit with a Local Time of Ascending Node of 13:30 hours. Tropomi instrument Sentinel-5 Precursor carries a single instrument, Tropomi (TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument), which is a spectrometer sensing ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), near (NIR) and short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) to monit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel-2B
Sentinel-2B is a European optical imaging satellite that was launched on 7 March 2017. It is the second Sentinel-2 satellite launched as part of the European Space Agency's Copernicus Programme, and its orbit will be phased 180° against Sentinel-2A. The satellite carries a wide swath high-resolution multispectral imager with 13 spectral bands. It will provide information for agriculture and forestry, among others allowing for prediction of crop yields. Mission history A €105 million contract for the construction of the spacecraft was signed in March 2010 by ESA's Director of Earth Observation Programmes and the CEO of Astrium Satellites. It was completed in June 2016, and the satellite was transported to the European Space Research and Technology Centre The European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) is the European Space Agency's main technology development and test centre for spacecraft and space technology. It is situated in Noordwijk, South Holland, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel-1B
Sentinel-1 is the first of the Copernicus Programme satellite constellation conducted by the European Space Agency. This mission was originally composed of a constellation of two satellites, Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B, which shared the same orbital plane. Two more satellites, Sentinel-1C and Sentinel-1D are in development. Sentinel-1B has been retired, leaving Sentinel-1A the only satellite of the constellation. The Sentinel-1 satellites carry a C-band synthetic-aperture radar instrument which provides a collection of data in all-weather, day or night. This instrument has a spatial resolution of down to 5 m and a swath of up to 400 km. The satellites orbit a Sun synchronous, near-polar (98.18°) orbit. The orbit has a 12-day repeat cycle and completes 175 orbits per cycle. The first satellite, Sentinel-1A, launched on 3 April 2014, and Sentinel-1B was launched on 25 April 2016. Both satellites lifted off from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana, and each on a S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel-1A
Sentinel-1A is a European radar imaging satellite launched in 2014. It is the first Sentinel-1 satellite launched as part of the European Union's Copernicus programme. The satellite carries a C-band Synthetic Aperture Radar which will provide images in all light and weather conditions. It will track many aspects of our environment, from detecting and tracking oil spills and mapping sea ice to monitoring movement in land surfaces and mapping changes in the way land is used. Program Copernicus is the long-term European Union Earth observation and monitoring programme under the former name of GMES (Global Monitoring for Environment and Security) and established by a Regulation that entered into force in 2014. It is a user-driven programme under civil control, which will notably encompass the launch of six families of dedicated, EU-owned earth observation satellites and instruments – the so-called Sentinels – and the ramp-up of the 6 Copernicus Services in the fields of atmosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)