|
European Grid Infrastructure
EGI (originally an initialism for European Grid Infrastructure) is a federation of computing and storage resource providers that deliver advanced computing and data analytics services for research and innovation. The Federation is governed by its participants represented in the EGI Council and coordinated by the EGI Foundation. As of 2024, the EGI Federation supports 160 scientific communities worldwide and over 95,000 users in their intensive data analysis. The most significant scientific communities supported by EGI in 2022 were Medical and Health Sciences, High Energy Physics, and Engineering and Technology. The EGI Federation provideds services through over 150 data centres, of which 25 are cloud sites, in 43 countries and 64 Research Infrastructures (4 of which are members of the Federation). Name Originally, EGI stood for European Grid Infrastructure. This reflected its focus on providing access to high-throughput computing resources across Europe using Grid computing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks that consists of Private network, private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, Wireless network, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and Web application, applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), email, electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data-intensive Computing
Data-intensive computing is a class of parallel computing applications which use a data parallel approach to process large volumes of data typically terabytes or petabytes in size and typically referred to as big data. Computing applications that devote most of their execution time to computational requirements are deemed compute-intensive, whereas applications are deemed data-intensive if they require large volumes of data and devote most of their processing time to input/output and manipulation of data. Introduction The rapid growth of the Internet and World Wide Web led to vast amounts of information available online. In addition, business and government organizations create large amounts of both structured and unstructured information, which need to be processed, analyzed, and linked. Vinton Cerf described this as an “information avalanche” and stated, “we must harness the Internet’s energy before the information it has unleashed buries us”. An International Data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001 is an information security standard. It specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS). Organizations with an ISMS that meet the standard's requirements can choose to have it certified by an accredited certification body following successful completion of an audit. There are also numerous recognized national variants of the standard. It was originally published jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 2005, with revisions in 2013 and 2022. Rationale Most organizations have a number of information security controls. However, without an information security management system (ISMS), controls tend to be somewhat disorganized and disjointed, having been implemented often as point solutions to specific situations or simply as a matter of convention. Security controls in operation typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
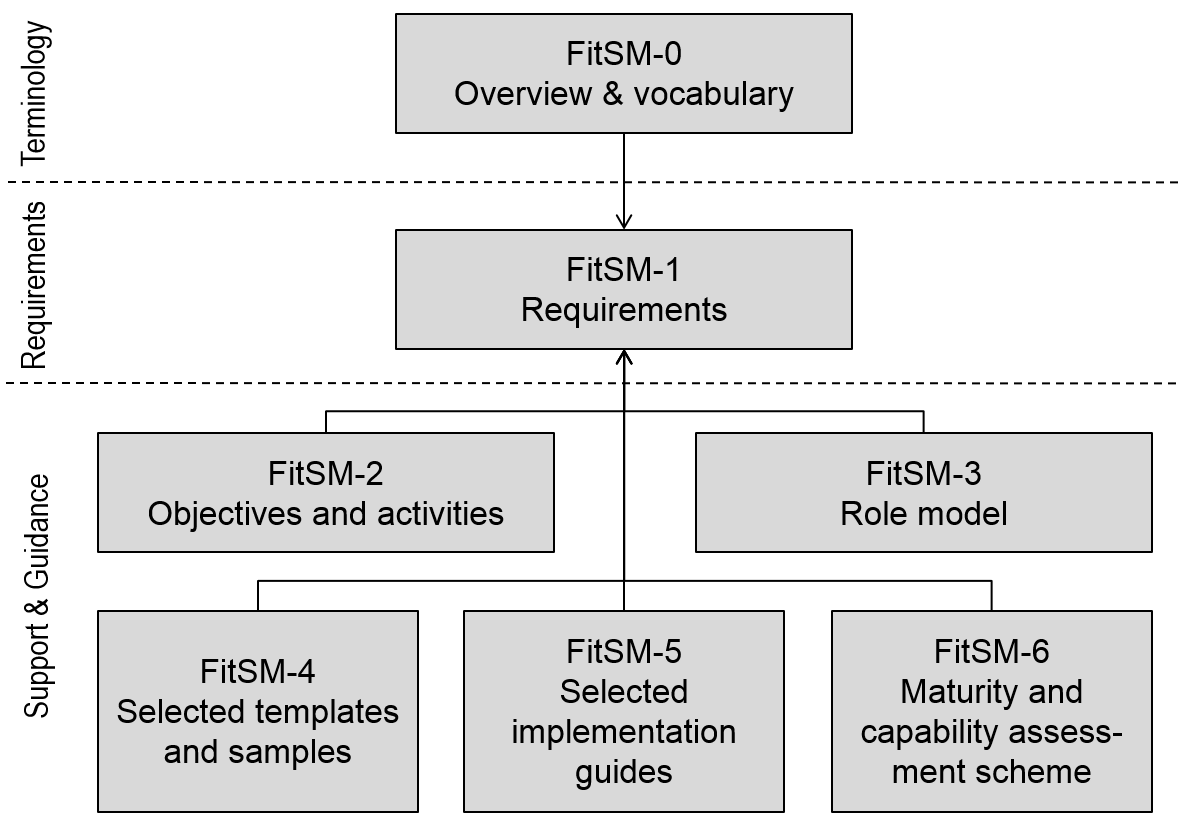
FitSM
FitSM is the name for a family of standards for lightweight IT service management (ITSM). Overview and parts FitSM calls itself a standard, but is not published or managed by an established standards organisation like ISO. However, in a way very similar to that of many ISO and ISO/IEC standard families, it structures its documents into several numbered parts and defines requirements for an effective service management system in its part 1. All parts are published under Creative Common licenses. FitSM-0: Overview and vocabulary A single document containing about 70 definitions of ITSM terms. FitSM-1: Requirements A single document containing about 85 auditable requirements for an effective service management system. The requirements are divided into general requirements (GR) and requirements for 14 different service management processes (PR). FitSM is similar in scope and style to part 1 of ISO/IEC 20000, but significantly shorter. FitSM-2: Objectives and activities A single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File-hosting Service
