|
Eumecichthys
''Eumecichthys fiski'', the unicorn crestfish or unicornfish, is a very rare, little-known species of crestfish in the family Lophotidae, and the only member of the genus ''Eumecichthys''. It likely has a worldwide distribution, having been first discovered offshore of Kalk Bay, South Africa, and subsequently reported from the Sea of Japan, southwest Florida, Clarion Island off Mexico, Hawaii, and India. A report from the Bering Sea may have been in error. It is found in the bathypelagic zone, at a depth of around 1,000 m (3,300 ft). This fish has ribbon-like body measuring up to 150 cm (59 in) in length. Its common name comes from a horn-like supraoccipital process projecting forward of its eyes. The upper jaw is protrusible, and the jaws contain small conical teeth. The dorsal fin runs along the entire length of the body and contains 310-392 soft rays; the first three to five dorsal rays at the tip of the projecting ridge are elongated into a pennant. The pect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumecichthys Fiski
''Eumecichthys fiski'', the unicorn crestfish or unicornfish, is a very rare, little-known species of crestfish in the family Lophotidae, and the only member of the genus ''Eumecichthys''. It likely has a worldwide distribution, having been first discovered offshore of Kalk Bay, South Africa, and subsequently reported from the Sea of Japan, southwest Florida, Clarion Island off Mexico, Hawaii, and India. A report from the Bering Sea may have been in error. It is found in the bathypelagic zone, at a depth of around 1,000 m (3,300 ft). This fish has ribbon-like body measuring up to 150 cm (59 in) in length. Its common name comes from a horn-like supraoccipital process projecting forward of its eyes. The upper jaw is protrusible, and the jaws contain small conical teeth. The dorsal fin runs along the entire length of the body and contains 310-392 soft rays; the first three to five dorsal rays at the tip of the projecting ridge are elongated into a pennant. The pect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crestfish
Crestfishes, family Lophotidae, are lampriform fishes found in most oceans. It consists of two extant and four extinct genera. They are elongated, ribbon-like fishes, silver in color, found in deep tropical and subtropical waters worldwide. Their scientific name is from Greek ''lophos'' meaning "crest" and refer to the crest (part of the dorsal fin A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through c ...) that emerges from the snout and head; this structure gives them their other name of unicorn fishes. The extant genera all possess ink sacs that open into their cloacae from which they can produce a cloud of black ink when threatened (as in many cephalopods). References Lophotidae {{Lampriformes-stub Animal families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophotidae
Crestfishes, family Lophotidae, are lampriform fishes found in most oceans. It consists of two extant and four extinct genera. They are elongated, ribbon-like fishes, silver in color, found in deep tropical and subtropical waters worldwide. Their scientific name is from Greek ''lophos'' meaning "crest" and refer to the crest (part of the dorsal fin) that emerges from the snout and head; this structure gives them their other name of unicorn fishes. The extant genera all possess ink sacs that open into their cloacae from which they can produce a cloud of black ink when threatened (as in many cephalopod A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...s). References Lophotidae {{Lampriformes-stub Animal families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Tate Regan
Charles Tate Regan FRS (1 February 1878 – 12 January 1943) was a British ichthyologist, working mainly around the beginning of the 20th century. He did extensive work on fish classification schemes. Born in Sherborne, Dorset, he was educated at Derby School and Queens' College, Cambridge and in 1901 joined the staff of the Natural History Museum, where he became Keeper of Zoology, and later director of the entire museum, in which role he served from 1927 to 1938. Regan was elected Fellow of the Royal Society in 1917. Regan mentored a number of scientists, among them Ethelwynn Trewavas, who continued his work at the British Natural History Museum. Species Among the species he described is the Siamese fighting fish (''Betta splendens''). In turn, a number of fish species have been named ''regani'' in his honour: *A Thorny Catfish '' Anadoras regani'' (Steindachner, 1908) *The Dwarf Cichlid '' Apistogramma regani'' *'' Apogon regani'' *A Catfish '' Astroblepus regani'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampriformes
Lampriformes is an order of ray-finned fish. Members are collectively called lamprids (which is more properly used for the Lampridae) or lampriforms, and unite such open-ocean and partially deep-sea Teleostei as the crestfishes, oarfish, opahs, and ribbonfishes. A synonym for this order is Allotriognathi, while an often-seen, but apparently incorrect, spelling variant is Lampridiformes. They contain seven extant families which are generally small but highly distinct, and a mere 12 lampriform genera with some 20 species altogether are recognized. The scientific name literally means "shaped (like the) bright (one)", as "lampr-", meaning bright, comes from ''lampris'', the generic name for the opah. In contrast, most other living lampriforms are actually ribbon-like and not very similar to the disc-shaped opahs in habitus. They are, however, quite distinctly united by their anatomy, and the family's phylogeny, as well as the most ancient fossils of this order suggest the origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral surface of fish. The paired pelvic fins are homologous to the hindlimbs of tetrapods. Structure and function Structure In actinopterygians, the pelvic fin consists of two endochondrally-derived bony girdles attached to bony radials. Dermal fin rays (lepidotrichia) are positioned distally from the radials. There are three pairs of muscles each on the dorsal and ventral side of the pelvic fin girdle that abduct and adduct the fin from the body. Pelvic fin structures can be extremely specialized in actinopterygians. Gobiids and lumpsuckers modify their pelvic fins into a sucker disk that allow them to adhere to the substrate or climb structures, such as waterfalls. In priapiumfish, males have modified their pelvic structures into a spiny copulatory device that grasps the female during mating. File:Pelvic fin skeleton.png, Pelvic fin skeleton for ''Danio rerio'', zebrafish. File:Zuignap waarmee de zwartbekgrond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
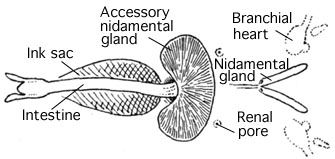
Ink Sac
An ink sac is an anatomical feature that is found in many cephalopod mollusks used to produce the defensive cephalopod ink. With the exception of nocturnal and very deep water cephalopods, all Coleoidea (squid, octopus and cuttlefish) which dwell in light conditions have an ink sac, which can be used to expel a cloud of dark ink in order to confuse predators. The ink sac is a muscular bag which originated as an extension of the hind gut; it is a modified hypobranchial gland.Nair, J.R., D. Pillai, S.M. Joseph, P. Gomathi, P.V. Senan & P.M. Sherief (2011). ''Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences'' 40(1): 13–27. It lies beneath the gut and opens into the anus, into which its contents – almost pure melanin – can be squirted; its proximity to the base of the funnel means that the ink can be distributed by ejected water as the cephalopod uses its jet propulsion. The ejected cloud of melanin is bound by mucus Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, and a few mammals ( monotremes, tenrecs, golden moles, and marsupial moles), have this orifice, from which they excrete both urine and feces; this is in contrast to most placental mammals, which have two or three separate orifices for evacuation. Excretory openings with analogous purpose in some invertebrates are also sometimes referred to as cloacae. Mating through the cloaca is known as cloacal copulation, commonly referred to as cloacal kiss. The cloacal region is also often associated with a secretory organ, the cloacal gland, which has been implicated in the scent-marking behavior of some reptiles, marsupials, amphibians, and monotremes. Etymology The word is from the Latin verb ''cluo'', "(I) cleanse", thus the noun ''cloaca'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

_with_its_prey.jpg)