|
Eton Montem
Eton Montem (or ''ad Montem'' – literally ''to the Mountain'') was a custom observed by Eton College from at least 1561 until it was finally suppressed in 1847, at the Montem Mound (or Salt Hill) in Chalvey, Slough, Buckinghamshire (later Berkshire). The mound is situated some 2 miles from the college near the London to Bath coach road, now the A4. Montem is first reported in List of headmasters at Eton College, William Malim's ''consuetudinarium'' (book of customs) of 1561, when it seems to have been an initiation ceremony for new boys, who were scattered with salt (which can mean 'wit' as well as 'salt') at the mound. By the 18th century, the ceremony had changed to a glorified flag day. Salt was no longer scattered on scholars; instead, pinches of salt and little blue tickets were sold to passers-by (the blue ticket – inscribed on alternate celebrations with 'Mos Pro Lege' or 'Pro More et Monte' – acted as a ticket of exemption from further contributions) for 'salt' – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of List of monarchs in Britain by length of reign, any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India. Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was Kensington System, raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-druidism
Druidry, sometimes termed Druidism, is a modern spirituality, spiritual or religion, religious movement that promotes the cultivation of honorable relationships with the physical landscapes, flora, fauna, and diverse peoples of the world, as well as with nature deities, and spirits of nature and place. Theological beliefs among modern Druids are diverse; however, all modern Druids venerate the divine essence of nature. While there are significant interregional and intergroup variations in modern Druidry practice, Druids across the globe are unified by a core set of shared spiritual and devotional practices: meditation; prayer/conversation with deities and spirits; the use of extra-sensory methods of seeking wisdom and guidance; the use of nature-based spiritual frameworks to structure devotional practices and rituals; and a regular practice of nature connection and environmental stewardship work. Arising from the 18th century Romanticism, Romanticist movement in Britain, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Montem Procession BBO ETCO FDA P 52 2010
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
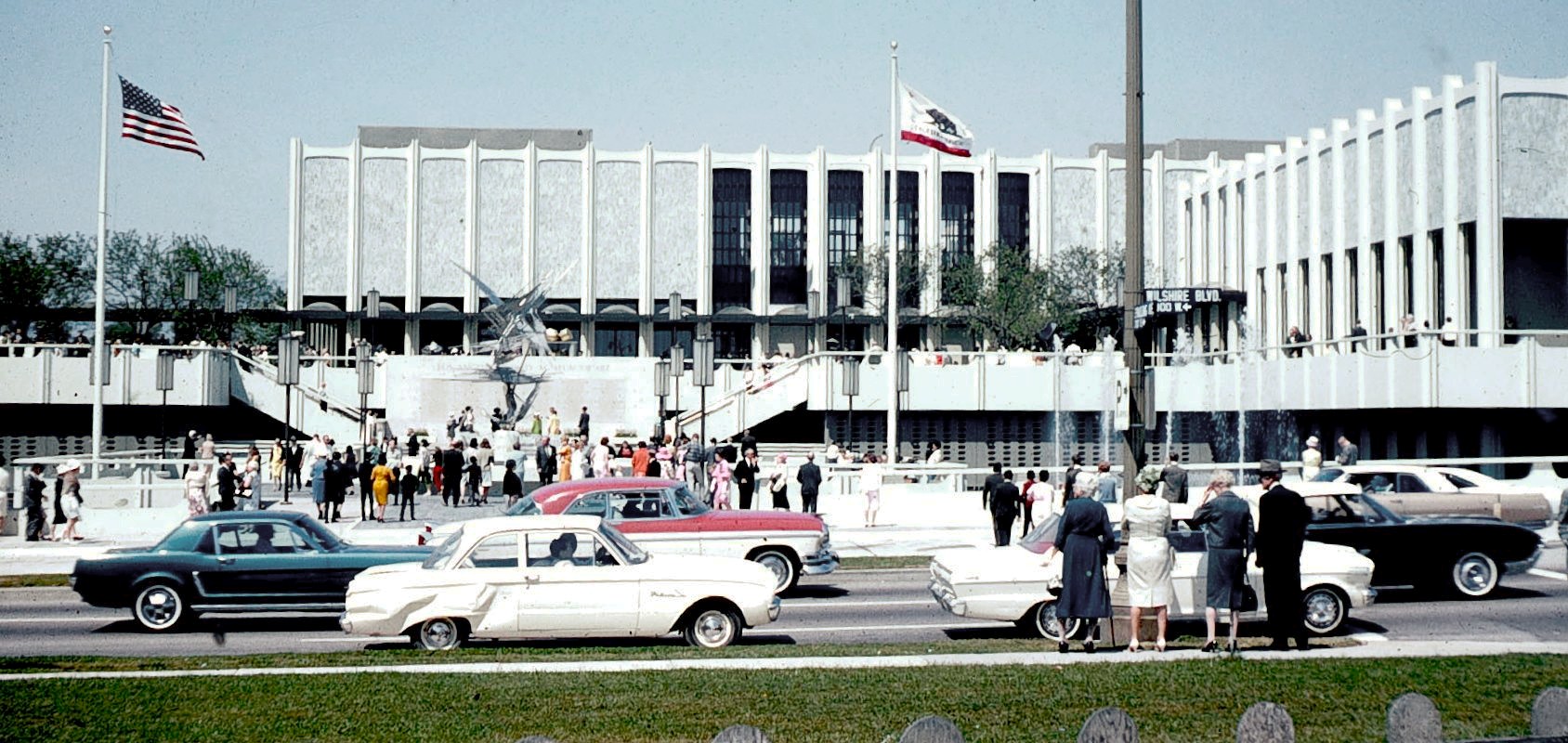
Los Angeles County Museum Of Art
The Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA) is an art museum located on Wilshire Boulevard in the Miracle Mile, Los Angeles, California, Miracle Mile vicinity of Los Angeles. LACMA is on Museum Row, adjacent to the La Brea Tar Pits (George C. Page Museum). LACMA was founded in 1961, splitting from the Los Angeles Museum of History, Science and Art. Four years later, it moved to the Wilshire Boulevard complex designed by William Pereira. The museum's wealth and collections grew in the 1980s, and it added several buildings beginning in that decade and continuing in subsequent decades. In 2020, four buildings on the campus were demolished to make way for a reconstructed facility designed by Peter Zumthor. His design drew strong community opposition and was lambasted by architectural critics and museum curators, who objected to its reduced gallery space, poor design, and exorbitant costs. LACMA is the list of largest art museums, largest art museum in the western United States. It a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Lawrence (painter)
Sir Thomas Lawrence (13 April 1769 – 7 January 1830) was an English portrait painter and the fourth president of the Royal Academy. A child prodigy, he was born in Bristol and began drawing in Devizes, where his father was an innkeeper at the Bear Hotel in the Market Square. At age ten, having moved to Bath, he was supporting his family with his pastel portraits. At 18 he went to London and soon established his reputation as a portrait painter in oils, receiving his first royal commission, a portrait of Queen Charlotte, in 1790. He stayed at the top of his profession until his death, aged 60, in 1830. Self-taught, he was a brilliant draughtsman and known for his gift of capturing a likeness, as well as his virtuoso handling of paint. He became an associate of the Royal Academy in 1791, a full member in 1794, and president in 1820. In 1810 he acquired the generous patronage of the Prince Regent, was sent abroad to paint portraits of allied leaders for the Waterloo chamber at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southampton (UK Parliament Constituency)
Southampton was a United Kingdom constituencies, parliamentary constituency which was represented in the British House of Commons. Centred on the town of Southampton, it returned two members of parliament (MPs) from 1295 until it was abolished for the 1950 United Kingdom general election, 1950 general election. Members of Parliament MPs 1295–1660 MPs 1660–1832 MPs 1832–1950 Elections Elections in the 1830s Chamberlayne's death caused a by-election. * On petition, Hoy was unseated in favour of Penleaze Elections in the 1840s The election was declared void on petition on 6 May 1842, due to bribery by Bruce and Martyn's agents, and a writ for a by-election was not moved until 1 August 1842. Elections in the 1850s Cockburn was appointed Solicitor General for England and Wales, requiring a by-election. Cockburn was appointed Attorney General for England and Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Atherley
Arthur Atherley (12 June 1772 – 1 October 1844) was an English Member of Parliament, serving the Southampton constituency three times, as Whig (a Liberal Party predecessor) and Reformer. Atherley was born in Southampton, the son of Arthur Atherley and Susanna Carter, and was the fifth successive member of the Atherley family to be baptised as "Arthur". He was educated at Eton College where, in 1791, he had his portrait painted by Sir Thomas Lawrence (it now hangs in the Los Angeles County Museum of Art). At Eton, he was captain of the Ad Montem club, an institution with roots in medieval times that survived until 1847. One of the club's traditions was to take part in a procession to Salt Hill during which boys in fancy costume, the salt bearers, participated in the maintenance of their "captain" at university by levying contributions from passers-by. After finishing his education at Eton, he went up to Trinity College, Cambridge, where he was admitted a pensioner on 6 May 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Hodgson
Francis Hodgson (16 November 1781 – 29 December 1852; also known as Frank Hodgson in correspondence) was a reforming Provost of Eton, educator, cleric, writer of verse, and friend of Byron. Life Hodgson was born on 16 November 1781, son of Rev. James Hodgson, Headmaster of Whitgift School, whose father James Hodgson had moved from Hawkshead, Cumbria, to be rector of Humber, Herefordshire. Francis and one of his half-sisters were the only two of his father's seven children to live beyond the age of 15. He was educated first at Whitgift School, before proceeding to Eton College as a King's Scholar, and then as a Scholar to King's College, Cambridge. In 1806 he was appointed assistant master at Eton, a post which he resigned after a year to become a resident tutor and Fellow at King's College, Cambridge. It was there that he met and formed a lifelong friendship with the poet Lord Byron, who was at that time an undergraduate at Trinity College. Their friendship is recorded in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Craven Hawtrey
Edward Craven Hawtrey (7 May 178927 January 1862) was an English educationalist, headmaster and later provost of Eton College. Life He was born at Burnham, Bucks, the son of the vicar of the parish. He was educated at Eton College and King's College, Cambridge, and in 1814 was appointed assistant master at Eton under John Keate. In 1834 he became headmaster of Eton, which role he performed until 1853, when he was elected Provost of Eton following the death of Francis Hodgson. While he was headmaster and Hodgson was Provost, new buildings were erected, including the school library and the sanatorium, the college chapel was restored, the Old Christopher Inn was closed, and the custom of Montem, the collection by street begging of funds for the university expenses of the captain of the school, was suppressed. Hawtrey is supposed to have suggested the modern language prizes given by Prince Albert, and himself founded the prize for English essay. In 1852 he became provost of Eto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of —later slightly widened to —but, from 1854, a series of amalgamations saw it also operate standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892. The GWR was the only company to keep its identity through the Railways Act 1921, which amalgamated it with the remaining independent railways within its territory, and it was finally merged at the end of 1947 when it was nationalised and became the Western Region of British Railways. The GWR was called by some "God's Wonderful Railway" and by others the "Great Way Round" but it was famed as the "Holiday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
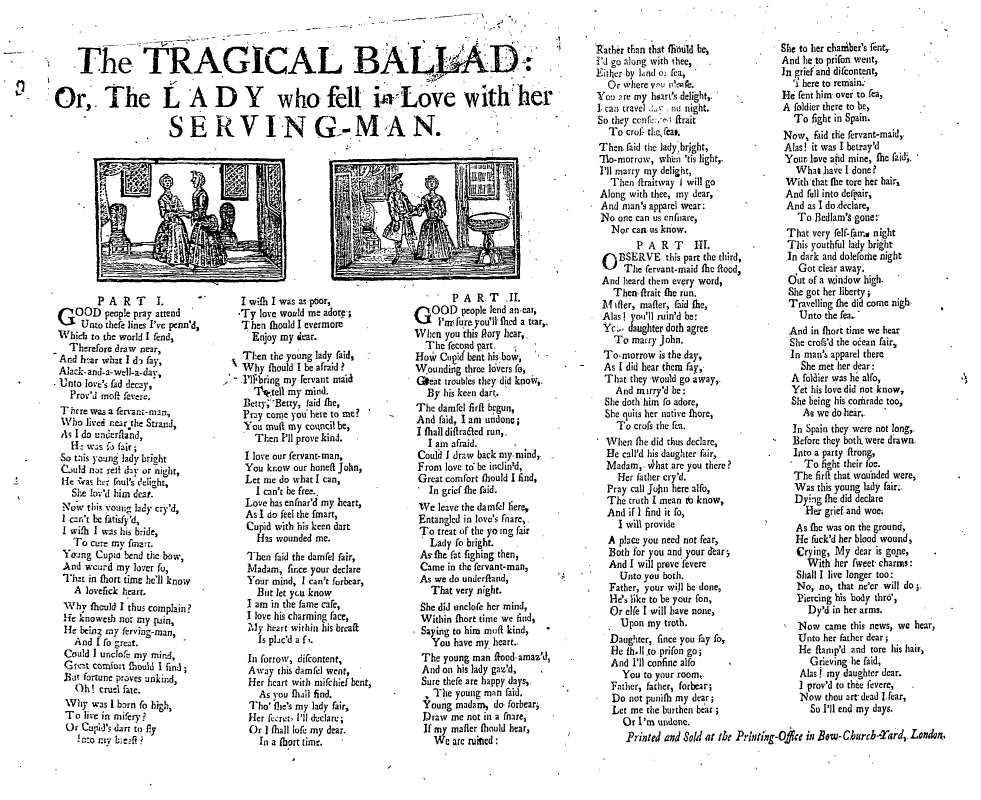
Broadside (music)
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
.png)