A file-hosting service, also known as cloud-storage service, online file-storage provider, or cyberlocker, is an internet hosting service specifically designed to host user files. These services allow users to upload files that can be accessed over the internet after providing a username and password or other authentication. Typically, file hosting services allow HTTP access, and in some cases, FTP access. Other related services include content-displaying hosting services (i.e. video and image), virtual storage, and remote backup solutions. Uses Personal file storage Personal file storage services are designed for private individuals to store and access their files online. Users can upload their files and share them publicly or keep them password-protected. Document-sharing services allow users to share and collaborate on document files. These services originally targeted files such as PDFs, word processor documents, and spreadsheets. However many remote file storage servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workload Manager
In IBM mainframes, Workload Manager (WLM) is a base component of MVS/ESA mainframe operating system, and its successors up to and including z/OS. It controls the access to system resources for the work executing on z/OS based on administrator-defined goals. Workload Manager components also exist for other operating systems. For example, an IBM Workload Manager is also a software product for AIX operating system. Workload Manager On a mainframe computer many differents applications execute at the same time. The expectations for executing work are consistent execution times and predictable access to databases. On z/OS the Workload Manager (WLM) component fulfills these needs by controlling work's access to system resources based on external specifications by the system administrator... The system administrator classifies work to service classes. The classification mechanism uses work attributes like transaction names, user identifications or program names which specific applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Distribution
Software distribution is the process of delivering software to the end user. Free software distribution tools GNU Autotools are widely used for which consist of source files written in C++ and the C programming language, but are not limited to these. Commercial software distribution tools * LANDesk Management Suite provides software distribution for Windows, OS X, and Linux. * Dell KACE provides remote administration, software distribution, and software installation to any Windows, Mac, or Linux desktop or server. Distribution tools for mobile devices Distribution of software to small mobile devices such as phones, PDAs and other hand-held terminals is a particular challenge due to their inconsistent connection to the Internet. Some tools that cater to this category of devices are: * Sybase iAnywhere Afaria See also *Provisioning (technology) In telecommunications, provisioning involves the process of preparing and equipping a network to allow it to provide new servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kubernetes
Kubernetes (), also known as K8s is an open-source software, open-source OS-level virtualization, container orchestration (computing), orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management. Originally designed by Google, the project is now maintained by a worldwide community of contributors, and the trademark is held by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. The name ''Kubernetes'' originates from the Greek language, Greek κυβερνήτης (kubernḗtēs), meaning 'governor', 'helmsman' or 'pilot'. ''Kubernetes'' is often abbreviated as ''K8s'', counting the eight letters between the ''K'' and the ''s'' (a numeronym). Kubernetes assembles one or more computers, either virtual machines or bare machine, bare metal, into a Computer cluster, cluster which can run workloads in containers. It works with various container runtimes, such as containerd and Cloud Native Computing Foundation#CRI-O, CRI-O. Its suitability for running and managing workloads of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchestration (computing)
In system administration, orchestration is the automated configuration, coordination, deployment, development, and management of computer systems and software. Many tools exist to automate server configuration and management. Usage Orchestration is often discussed in the context of service-oriented architecture, virtualization, provisioning, converged infrastructure and dynamic data center topics. Orchestration in this sense is about aligning the business request with the applications, data, and infrastructure. In the context of cloud computing, the main difference between workflow automation and orchestration is that workflows are processed and completed as processes within a single domain for automation purposes, whereas orchestration includes a workflow and provides a directed action towards larger goals and objectives. In this context, and with the overall aim to achieve specific goals and objectives (described through the quality of service parameters), for example, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Resource
In computing, a system resource, or simply resource, is any physical or virtual component of limited availability that is accessible to a computer. All connected devices and internal system components are resources. Virtual system resources include files (concretely file handles), network connections (concretely network sockets), and memory areas. Managing resources is referred to as resource management, and includes both preventing resource leaks (not releasing a resource when a process has finished using it) and dealing with resource contention (when multiple processes wish to access a limited resource). Computing resources are used in cloud computing to provide services through networks. Major resource types * Interrupt request (IRQ) lines * Direct memory access (DMA) channels * Port-mapped I/O * Memory-mapped I/O * Locks * External devices * External memory or objects, such as memory managed in native code, from Java; or objects in the Document Object Model (DOM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Twin
A digital twin is a digital model of an intended or actual real-world physical product, system, or process (a ''physical twin'') that serves as a digital counterpart of it for purposes such as simulation, integration, testing, monitoring, and maintenance. A digital twin is set of adaptive models that emulate the behaviour of a physical system in a virtual system getting real time data to update itself along its life cycle. The digital twin replicates the physical system to predict failures and opportunities for changing, to prescribe real time actions for optimizing and/or mitigating unexpected events observing and evaluating the operating profile system. Though the concept originated earlier (as a natural aspect of computer simulation generally), the first practical definition of a digital twin originated from NASA in an attempt to improve the physical-model simulation of spacecraft in 2010. Digital twins are the result of continual improvement in modeling and engineering. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity And Access Management
Identity and access management (IAM or IdAM) or Identity management (IdM), is a framework of policies and technologies to ensure that the right users (that are part of the ecosystem connected to or within an enterprise) have the appropriate access to technology resources. IAM systems fall under the overarching umbrellas of IT security and data management. Identity and access management systems not only identify, authenticate, and control access for individuals who will be utilizing IT resources but also the hardware and applications employees need to access. The terms "identity management" (IdM) and "identity and access management" are used interchangeably in the area of identity access management. Identity-management systems, products, applications and platforms manage identifying and ancillary data about entities that include individuals, computer-related hardware, and software applications. IdM covers issues such as how users gain an identity, the roles, and sometimes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |