|
Ethiopian Book Of The Dead
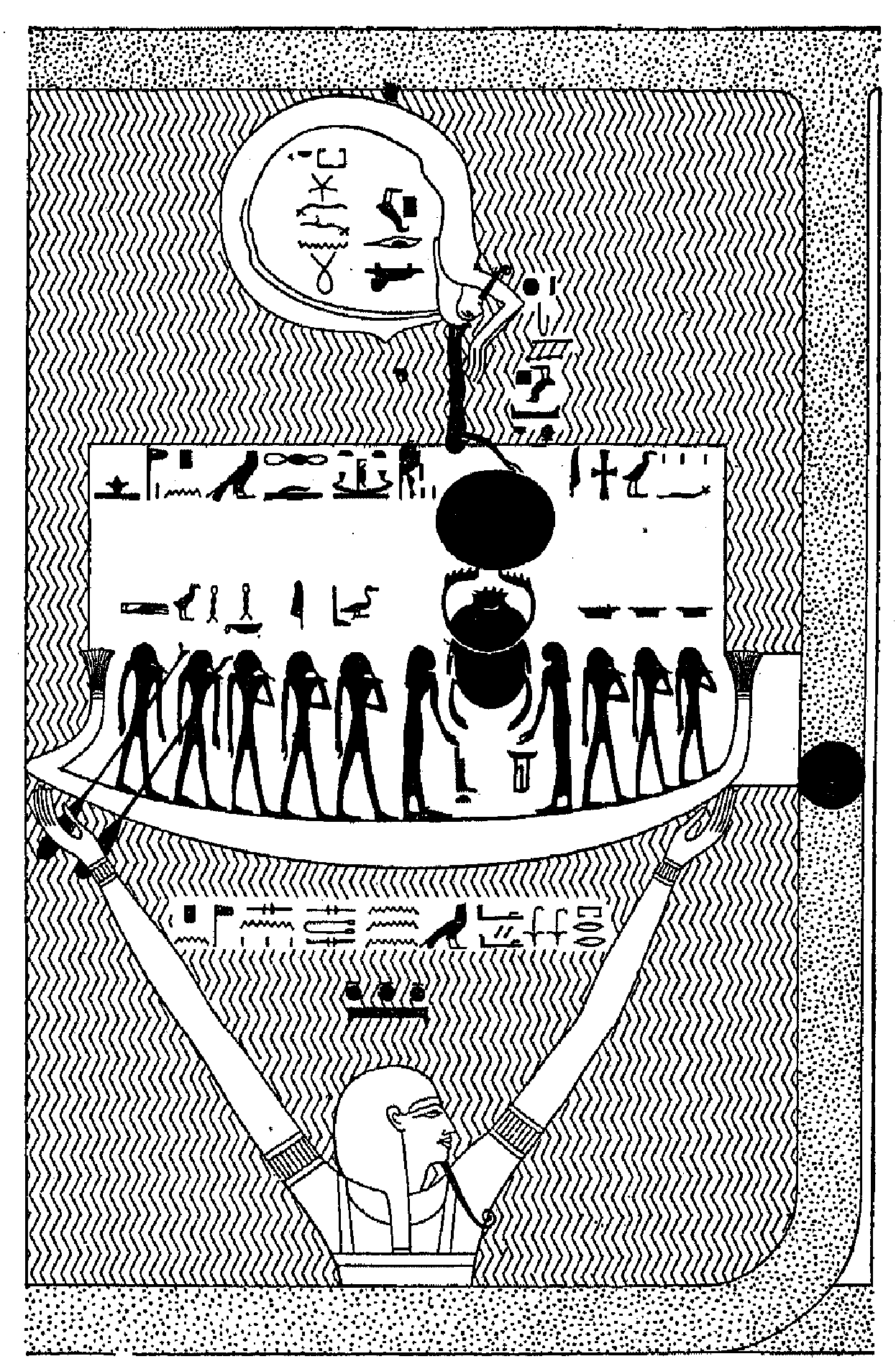
The ''Bandlet of Righteousness'' ( Ethiopic: ''Lefāfa Ṣedeḳ''), also known as the ''Ethiopian Book of the Dead'', is an anonymous Ethiopic magico-religious funerary text. It consists of a frame story about how God the Father revealed the secret names of God to his son, Jesus Christ, who then gave them to his mother, the Virgin Mary, who passed them on to her relatives. The names revealed in the work function as an amulet. When written out on a scroll and wrapped around the deceased, they will bring him to Heaven. The text cannot be traced earlier than the sixteenth century. Two copies are known. It fuses Christian and non-Christian elements. Most notably, it has strong similarities to the Ancient Egyptian ''Book of the Dead''. Origins and manuscripts The ''Bandlet'' is anonymous and its date of composition is unknown. The existing redaction is probably not earlier than the sixteenth century. It is a long text that "takes up an entire scroll". Two manuscripts are known t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Ephesus
The Council of Ephesus was a council of Christian bishops convened in Ephesus (near present-day Selçuk in Turkey) in AD 431 by the Roman Emperor Theodosius II. This third ecumenical council, an effort to attain consensus in the church through an assembly representing all of Christendom,Richard Kieckhefer (1989). "Papacy". ''Dictionary of the Middle Ages''. . confirmed the original Nicene Creed, * * * and condemned the teachings of Nestorius, Patriarch of Constantinople, who held that the Virgin Mary may be called the ''Christotokos'', "Christ-bearer" but not the '' Theotokos'', "God-bearer". It met in June and July 431 at the Church of Mary in Ephesus in Anatolia. Background Nestorius' doctrine, Nestorianism, which emphasized the distinction between Christ's human and divine natures and argued that Mary should be called ''Christotokos'' (Christ-bearer) but not ''Theotokos'' (God-bearer), had brought him into conflict with other church leaders, most notably Cyril, Pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Apocrypha
The Jewish apocrypha () are books written in large part by Jews, especially during the Second Temple period, not accepted as sacred manuscripts when the Hebrew Bible was canonized. Some of these books are considered sacred by most Christians, and are included in their versions of the Old Testament. The Jewish apocrypha is distinctive from the New Testament apocrypha and biblical apocrypha as it is the only one of these collections which works within a Jewish theological framework. Apocrypha in Judaism Certain circles in Judaism, such as the Essenes in Judea and the Therapeutae in Egypt, were said to have a "secret" literature (see Dead Sea scrolls). The Pharisees were also familiar with these texts. A large part of this "secret" literature was the apocalypses. Based on unfulfilled prophecies, these books were not considered scripture, but rather part of a literary form that flourished from 200 BCE to 100 CE. These works usually bore the names of ancient Hebrew worthies to estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnostic Texts
Gnosticism used a number of religious texts that are preserved, in part or whole, in ancient manuscripts, or lost but mentioned critically in Patristic writings. Gnostic texts Gnostic texts preserved before 1945 Prior to the discovery at Nag Hammadi, only the following texts were available to students of Gnosticism. Reconstructions were attempted from the records of the heresiologists, but these were necessarily coloured by the motivation behind the source accounts. * Works preserved by the Church: ** ''Acts of Thomas'' (Especially ''Hymn of the Pearl'' or ''The Hymn of the Robe of Glory'') ** ''The Acts of John'' (Especially ''The Hymn of Jesus'') * The Bruce Codex (purchased in 1769 by James Bruce): ** '' Books of Jeu'', also known as ''The Gnosis of the Invisible God'' ** The '' Untitled Text'' * The Askew Codex (British Museum, bought in 1784): ** ''Pistis Sophia: Books of the Savior'' * The Berlin Codex or The Akhmim Codex (found in Akhmim, Egypt; bought in 1896 by Carl Rei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Egypt
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt , common_name = Egypt , subdivision = Province , nation = the Roman Empire , era = Late antiquity , capital = Alexandria , title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis , image_map = Roman Empire - Aegyptus (125 AD).svg , image_map_caption = Province of Aegyptus in AD 125 , year_start = 30 BC , event_start = Conquest of Ptolemaic Kingdom , event1 = Formation of the Diocese , date_event1 = 390 , year_end = 641 , event_end = Muslim conquest , life_span = 30 BC – 641 AD , stat_year1 = 1st century AD , stat_pop1 = . , today = Egypt , p1 = Ptolemaic Kingdom , flag_p1 = Ptolemaic-Empire 200bc.jpg , s1 = Sasanian Egypt , flag_s1 = Derafsh Kaviani flag of the late Sassanid Empire.svg , s2 = Rashidun Caliphate , flag_s2 = Mohammad adil-Rashidun-empire-at-its-peak-close.PNG , demonym= Egypt ( ; ) was a subdivision of the Roman Empire fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallis Budge
Sir Ernest Alfred Thompson Wallis Budge (27 July 185723 November 1934) was an English Egyptologist, Orientalist, and philologist who worked for the British Museum and published numerous works on the ancient Near East. He made numerous trips to Egypt and the Sudan on behalf of the British Museum to buy antiquities, and helped it build its collection of cuneiform tablets, manuscripts, and papyri. He published many books on Egyptology, helping to bring the findings to larger audiences. In 1920, he was knighted for his service to Egyptology and the British Museum. Earlier life E. A. Wallis Budge was born in 1857 in Bodmin, Cornwall, to Mary Ann Budge, a young woman whose father was a waiter in a Bodmin hotel. Budge's father has never been identified. Budge left Cornwall as a boy, and eventually came to live with his maternal aunt and grandmother in London. Budge became interested in languages before he was ten years old, but left school at the age of twelve in 1869 to work as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prayer Of Our Lady After Her Departure From Jerusalem
Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through deliberate communication. In the narrow sense, the term refers to an act of supplication or intercession directed towards a deity or a deified ancestor. More generally, prayer can also have the purpose of thanksgiving or praise, and in comparative religion is closely associated with more abstract forms of meditation and with charms or spells. Prayer can take a variety of forms: it can be part of a set liturgy or ritual, and it can be performed alone or in groups. Prayer may take the form of a hymn, incantation, formal creedal statement, or a spontaneous utterance in the praying person. The act of prayer is attested in written sources as early as 5000 years ago. Today, most major religions involve prayer in one way or another; some ritualize the act, requiring a strict sequence of actions or placing a restriction on who is permitted to pray, while others teach that pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phanuel (angel)
Phanuel is the name given to the fourth angel who stands before God in the '' Book of Enoch'' (ca. 300 BC), after the angels Michael, Raphael, and Gabriel. Other spellings of Phanuel ( or פְּנִיאֵל ''Pənūʾēl/Pənīʾēl,'' Tiberian: ''Pănūʾēl/Pănīʾēl'') include Panuel, Paniel, Peniel, Penuel, Fanuel and Feniel. As Panuel his name means "God has turned", but as Paniel his name means "God is my face". Narrative Phanuel was one of the four voices Enoch heard praising God. Interpretations As an angel, Phanuel is reputedly a member of the four Angels of Presence. In 1st Enoch, he is also listed as an angel of exorcism (he is heard "expelling Satans"). Phanuel has also been linked with the Angel of Penance mentioned in the Shepherd of Hermas. Some associate Phanuel with Uriel Uriel or Auriel ( he, אוּרִיאֵל ''ʾŪrīʾēl'', " El/God is my flame"; el, Οὐριήλ ''Oúriēl''; cop, ⲟⲩⲣⲓⲏⲗ ''Ouriēl''; it, Uriele; Geʽez and Amhari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphael (archangel)
Raphael (, "God has healed"), ''Rəfāʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Răp̄āʾēl''; lit. 'God has healed'; grc, Ραφαήλ, ''Raphaḗl''; cop, ⲣⲁⲫⲁⲏⲗ, ''Rafaêl''; ar, رافائيل, ''Rāfā’īl'', or , ''Isrāfīl''; am, ሩፋኤል, ''Rufaʾel''. is an archangel first mentioned in the Book of Tobit and in 1 Enoch, both estimated to date from between the 3rd and 2nd century BCE. In later Jewish tradition, he became identified as one of the three heavenly visitors entertained by Abraham at the Oak of Mamre. He is not named in either the New Testament or the Quran, but later Christian tradition identified him with healing and as the angel who stirred waters in the Pool of Bethesda in John 5:2–4, and in Islam, where his name is Israfil, he is understood to be the unnamed angel of Quran 6:73, standing eternally with a trumpet to his lips, ready to announce the Day of Judgment. In Gnostic tradition, Raphael is represented on the Ophite Diagram. Origins in post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel (archangel)
In Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity and Islam), Gabriel (); Greek language, Greek: grc, Γαβριήλ, translit=Gabriḗl, label=none; Latin language, Latin: ''Gabriel''; Coptic language, Coptic: cop, Ⲅⲁⲃⲣⲓⲏⲗ, translit=Gabriêl, label=none; Amharic: am, ገብርኤል, translit=Gabrəʾel, label=none; arc, ܓ݁ܰܒ݂ܪܺܝܐܝܶܠ, translit=Gaḇrīʾēl; ar, جِبْرِيل, Jibrīl, also ar, جبرائيل, Jibrāʾīl or ''Jabrāʾīl'', group="N" is an archangel with power to announce God's will to men. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament, and the Quran. Many Christian traditions — including Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Roman Catholicism — revere Gabriel as a saint. In the Hebrew Bible, Gabriel appears to the prophet Daniel (biblical figure), Daniel to explain his visions (Daniel 8:15–26, Daniel 9, 9:21–27). The archangel also appears in the Book of Enoch and other ancient Jewish writings not preserved in Heb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael (archangel)
Michael (; he, מִיכָאֵל, lit=Who is like El od, translit=Mīḵāʾēl; el, Μιχαήλ, translit=Mikhaḗl; la, Michahel; ar, ميخائيل ، مِيكَالَ ، ميكائيل, translit=Mīkāʾīl, Mīkāl, Mīkhāʾīl), also called Saint Michael the Archangel, Saint Michael the Taxiarch in Orthodoxy and Archangel Michael is an archangel in Judaism, Christianity, Islam and the Baha'i faith. The earliest surviving mentions of his name are in 3rd- and 2nd-century BC Jewish works, often but not always apocalyptic, where he is the chief of the angels and archangels and responsible for the care of Israel. Christianity adopted nearly all the Jewish traditions concerning him, and he is mentioned explicitly in Revelation 12:7–12, where he does battle with Satan, and in the Epistle of Jude, where the author denounces heretics by contrasting them with Michael. Second Temple Jewish writings The earliest surviving mention of Michael is in a 3rd century BC Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)
