|
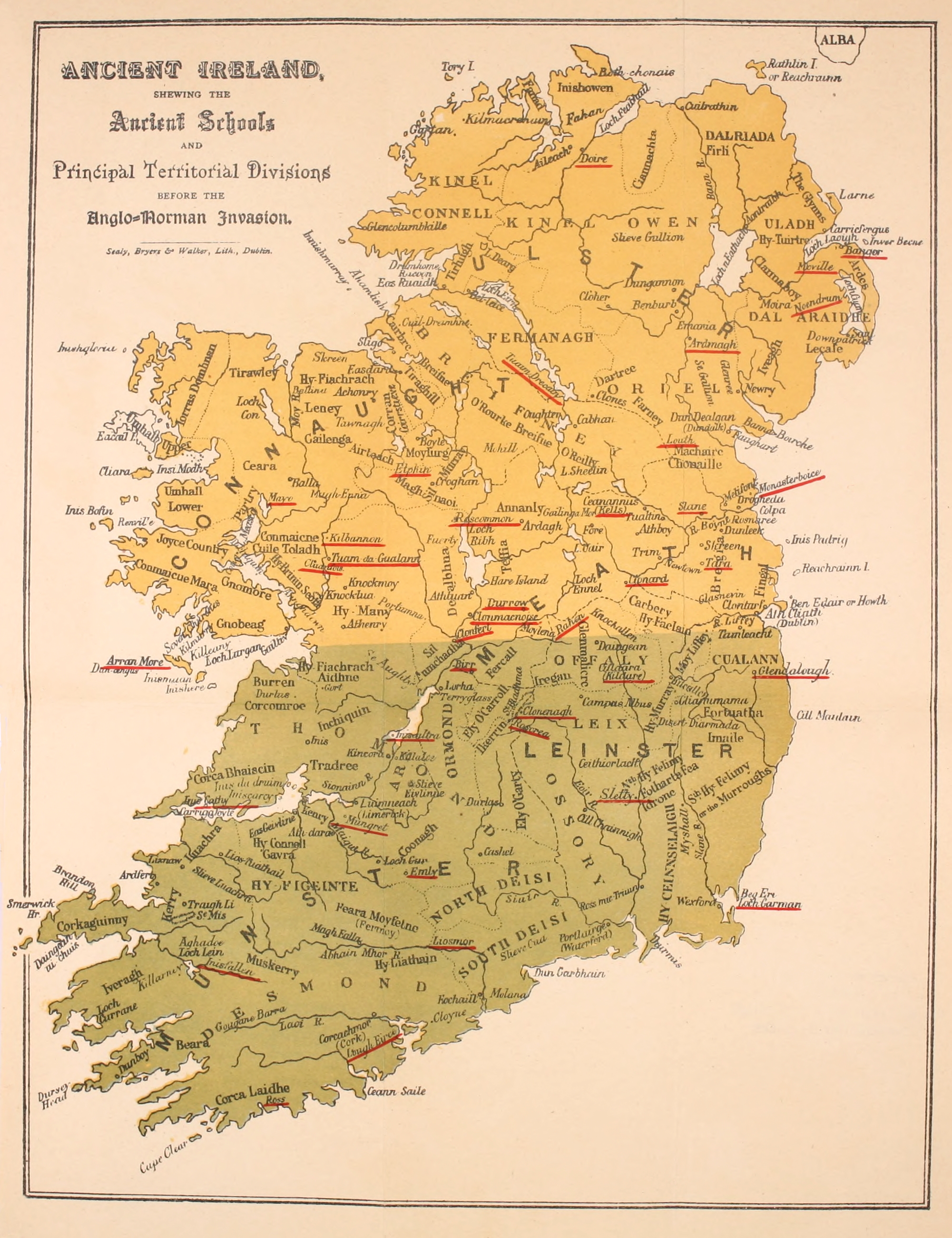
Esker Riada
The Esker Riada ( ga, Eiscir Riada) is a system of eskers that stretch across the middle of Ireland, between Dublin and Galway. Geography The Esker Riada is a collection of eskers that passes through the counties of Dublin, Meath, Kildare, Westmeath, Offaly, Leitrim, Longford, Roscommon and Galway. A large remnant of the Esker exists in the Teernacreeve region of Westmeath, and stretches from Kilbeggan to Tyrrellspass. The eskers take the form of relatively low-lying ridges composed of sand, gravel and boulders; deposited by water flowing beneath a glacier; that became exposed when the glacier melted at the end of the last ice age, around 10,000 years ago. Historical significance The Irish name 'Eiscir Riada' provides an indication of the significance of the eskers, 'Eiscir' meaning 'divide' and 'Riada' meaning 'road'. Following a battle at Maynooth, in the year 123 AD, the island of Ireland was divided into two political entities along the line of the eskers – ‘Leath Cui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esker
An esker, eskar, eschar, or os, sometimes called an ''asar'', ''osar'', or ''serpent kame'', is a long, winding ridge of stratified sand and gravel, examples of which occur in glaciated and formerly glaciated regions of Europe and North America. Eskers are frequently several kilometres long and, because of their uniform shape, look like railway embankments. Etymology The term ''esker'' is derived from the Irish word ''eiscir'' ( Old Irish: ''escir''), which means "ridge or elevation, especially one separating two plains or depressed surfaces". The Irish word was and is used particularly to describe long sinuous ridges, which are now known to be deposits of fluvio-glacial material. The best-known example of such an ''eiscir'' is the '' Eiscir Riada'', which runs nearly the whole width of Ireland from Dublin to Galway, a distance of , and is still closely followed by the main Dublin-Galway road The synonym ''os'' comes from the Swedish word ''ås'', "ridge". Geology M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leath Cuinn
Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) are legendary ancient divisions of Ireland. Leath Cuinn was the island north of the Esker Riada (east-west drumlin belt from Dublin to Galway Bay). Conn Cétchathach, for whom this division is named, was a retrospective ancestor of the Connachta and Uí Néill dynasties. Ireland's legendary ancient division into Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) resulted from the battle of Maigh Nuadad in 123 A.D. Conn, defeated by Eoghan Mor (also known as Mug Nuadat), was forced to accede to the division of Ireland into two halves: * The North - taking in Connacht, Ulster and Meath - would be Conn's Half * The South - taking in Munster, Osraighe and Leinster - would be Eoghan's Half. To solidify the arrangement, Conn's daughter, Sadhbh was married to Ailill Aulom, son of Eoghan. The Eoganacht dynasty in Munster claimed, as descendants of Oiloill Olum, the historical right as overkings of Leath Moga (i.e. over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Ireland
:Ireland is an island in Northwestern Europe in the north Atlantic Ocean. The island lies on the European continental shelf, part of the Eurasian Plate. The island's main geographical features include low central plains surrounded by coastal mountains. The highest peak is Carrauntoohil ( ga, Corrán Tuathail), which is above sea level. The western coastline is rugged, with many islands, peninsulas, headlands and bays. The island is bisected by the River Shannon, which at with a estuary is the longest river in Ireland and flows south from County Cavan in Ulster to meet the Atlantic just south of Limerick. There are a number of sizeable lakes along Ireland's rivers, of which Lough Neagh is the largest. Politically, the island consists of the Republic of Ireland, with jurisdiction over about five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, a constituent country of the United Kingdom, with jurisdiction over the remaining sixth. Located west of the island of Great Britain, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Ireland
The geology of Ireland consists of the study of the rock formations on the island of Ireland. It includes rocks from every age from Proterozoic to Holocene and a large variety of different rock types is represented. The basalt columns of the Giant's Causeway together with geologically significant sections of the adjacent coast have been declared a World Heritage Site. The geological detail follows the major events in Ireland's past based on the geological timescale. Timeline The oldest known Irish rock is about 1.7 billion years old and is found on Inishtrahull Island off the north coast of Ulster. Outcrops at Annagh Head on the Mullet Peninsula are almost as old. In other parts of Donegal, scientists have discovered rocks that originated as glacial deposits, demonstrating that at this early period, part of what was to become Ireland was in the grip of an ice age. However, because of the effects of later upheavals, it is almost impossible to sequence these early rock layers co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N6 Road (Ireland)
The N6 road is a national primary road in Ireland from junction 11 on the M4 motorway at Kinnegad to Galway city. The N6 and N4 form a continuous motorway or dual carriageway from Dublin city centre to Galway City passing in an east–west direction through the midlands of Ireland. Most of the road is motorway standard (designated as M6 motorway) with the exception of the Athlone bypass and stretches of urban road in Galway City, which are the only sections of the road that remain designated as N6 dual carriageway. There is one toll on the road outside Galway city. Major upgrades to the road were completed in December 2009 completing the first intercity motorway/dual carriageway in Ireland and the New Junctions of M6 are built and will be 164 km. History Prior to the 2005–2009 construction of the road currently designated as the N6, the designation applied to the older, parallel Dublin–Galway route which went directly through most of the now bypassed towns from Kinn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Shannon
The River Shannon ( ga, Abhainn na Sionainne, ', '), at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of the island of Ireland. The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south ( Leinster and most of Munster). (County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception.) The river represents a major physical barrier between east and west, with fewer than thirty-five crossing points between Limerick city in the south and the village of Dowra in the north. The river takes its name after ''Sionna'', a Celtic goddess. Known as an important waterway since antiquity, the Shannon first appeared in maps by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy ( 100 – 170 AD). The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonmacnoise
Clonmacnoise ( Irish: ''Cluain Mhic Nóis'') is a ruined monastery situated in County Offaly in Ireland on the River Shannon south of Athlone, founded in 544 by Saint Ciarán, a young man from Rathcroghan, County Roscommon. Until the 9th century it had close associations with the kings of Connacht. Saint Ciarán founded the monastery in the ancient territory of Uí Maine at a point where the major east–west land route ( Slighe Mhor) meets the River Shannon after crossing the bogs of Central Ireland known as the Esker Riada. The strategic location of the monastery helped it become a major center of religion, learning, craftsmanship and trade by the 9th century;Moss (2014), p. 126 and together with Clonard it was one of the most famous places in Ireland, visited by scholars from all over Europe. From the ninth until the eleventh century it was allied with the kings of Meath. Many of the high kings of Tara ( ''ardrí'') and of Connacht were buried here. Clonmacnoise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durrow Abbey
Durrow Abbey is a historic site in Durrow, County Offaly in Ireland. It is located off the N52 some 5 miles from Tullamore. Largely undisturbed, the site is an early medieval monastic complex of ecclesiastical and secular monuments, visible and sub-surface. The extant monuments at the site include a large ecclesiastical enclosure, five Early Christian grave slabs, a fine mid-ninth century high cross, a fragment of a cross shaft, a complete cross-head (housed in the National Museum of Ireland) and cross base, a holy well and other extensive archaeological features. Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath built a motte for the Abbey in 1180, and he was killed at the Abbey in 1186 by an Irishman. Early history Durrow was probably founded by Columba in the 580s. In the ''Vita Columbae'', Laisrén, who would become the third abbot of Iona, acts as a leader of the monastery. Not much is known about the early history of Durrow, although Bede says it was an important centre from which more mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonard Abbey
Clonard Abbey (Irish, ''Cluain Eraird'', or ''Cluain Iraird'', "Erard's Meadow") was an early medieval monastery situated on the River Boyne in Clonard, County Meath, Ireland. Early history The monastery was founded in about 520 by Saint Finnian, who initially constructed a single cell at the site. The original site may have been at nearby Ard Relec. According to medieval chronicles, Finnian was led to the site by an angel who told him that it would be the place of his resurrection. He was well-travelled, and based his monastery on the training he received at Tours and Llancarfan. Finnian was buried on the site after his death in about 549. During the sixth century, some of the most significant names in the history of Irish Christianity (who would go on to be known as the Twelve Apostles of Ireland) studied at the monastery. Clonard was situated on the Esker Riada, Ireland's main east-west road in early medieval times, adding to its prominence. However, it was also on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Great Roads Of Ireland
There have been routes and trackways in Ireland connecting settlements and facilitating trade since ancient times and the country now has an extensive network of public roads connecting all parts of the island. Early history The first routes in Ireland were prehistoric trackways, some of which were later developed into roads suited for wheeled vehicles. Many of Ireland's minor roads "may well have had their origin in pre-existing paths and trackways aligned in direct response to the physical environment". Traces of these ''evolved roads'' which developed over very long periods, frequently from tracks of the prehistoric period, are still evident. The routes of such roads usually followed the natural landscape, following the tops of ridges and crossing rivers and streams at fording points. There is almost no evidence that large roads were constructed in Ireland during the Stone Age. However, a very large oval henge enclosure, thought to date from c. 2500 BC (the Neolithic perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (an Caighdeán Oifigiúil, Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic languages, Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous language, indigenous to the Ireland, island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became Linguistic imperialism, dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as County Cork, Cork, County Donegal, Donegal, County Galway, Galway, and County Kerry, Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties County Mayo, Mayo, County Meath, Meath, and County Waterford, Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second language, second-language speakers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Athlone%2C_2022-12-20.jpg)
.jpg)



