|
Eukaryotic Release Factors
A release factor is a protein that allows for the termination of translation by recognizing the termination codon or stop codon in an mRNA sequence. They are named so because they release new peptides from the ribosome. Background During translation of mRNA, most codons are recognized by "charged" tRNA molecules, called aminoacyl-tRNAs because they are adhered to specific amino acids corresponding to each tRNA's anticodon. In the standard genetic code, there are three mRNA stop codons: UAG ("amber"), UAA ("ochre"), and UGA ("opal" or "umber"). Although these stop codons are triplets just like ordinary codons, they are not decoded by tRNAs. It was discovered by Mario Capecchi in 1967 that, instead, tRNAs do not ordinarily recognize stop codons at all, and that what he named "release factor" was not a tRNA molecule but a protein. Later, it was demonstrated that different release factors recognize different stop codons. Classification There are two classes of release factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Releasing Hormone
Releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones are hormones whose main purpose is to control the release of other hormones, either by stimulating or inhibiting their release. They are also called liberins () and statins () (respectively), or releasing factors and inhibiting factors. The principal examples are hypothalamic-pituitary hormones that can be classified from several viewpoints: they are hypothalamic hormones (originating in the hypothalamus), they are hypophysiotropic hormones (affecting the hypophysis, that is, the pituitary gland), and they are tropic hormones (having other endocrine glands as their target). For example, thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is released from the hypothalamus in response to low levels of secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland. The TSH in turn is under feedback control by the thyroid hormones T4 and T3. When the level of TSH is too high, they feed back on the brain to shut down the secretion of TRH. Syntheti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MTRF1L
Mitochondrial translational release factor 1-like is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTRF1L gene. Mitochondrial DNA encodes 13 proteins that play essential roles in the respiratory chain, while all proteins involved in mitochondrial translation are encoded by nuclear genes that are imported from the cytoplasm. MTRF1L is a nuclear-encoded protein that functions as a releasing factor that recognizes termination codons and releases mitochondrial ribosomes from the synthesized protein (summary by Nozaki et al., 2008 ubMed 18429816. upplied by OMIM Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of MTRF1L function. A conditional knockout mouse line, called ''Mtrf1ltm1a(KOMP)Wtsi'' was generated as part of the International Knockout Mouse Consortium program — a high-throughput mutagenesis project to generate and distribute animal models of disease to interested scientists — at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. Male and female animals underwent a standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PELO
Pelo is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Brad Pelo Brad Pelo (born February 6, 1963) is an American businessman, entrepreneur, and co-founder and chief executive officer of i.TV, the company behind tvtag, a second screen app for iOS. Backed by Union Square Ventures, RRE Ventures, Rho Ventures, ... (born 1963), American businessman * Dimitri Pelo (born 1985), French rugby league player * Vincent Pelo (born 1988), French rugby union player See also * PELO, a protein * Pelo Madueño (born 1968), Peruvian musician and actor * * {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
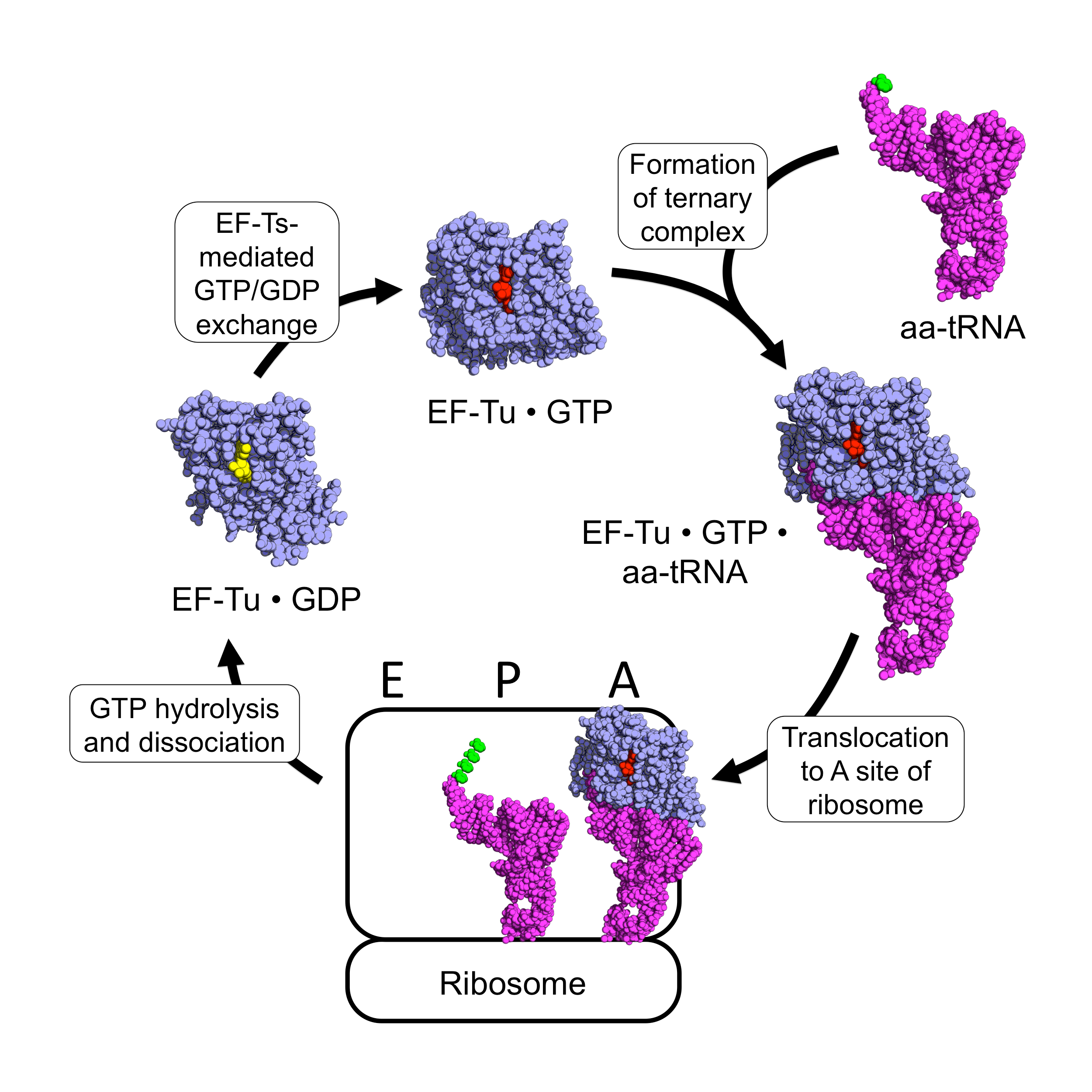
EF-Tu
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM. As a family of elongation factors, EF-Tu also includes its eukaryotic and archaeal homolog, the alpha subunit of eEF-1 (EF-1A). Background Elongation factors are part of the mechanism that synthesizes new proteins through translation in the ribosome. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) carry the individual amino acids that become integrated into a protein sequence, and have an anticodon for the specific amino acid that they are charged with. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information that encodes the primary structure of a protein, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
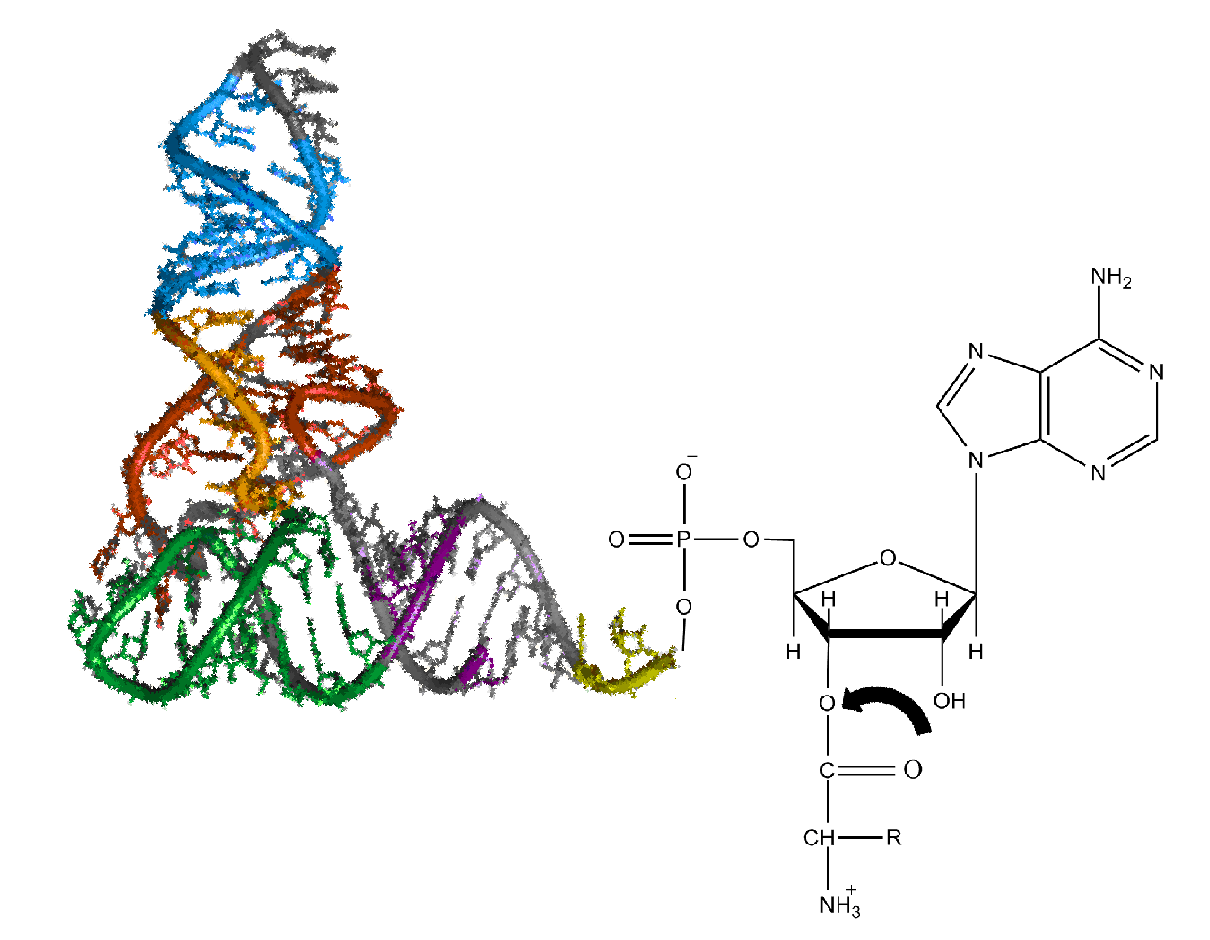
Aa-tRNA
Aminoacyl-tRNA (also aa-tRNA or charged tRNA) is tRNA to which its cognate amino acid is chemically bonded (charged). The aa-tRNA, along with particular elongation factors, deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypeptide chain that is being produced during translation. Alone, an amino acid is not the substrate necessary to allow for the formation of peptide bonds within a growing polypeptide chain. Instead, amino acids must be "charged" or aminoacylated with a tRNA to form their respective aa-tRNA. Every amino acid has its own specific aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, which is utilized to chemically bind to the tRNA that it is specific to, or in other words, "cognate" to. The pairing of a tRNA with its cognate amino acid is crucial, as it ensures that only the particular amino acid matching the anticodon of the tRNA, and in turn matching the codon of the mRNA, is used during protein synthesis. In order to prevent translational errors, in which the wrong ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toeprinting Assay
The toeprinting assay, also known as the primer extension inhibition assay, is a method used in molecular biology that allows one to examine the interactions between messenger RNA and ribosomes or RNA-binding proteins. It is different from the more commonly used DNA footprinting assay. The toeprinting assay has been utilized to examine the formation of the translation initiation complex. To do a toeprint assay, one needs the mRNA of interest, ribosomes, a DNA primer, free nucleotides, and reverse transcriptase (RT), among other reagents. The assay involves letting the RT generate cDNA In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a sp ... until it gets blocked by any bound ribosomes, resulting in shorter fragments called toeprints when the results are observed on a sequencing gel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome Recycling Factor
Ribosome recycling factor or ribosome release factor (RRF) is a protein found in bacterial cells as well as eukaryotic organelles, specifically mitochondria and chloroplasts. It functions to recycle ribosomes after completion of protein synthesis (bacterial translation). In humans, the mitochrondrial version is coded by the MRRF gene. Discovery The ribosome recycling factor was discovered in the early 1970s by the work of Akira Kaji and Akikazu Hiroshima at the University of Pennsylvania. Their work described the requirement for two protein factors to release ribosomes from mRNA. These two factors were identified as RRF, an unknown protein until then, and Elongation Factor G (EF-G), a protein already identified and known to function in protein synthesis. RRF was originally called Ribosome ''Releasing'' Factor but is now called Ribosome ''Recycling'' Factor. Function RRF accomplishes the recycling of ribosomes by splitting ribosomes into subunits, thereby releasing the bound m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic Initiation Factor-3
In molecular biology, translation initiation factor IF-3 (gene infC) is one of the three factors required for the initiation of protein biosynthesis in bacteria. IF-3 is thought to function as a fidelity factor during the assembly of the ternary initiation complex which consists of the 30S ribosomal subunit, the initiator tRNA and the messenger RNA. IF-3 is a basic protein that binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit. The chloroplast homolog enhances the poly( A, U, G)-dependent binding of the initiator tRNA to its ribosomal 30s subunits. IF1–IF3 may also perform ribosome recycling. IF3 is not universally found in all bacterial species. However, in '' E. coli'', it is required for the 30S subunit to bind to the initiation site in mRNA. In addition, it has several other jobs including the stabilization of free 30S subunits, enables 30S subunits to bind to mRNA and checks for accuracy against the first aminoacyl-tRNA. It also allows for rapid codon-anticodon pairing for the initiato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic Initiation Factor-1
Bacterial initiation factor 1 is a bacterial initiation factor. IF1 associates with the 30S ribosomal subunit in the A site and prevents an aminoacyl-tRNA Aminoacyl-tRNA (also aa-tRNA or charged tRNA) is tRNA to which its cognate amino acid is chemically bonded (charged). The aa-tRNA, along with particular elongation factors, deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypept ... from entering. It modulates IF2 binding to the ribosome by increasing its affinity. It may also prevent the 50S subunit from binding, stopping the formation of the 70S subunit. It also contains a β-domain fold common for nucleic acid binding proteins. IF1– IF3 may also perform ribosome recycling. References {{GeneticTranslation Molecular biology Protein biosynthesis Gene expression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryo-EM
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a cryomicroscopy technique applied on samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An aqueous sample solution is applied to a grid-mesh and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane or a mixture of liquid ethane and propane. While development of the technique began in the 1970s, recent advances in detector technology and software algorithms have allowed for the determination of biomolecular structures at near-atomic resolution. This has attracted wide attention to the approach as an alternative to X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy for macromolecular structure determination without the need for crystallization. In 2017, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jacques Dubochet, Joachim Frank, and Richard Henderson "for developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution." ''Nature M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSPT2
Eukaryotic peptide chain release factor GTP-binding subunit ERF3B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GSPT2'' gene. GSPT2 is closely related to GSPT1 (MIM 139259), a GTP-binding protein that plays an essential role at the G1- to S-phase transition of the cell cycle in yeast and human cells. GSPT1 is a positive regulator of translational accuracy and, in a binary complex with eRF1 (MIM 600285), functions as a polypeptide chain release factor. upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"/> Interactions GSPT2 has been shown to interact with PABPC1 Polyadenylate-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PABPC1'' gene. The protein PABP1 binds mRNA and facilitates a variety of functions such as transport into and out of the nucleus, degradation, translation, and stabili .... References Further reading * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSPT1
Eukaryotic peptide chain release factor GTP-binding subunit ERF3A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GSPT1'' gene. Interactions GSPT1 has been shown to interact with BIRC2 Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 2 (also known as cIAP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BIRC2'' gene. Function cIAP1 is a member of the Inhibitor of Apoptosis family that inhibit apoptosis by interfering with the acti .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-16-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |