|
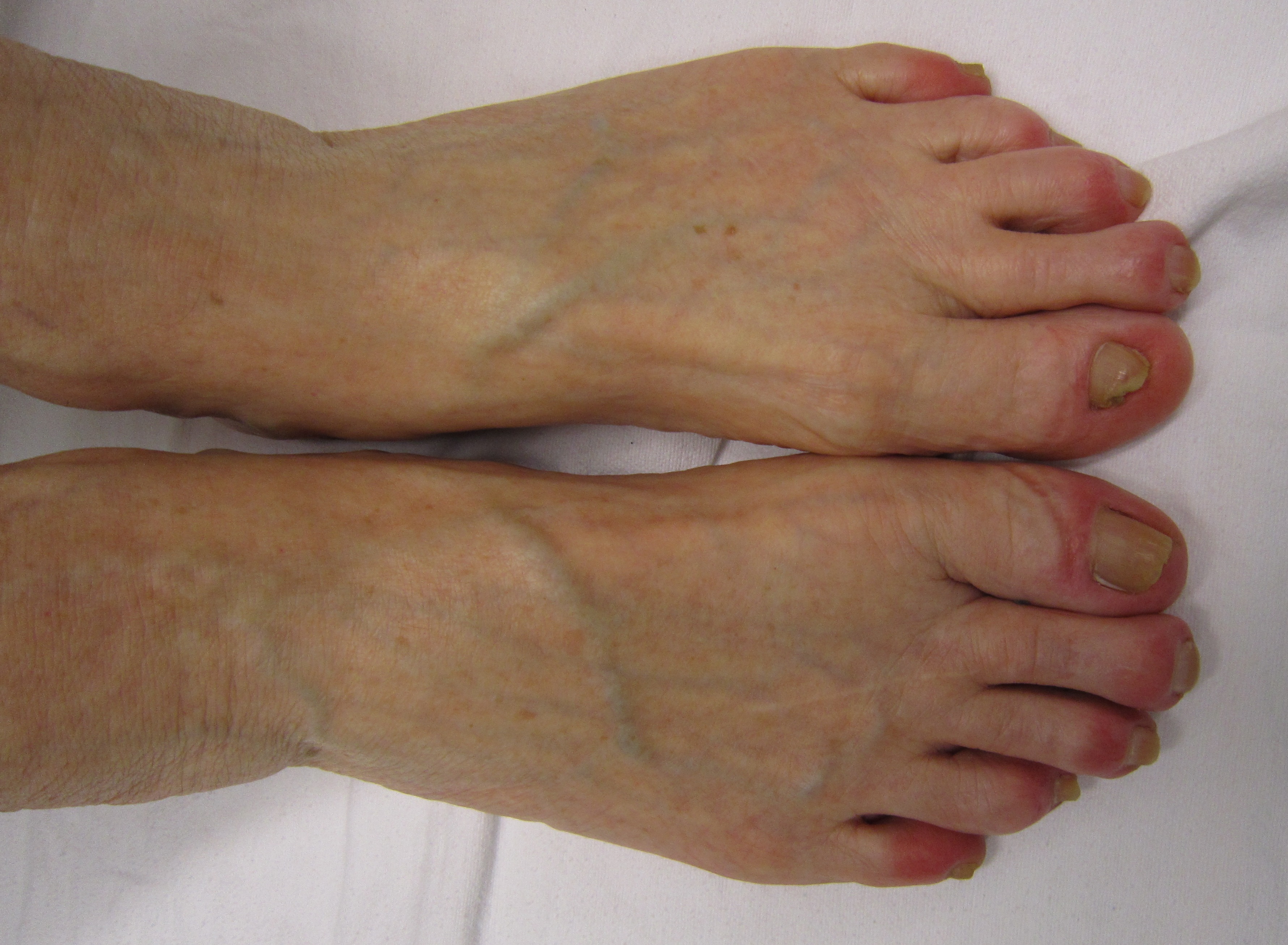
Erythema Induratum
Erythema induratum is a panniculitis on the calves. It occurs mainly in women, but it is very rare now. Historically, when it has occurred, it has often been concomitant with cutaneous tuberculosis, and it was formerly thought to be always a reaction to the TB bacteria. It is now considered a panniculitis that is not associated with just a single defined pathogen. The medical eponym Bazin disease was historically synonymous, but it applies only to the tuberculous form and is dated. Pathophysiology Predisposing factors include abnormal amount of subcutaneous fat, thick ankles and abnormally poor arterial supply. Abnormal arterial supply causes low-grade ischemia of ankle region. The ankle skin becomes sensitive to temperature changes. When weather is cold, ankle is cold, blue and often tender. In hot weather, ankle becomes hot, edematous, swollen and painful. Chilblains may be present. On palpation, small superficial and painful nodules are felt. They break down to form small and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panniculitis
Panniculitis is a group of diseases whose hallmark is inflammation of subcutaneous adipose tissue (the fatty layer under the skin – panniculus adiposus). Symptoms include tender skin nodules, and systemic signs such as weight loss and fatigue. Restated, an inflammatory disorder primarily localized in the subcutaneous fat is termed a "panniculitis", a group of disorders that may be challenging both for the clinician and the dermatopathologist. The general term for inflammation of any adipose tissue is steatitis. Signs and symptoms Panniculitis can also be classified based on the presence or absence of systemic symptoms. Panniculitis without systemic disease can be a result of trauma or cold. Panniculitis with systemic disease can be caused by: * connective tissue disorders such as lupus erythematosus or scleroderma; * lymphoproliferative disease such as lymphoma or histiocytosis; * pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer; * sarcoidosis with cutaneous involvement (seen in up to 20 pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calf (leg)
The calf ( : calves; Latin: ''sura'') is the back portion of the lower leg in human anatomy. The muscles within the calf correspond to the posterior compartment of the leg. The two largest muscles within this compartment are known together as the calf muscle and attach to the heel via the Achilles tendon. Several other, smaller muscles attach to the knee, the ankle, and via long tendons to the toes. Etymology From Middle English ''calf'', ''kalf'', from Old Norse ''kalfi'', possibly derived from the same Germanic root as English ''calf'' ("young cow"). Cognate with Icelandic ''kálfi'' ("calf of the leg"). ''Calf'' and ''calf of the leg'' are documented in use in Middle English circa AD 1350 and AD 1425 respectively. Historically, the ''absence of calf'', meaning a lower leg without a prominent calf muscle, was regarded by some authors as a sign of inferiority: ''it is well known that monkeys have no calves, and still less do they exist among the lower orders of mammals''. Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation And Dependence
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are ''linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the so-called demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, ''M. tuberculosis'' can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fastness, Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen stain, Ziehl–Neelsen, or Fluorescence, fluorescent stains such as Auramine O, auramine are used instead to identify ''M. tuberculosis'' with a microscope. The physiology of ''M. tuberculosis'' is highly aerobic organism, aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the Mantoux test, tuberculin skin test, Acid-Fast Stain, acid-fast stain, Microbiological cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Eponyms
Medical eponyms are terms used in medicine which are named after people (and occasionally places or things). In 1975, the Canadian National Institutes of Health held a conference that discussed the naming of diseases and conditions. This was reported in ''The Lancet'' where the conclusion was summarized as: "The possessive use of an eponym should be discontinued, since the author neither had nor owned the disorder." New discoveries are often attached to the people who made the discovery because of the nature of the history of medicine. * List of eponymous diseases * List of eponymous fractures * List of eponymous medical signs * List of eponymous surgical procedures * List of eponymous tests * List of human anatomical parts named after people * List of eponymous medical devices * List of eponymous medical treatments * List of medical eponyms with Nazi associations * List of orthopaedic eponyms * List of eponyms in neuroscience, neurology and neurosurgery References {{Reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilblains
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly blisters. It occurs most frequently when predisposed individuals, predominantly women, are exposed to cold and humidity. Ulcerated chilblains are referred to as kibes. Temperature-related chilblains can be prevented by keeping the feet and hands warm in cold weather and avoiding exposing these areas to extreme temperature changes. Once the diagnosis of chilblains is made, first-line treatment includes avoiding cold, damp environments and wearing gloves and warm socks. Chilblains can be idiopathic (spontaneous and unrelated to another disease), but similar symptoms may also be a manifestation of another serious medical condition that must be investigated. Related medical conditions include Raynaud syndrome, erythromelalgia, frostbite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine its size, shape, firmness, or location (for example, a veterinarian can feel the stomach of a pregnant animal to ensure good health and successful delivery). Palpation is an important part of the physical examination; the sense of touch is just as important in this examination as the sense of sight is. Physicians develop great skill in palpating problems below the surface of the body, becoming able to detect things that untrained persons would not. Mastery of anatomy and much practice are required to achieve a high level of skill. The concept of being able to detect or notice subtle tactile signs and to recognize their significance or implications is called appreciating them (just as in general vocabulary one can speak of appreciating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Antoine-Ernest Bazin
Pierre-Antoine-Ernest Bazin (20 February 1807 – 14 December 1878) was a French physician and dermatologist born in Saint-Brice-sous-Forêt. His brother, Antoine-Pierre-Louis Bazin (1799-1863), was a noted Sinologist. In 1828 he started work as a hospital interne, earning his doctorate from the faculty of Paris in 1834. In 1836 he became ''médecin des hôpitaux'', later working at the Hôpital Lourcine from 1841 to 1844, followed by three years at Hôpital Saint-Antoine. From 1847 he was departmental head at Hôpital Saint-Louis. Eponyms * Bazin's disease: Also known as erythema induratum. * Alibert-Bazin syndrome: Historical name for mycosis fungoides. Named with dermatologist Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert (1768-1837). Selected publications * ''Recherches sur la nature et le traitement des teignes'' (1853); (Research on the nature and treatment of ringworm Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ILDS
The International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) is a non-governmental organization that works closely with the World Health Organization. It was founded in 1935, but because of World War II no congresses were held until 1952. It is governed by the International Committee of Dermatology. The ILDS is the parent organization of the International Foundation for Dermatology, founded in 1987. After the publication of ICD-10, the ILDS produced a series of compatible extensions for use in dermatology Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical .... References External links Official site HistoryInternational Foundation for DermatologyApplication to Dermatology of International Classification of Disease (ICD-11) Organizations established in 1935 Dermatology organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |