|
Esperanto In Slovakia
Esperanto has been used in Slovakia since the 19th century. The Slovak Esperanto movement was suppressed by Nazi and Communist regimes in the 20th century before being restored in 1969. Slovakia is home to the Summer Esperanto Study and the Conference on the Application of Esperanto in Science and Technology. Linguistics The Slovak language has been compared with Esperanto due to its high intelligibility to speakers of other Slavic languages, and it has been described as the "Slavic Esperanto". The Esperanto word for Slovakia is . History Czechoslovakia was the only country in Eastern Europe where the Esperanto movement was not condemned by the government during the interwar period. By 1928, there were 8,967 recorded Esperantists in Czechoslovakia. Radio in Czechoslovakia began airing Esperanto broadcasts in the 1930s. The German Esperanto League in Czechoslovakia was dissolved in 1938 in response to the occupation of Czechoslovakia. Interhelpo was founded as a socialist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Czechoslovakia
The Communist Party of Czechoslovakia (Czech and Slovak: ''Komunistická strana Československa'', KSČ) was a communist and Marxist–Leninist political party in Czechoslovakia that existed between 1921 and 1992. It was a member of the Comintern. Between 1929 and 1953, it was led by Klement Gottwald. The KSČ was the sole governing party in the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic though it was a leading party along with the Slovak branch and four other legally permitted non-communist parties. After its election victory in 1946, it seized power in the 1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état and established a one-party state allied with the Soviet Union. Nationalization of virtually all private enterprises followed, and a command economy was implemented. The KSČ was committed to the pursuit of communism, and after Joseph Stalin's rise to power Marxism–Leninism became formalized as the party's guiding ideology and would remain so throughout the rest of its existence. Consequently, party ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palgrave Macmillan
Palgrave Macmillan is a British academic and trade publishing company headquartered in the London Borough of Camden. Its programme includes textbooks, journals, monographs, professional and reference works in print and online. It maintains offices in London, New York, Shanghai, Melbourne, Sydney, Hong Kong, Delhi, and Johannesburg. Palgrave Macmillan was created in 2000 when St. Martin's Press in the US united with Macmillan Publishers in the UK to combine their worldwide academic publishing operations. The company was known simply as Palgrave until 2002, but has since been known as Palgrave Macmillan. It is a subsidiary of Springer Nature. Until 2015, it was part of the Macmillan Group and therefore wholly owned by the German publishing company Holtzbrinck Publishing Group (which still owns a controlling interest in Springer Nature). As part of Macmillan, it was headquartered at the Macmillan campus in Kings Cross London with other Macmillan companies including Pan Macmil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the fifth and sixth centuries. In the seventh century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the ninth century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which then became the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
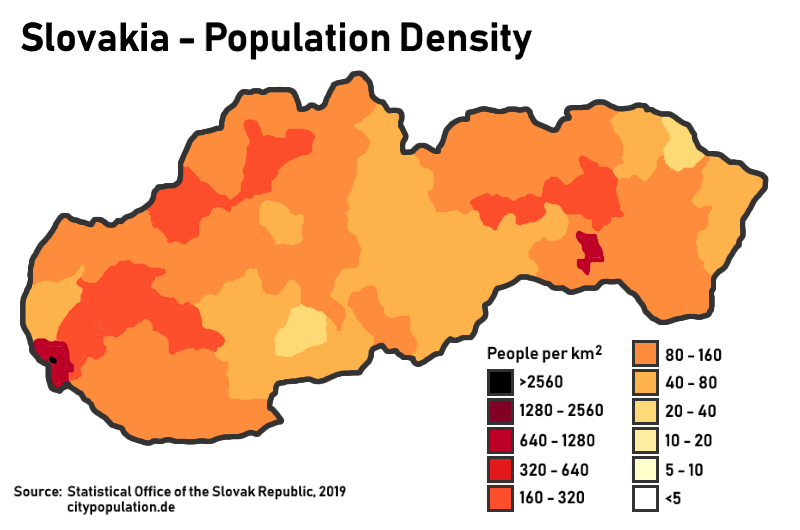
Demographics Of Slovakia
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Slovakia, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. The demographic statistics are from the Statistical Office of the SR, unless otherwise indicated. Population Total population: (as of ). Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2021. *One birth every 10 minutes *One death every 9 minutes *One net migrant every 480 minutes *Net gain of one person every 1440 minutes Population overtime Population growth rate :-0.08% (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 202nd Fertility The total fertility rate is the number of children born per woman. It is based on fairly good data for the entire period. Sources: Our World In Data and Gapminder Foundation. 1.45 children born/woman (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 211th Mother's mean age at first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperantist Of The Year
The Esperantist of the Year (''Esperantisto de la Jaro'') is an honorary designation bestowed each year by the editors of the Esperanto Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communi ...-language monthly ''La Ondo de Esperanto'' (English: ''The Wave of Esperanto''). The award recipient is selected by an international jury led by Halina Gorecka, the Russian publisher of the magazine. The Esperantist of the Year award was created in 1998. Laureates * 1998: William Auld (1924–2006), a Scottish poet and translator who wrote chiefly in Esperanto * 1999: Kep Enderby (b. 1926 in Dubbo, Australia), former president of World Esperanto Association (UEA) * 2000: three candidates received an equal number of votes and shared the award: ** Hans Bakker (b. 1937 in the Netherlands) ** Maŭro La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Baláž (Esperantist)
Peter Baláž (; born 8 October 1979 in Partizánske, Czechoslovakia), in Esperanto known as Petro (), is an Esperantist, publisher and editor; he was selected as the 2012 Esperantist of the Year. Baláž lives in his hometown of Partizánske and speaks Slovak language, Slovak, Czech language, Czech, German language, German, Polish language, Polish, Russian language, Russian and English language, English, as well as the international constructed language Esperanto.Estraro (Board) of E@I. Accessed 21 December 2012. Work After pursuing a hospitality management studies, vocational program in hospitality at ''Hotelová Akadémia Ľudovíta Wintera'' ("Ľudovít Winter Hotel Academy") in Piešťany, he worked for two years in Germany and Austria.[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Of Esperantists In The Slovakian Socialist Republic
Association may refer to: *Club (organization), an association of two or more people united by a common interest or goal *Trade association, an organization founded and funded by businesses that operate in a specific industry *Voluntary association, a body formed by individuals to accomplish a purpose, usually as volunteers Association in various fields of study *Association (archaeology), the close relationship between objects or contexts. *Association (astronomy), combined or co-added group of astronomical exposures *Association (chemistry) *Association (ecology), a type of ecological community *Genetic association, when one or more genotypes within a population co-occur *Association (object-oriented programming), defines a relationship between classes of objects *Association (psychology), a connection between two or more concepts in the mind or imagination *Association (statistics), a statistical relationship between two variables *File association, associates a file with a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Dubček
Alexander Dubček (; 27 November 1921 – 7 November 1992) was a Slovak politician who served as the First Secretary of the Presidium of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia (KSČ) (''de facto'' leader of Czechoslovakia) from January 1968 to April 1969. He attempted to reform the communist government during the Prague Spring but was forced to resign following the Warsaw Pact invasion in August 1968. During his leadership under the slogan "Socialism with a human face", Czechoslovakia lifted censorship on the media and liberalized society, fueling the so-called New Wave in filmography and paving the way for a period that became known as the Prague Spring. However, Dubček was put under pressure by Stalinists inside the party, as well as the Soviet leadership, who opposed the direction the country was taking and feared that Czechoslovakia could loosen ties with the Soviet Union and become more westernized. As a result, the country was invaded by Soviet- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Association In The Czechoslovakian Republic
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |