|
Euboea
Evia (, ; el, О•ПЌОІОїО№О± ; grc, О•бЅ”ОІОїО№О± ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (ОњО¬ОєПЃО№П‚) and ''Doliche'' (О”ОїО»ОЇП‡О·) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'', ''Aonia'' and ''Abantis'' from the tribes inhabiting it. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
О•ПЌОІОїО№О±
Evia (, ; el, wikt:О•ПЌОІОїО№О±, О•ПЌОІОїО№О± ; grc, wikt:О•бЅ”ОІОїО№О±, О•бЅ”ОІОїО№О± ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest List of islands of Greece, Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the Euboea (regional unit), regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in Ancient Greece, antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (ОњО¬ОєПЃО№П‚) and ''Doliche'' (О”ОїО»ОЇП‡О·) fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea Topo
Evia (, ; el, О•ПЌОІОїО№О± ; grc, О•бЅ”ОІОїО№О± ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (ОњО¬ОєПЃО№П‚) and ''Doliche'' (О”ОїО»ОЇП‡О·) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'', ''Aonia'' and ''Abantis'' from the tribes inhabiting it. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
О•бЅ”ОІОїО№О±
Evia (, ; el, О•ПЌОІОїО№О± ; grc, О•бЅ”ОІОїО№О± ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (ОњО¬ОєПЃО№П‚) and ''Doliche'' (О”ОїО»ОЇП‡О·) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'', ''Aonia'' and ''Abantis'' from the tribes inhabiting it. Its anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcis
Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida ( Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from antiquity and is derived from the Greek П‡О±О»ОєПЊП‚ (copper, bronze), though there is no trace of any mines in the area. In the Late Middle Ages, it was known as Negropont(e), an Italian name that has also been applied to the entire island of Euboea. History Ancient Greece The earliest recorded mention of Chalcis is in the Iliad, where it is mentioned in the same line as its rival Eretria. It is also documented that the ships set for the Trojan War gathered at Aulis, the south bank of the strait near the city. Chamber tombs at Trypa and Vromousa dated to the Mycenaean period were excavated by Papavasiliou in 1910. In the 8th and 7th centuries BC, colonists from Chalcis founded thirty townships on the peninsula of Chalcidice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea (regional Unit)
Euboea ( el, О ОµПЃО№П†ОµПЃОµО№О±ОєО® ОµОЅПЊП„О·П„О± О•ПЌОІОїО№О±П‚) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Central Greece. It consists of the islands of Euboea and Skyros, as well as a 260 kmВІ area on the Greek mainland. Its land area is 4,167.449 kmВІ, whereas the total land area of the municipalities actually on the island Euboea is 3,684.848 kmВІ, which includes that of numerous small offshore islets ( Petalies Islands) near Euboea's southern tip. Administration The Euboea regional unit is subdivided into 8 municipalities, numbered in the picture in the infobox. These are: *Chalcis (''Chalkida'', 1) * Dirfys-Messapia (2) * Eretria (3) * Istiaia-Aidipsos (4) * Karystos (5) * Kymi-Aliveri (6) * Mantoudi-Limni-Agia Anna (7) * Skyros (8) Prefecture As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the former Euboea Prefecture ( el, ОќОїОјПЊП‚ О•ПЌОІОїО№О±П‚) was transformed into a regional unit within the Cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euripus Strait
The Euripus Strait ( el, Εύριπος ) is a narrow channel of water separating the Greek island of Euboea in the Aegean Sea from Boeotia in mainland Greece. The strait's principal port is Chalcis on Euboea, located at the strait's narrowest point. The strait is subject to strong tidal currents which reverse direction approximately four times a day. Tidal flows are very weak in the Eastern Mediterranean, but the strait is a remarkable exception. Water flow peaks at about , either northwards or southwards, and lesser vessels are often incapable of sailing against it. When nearing flow reversal, sailing is even more precarious because of vortex formation. The Swiss scholar François-Alphonse Forel contributed to an understanding of the enigmatic phenomenon by his study of limnology and the discovery of seiche, where layers of water of differing temperature oscillate in thickness in a confined body of water. But the problem was solved completely only by D. Eginitis, director of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
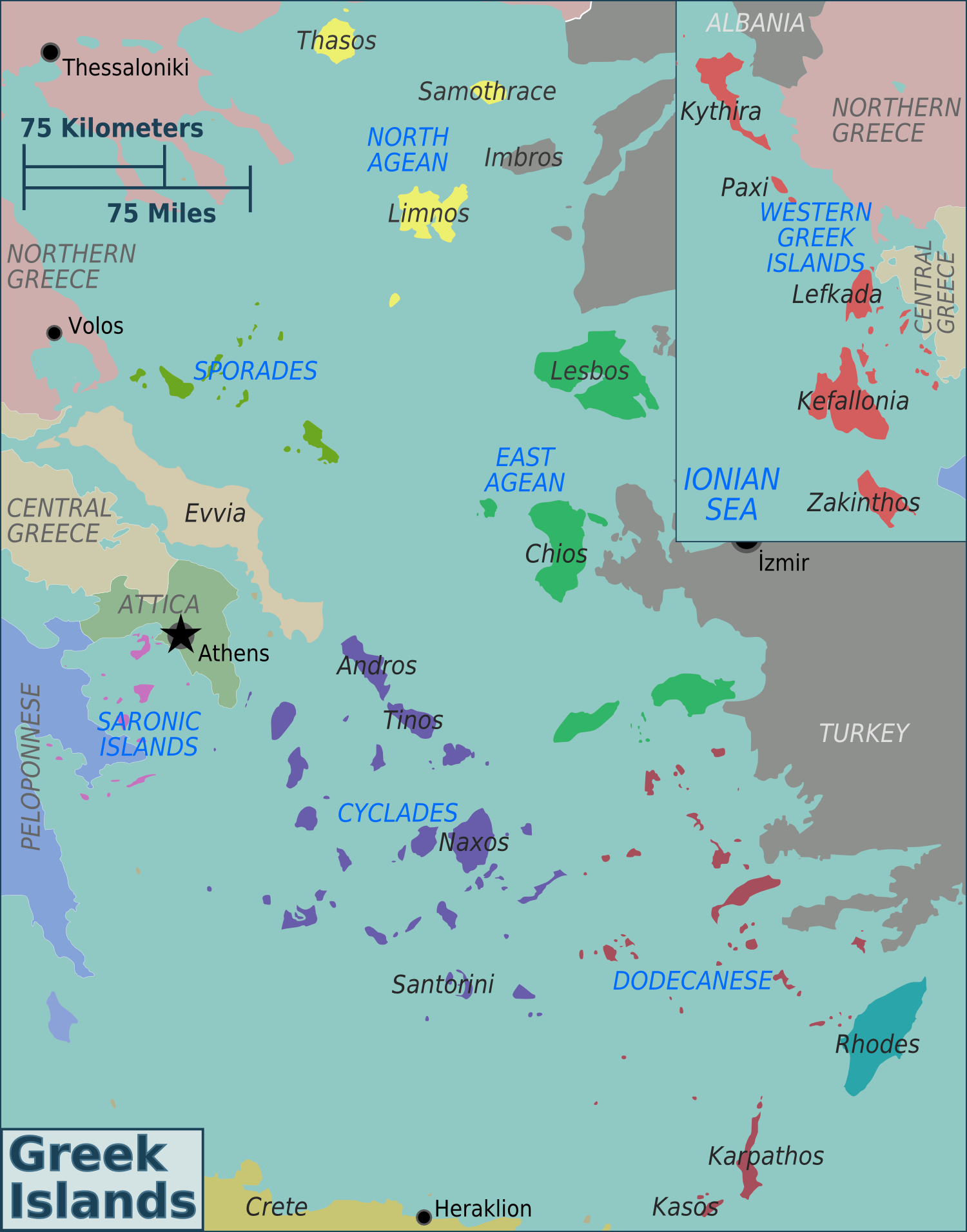
List Of Islands Of Greece
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by area is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection in the southeast between Crete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Greece (region)
Central Greece ( el, О ОµПЃО№П†ОПЃОµО№О± ОЈП„ОµПЃОµО¬П‚ О•О»О»О¬ОґО±П‚, translit=PerifГ©ria StereГЎs EllГЎdhas, , colloquially known as ОЎОїПЌОјОµО»О· (''RoГєmeli'')) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. The region occupies the eastern half of the traditional region of Central Greece, including the island of Euboea. To the south it borders the regions of Attica and the Peloponnese, to the west the region of West Greece and to the north the regions of Thessaly and Epirus. Its capital city is Lamia. Administration The region was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with Thessaly, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of Thessaly and Central Greece based at Larissa Larissa (; el, О›О¬ПЃО№ПѓО±, , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 144,6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skyros
Skyros ( el, ОЈОєПЌПЃОїП‚, ), in some historical contexts Latinized Scyros ( grc, ОЈОєбї¦ПЃОїП‚, ), is an island in Greece, the southernmost of the Sporades, an archipelago in the Aegean Sea The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: О‘О№ОіО±ОЇОї О ОО»О±ОіОїП‚: "EgГ©o PГ©lagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans an .... Around the 2nd millennium BC and slightly later, the island was known as The Island of the Magnetes where the Magnetes used to live and later Pelasgia and Dolopia and later Skyros. At it is the largest island of the Sporades, and has a population of about 3,000 (in 2011). It is part of the regional unit of Euboea (regional unit), Euboea. The Hellenic Air Force has a major base in Skyros, because of the island's strategic location in the middle of the Aegean. Municipality The municipality Skyros is part of the regional unit of Euboea (reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aidipsos
Aidipsos ( el, О‘О№ОґО·П€ПЊП‚, ) is a village and a former municipality in Euboea, Greece. The municipality Aidipsos was founded in 1997 by the merger of the municipality Loutra Aidipsou with the communities Agios and Gialtra. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Istiaia-Aidipsos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 115.461 km2. 80 of Greece's 752 hot springs are located in Aidipsos, making it a popular tourist destination. The spas date back more than 20,000 years. In 2011 the population was 6,141. Many famous personalities have visited the town so far, such as Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Sir Winston Churchill, Eleutherios Venizelos, Theodoros Deligiannis, Georgios Theotokis, Ioannis Kondilakis, Archbishop of Athens Theocletus I, Aristotelis Onassis, Maria Callas, Kostis Palamas, Marika Kotopouli and others. Within the modern borders of the municipal units are the remains of ancient town of Aedepsus Aedepsus or Aide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirfi
Dirfi ( el, О”ОЇПЃП†О·, older form О”ОЇПЃП†П…П‚ - ''Dirfys'') is a mountain in the central part of the island of Euboea, Greece. At 1,743 m elevation, it is the highest mountain of Euboea. The Dirfi gave its name to the municipal unit Dirfys. Its summit is 4 km west of Stropones, 5 km north of Steni Dirfyos and 28 km northeast of the city of Chalcis. There are forests on the lower slopes while most of the mountain is covered with grassland and in winter with permafrost and snow. Gallery File:Trekking path (Dirfi).JPG, A part of the trekking path located on Dirfi mountain. File:Dirfi river.JPG, A tiny river flowing by the Dirfi mountain. File:Dirfi Mountain.JPG, One of the peaks of Dirfi mountain. See also * List of European ultra prominent peaks This is a list of all the mountains in Europe with ultra-prominent peaks with topographic prominence greater than . The column "Col" denotes the highest elevation to which one must descend from a peak in order to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Units Of Greece
The 74 regional units of Greece Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ... ( el, ПЂОµПЃО№П†ОµПЃОµО№О±ОєОП‚ ОµОЅПЊП„О·П„ОµП‚, ; sing. , ) are the country's Seventy-four second-level administrative units. They are divisions of the country's 13 regions, and are further divided into municipalities. They were introduced as part of the Kallikratis administrative reform on 1 January 2011 and are comparable in area and, in the mainland, coterminous with the 'pre-Kallikratis' prefectures of Greece. List References {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of European countries Regional units Greece transport-related lists Subdivisions of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |