|
Ermua
Ermua is a town and municipality located in the province of Biscay, in the autonomous community of Basque Country, northern Spain. In 2019, Ermua had 15,880 inhabitants. Ermua is a town in the Durangaldea comarca of the province of Biscay in northern Spain. It is situated in a steep-sided valley beside the Río Ego, a tributary of the Deba River. Because of the steep, irregular terrain, building space is limited, and Ermua is one of the most densely populated towns in the Basque country. To the north of Ermua lies the municipality of Mallabia, to the east lies Eibar and to the south lies Zaldibar. Eibar is a larger town which lies just across the provincial border, in the province of Gipuzkoa, the two towns forming a single urban area. Ermua has grown greatly in size during the 1960s and 1970s and acts as a dormitory town to Eibar, both of them being industrial towns. Ermua and Eibar are linked by the N-634 and share a common exit from the Autopista AP-8 (AP-8), the toll road th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foro Ermua
The ''Foro Ermua'' ( en, Ermua Forum) was a Spanish civic association, the membership of which was composed of Spanish citizens (most of them living in the Basque Country). It was founded on 13 January 1998; its last president was Mikel Buesa. The organisation states that its formation was brought about by the killing of Miguel Ángel Blanco, a conservative city council member in Ermua in Biscay, by members of the Basque separatist group ETA. (This assassination had taken place on 12 July 1997, several months before the Foro Ermua was founded.) Prior to the Forum's official foundation, Blanco's killing also resulted in a local movement called ''espíritu de Ermua'', or "Ermua spirit", which was a general feeling of solidarity that sprung up amongst many local people after Blanco's kidnapping and death. Members of the organisation consider its foundation to be an attempt to continue the 'Ermua spirit'. The organisation views its activities as democratic in nature and in line with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Ángel Blanco
Miguel Ángel Blanco Garrido (13 May 1968 – 13 July 1997) was a Spanish politician who was a councillor in Ermua in the Basque Country for the People's Party (PP). He was kidnapped and subsequently murdered by the separatist group ETA. Biography Early life Miguel Ángel Blanco was born on 13 May 1968 in Ermua (Biscay) into a humble family. He had a sister, María del Mar. His father, Miguel Blanco, was a construction worker and his mother, Consuelo Garrido, was a housewife. They were Galician immigrants from Xunqueira de Espadanedo (Ourense, Galicia). Consuelo died on 1 April 2020 from coronavirus, three weeks after her husband's death. Miguel Ángel Blanco graduated in economics at the Euskal Herriko Unibertsitatea in Sarriko. For a long time he worked with his father in construction, but he found work at Eman Consulting, in Eibar, where he commuted to every day by train. He also played the drums in the bands Póker and Cañaveral. He was a sports fan and his dream was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallabia
Mallabia (in Basque and officially, in Spanish: ''Mallavia'') is an elizate, town and municipality located in the province of Biscay, in the Basque Country, northern Spain. Mallabia is part of the ''comarca'' of Durangaldea and has a population of 1.135 inhabitants as of 2006 and according to the Spanish National Statistics Institute. Etymology The etymology of the word ''Mallabia'' may come from the Basque word ''malla'' ("step", "level" or "height") and ''bi(a)'' ("two" or "the one with two"), then refers to the place with "two levels" or "two heights". History As it is common with the elizates, the date of foundation of Mallabia is unknown. Its origin is linked with the old ''Tierra Llana'' (Spanish for "flat lands") of the ancient ''merindad of Durango''. At some point, it possibly split from the elizate of Zenarruza (in which lands the elizate of Ermua was founded). Since 1635, Mallabia had voice and right to vote in the ''Juntas of Guerediaga'', where it occupied the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durangaldea
Durangaldea (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Duranguesado'') is a comarcas of Spain, comarca of Biscay located in the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, Spain. It is one of the seven ''eskualdeak/comarcas'' or regions that compose the province of Biscay. The capital city of Durangaldea is Durango, Biscay, Durango. Geography Durangaldea is located at the southeast of the province of Biscay, limiting with the provinces of Gipuzkoa and Álava. It spans the territory between Oiz mountain and the border with the province of Álava in the south. Its total area is . Most of the towns that compose the comarca are located on a great valley formed by the Ibaizabal river, that crosses it from east to west. Otxandio is the only town that belongs to Durangaldea but is not part of the valley. History Durangaldea (also known by its Spanish name, Duranguesado) was during the Middle Ages a district apart from Biscay (the ''Señorío'') and a dependency of Navarre, but was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ETA (separatist Group)
ETA, an acronym for Euskadi Ta Askatasuna ("Basque Homeland and Liberty"ETA BASQUE ORGANIZATION Encyclopaedia Britannica 20 October 2011 or "Basque Country and Freedom"), was an armed Basque nationalism, Basque nationalist and far left separatism, separatist organization in the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country (in northern Spain and southwestern France). The group was founded in 1959 and later evolved from a group promoting traditional Basque culture to a paramilitary group engaged in a violent campaign of bombing, assassinations, and kidnappings in the Southern Basque Country and throughout Spanish territory. Its goal was gaining independence for the Basque Country. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopista AP-8
The Autopista AP-8 is a highway ( autopista) in the north of Spain and crosses the Basque Country from east to west. It is known as the Autopista del Cantábrico (highway of the Cantabrian) and connects the French border with Bilbao. This toll road passes Donostia-San Sebastián, Zarautz, Eibar and Durango. At Bilbao the Autopista AP-8 changes into the Autovía A-8, which continues along the Spanish northern coast to Gijón Gijón () or () is a city and municipality in north-western Spain. It is the largest city and municipality by population in the autonomous community of Asturias. It is located on the coast of the Cantabrian Sea in the Bay of Biscay, in the cent ... and eventually the region of Galicia. List of junctions References {{DEFAULTSORT:AP-8 Roads in the Basque Country (autonomous community) Autopistas and autovías in Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaldibar
Zaldibar (in Basque and officially, in es, Zaldívar) is an elizate, town and municipality located in the province of Biscay, in the Basque Country, Spain. Zaldibar is part of the ''comarca'' of Durangaldea and has a population of 3,043 inhabitants as of 2019 and according to the Spanish National Statistics Institute. Etymology ''Zaldibar'' can be translated from Basque as "horse valley", from ''zaldi'' (horse) and ''ibar'' (valley). The coat of arms of the town then includes a horse. ''Zaldívar'' is the name in Spanish. However, the town was named ''Zaldua'' (Basque) or ''Zaldúa'' (Spanish) until 1932. ''Zaldua'' is then translated from Basque to Spanish as "el soto", which might be referred to a ''sotobosque'', Spanish word for understory. "Valley of the Soto" is then another possible origin of the current name. Currently, ''Zaldua'' is considered an archaism and it is not used, being since 1980 ''Zaldibar'' the official name of the municipality. History The eliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities In Biscay
Biscay is a province in the autonomous community of the Basque Country, Spain. It is divided into 111 municipalities. See also *Geography of Spain *List of cities in Spain {{Municipalities of Spain Biscay Biscay (; eu, Bizkaia ; es, Vizcaya ) is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country, heir of the ancient Lordship of Biscay, lying on the south shore of the eponymous bay. The capital and largest city is Bilbao. B ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eibar
Eibar ( eu, Eibar, es, Éibar) is a city and municipality within the province of Gipuzkoa, in the Basque Country of Spain. It is the head town of Debabarrena, one of the '' eskualde / comarca'' of Gipuzkoa. Eibar has 27,138 inhabitants ( Eustat, 2018). Its chief industry is metal manufacturing, and has been known since the 16th century for the manufacture of armaments, particularly finely engraved small arms. It was also the home of Serveta scooters. It is home to the SD Eibar football team. Geography Eibar lies at an altitude of 121m above sea level, in the west of the province of Gipuzkoa, right next to Biscay. Eibar has an oceanic climate. The town lies in a narrow valley in a mountainous area, the highest mountains are between 700 and 800 metres high. Eibar is traversed by river Ego, which is a tributary of the Deba. Apart from the urban area, the municipality consists of five rural neighbourhoods: Otaola-Kinarraga, Aginaga, Arrate, Mandiola and Gorosta. History The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Code
A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal address for the purpose of sorting mail. the Universal Postal Union lists 160 countries which require the use of a postal code. Although postal codes are usually assigned to geographical areas, special codes are sometimes assigned to individual addresses or to institutions that receive large volumes of mail, such as government agencies and large commercial companies. One example is the French CEDEX system. Terms There are a number of synonyms for postal code; some are country-specific; * CAP: The standard term in Italy; CAP is an acronym for ''codice di avviamento postale'' (postal expedition code). * CEP: The standard term in Brazil; CEP is an acronym for ''código de endereçamento postal'' (postal addressing code). * Eircode: Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
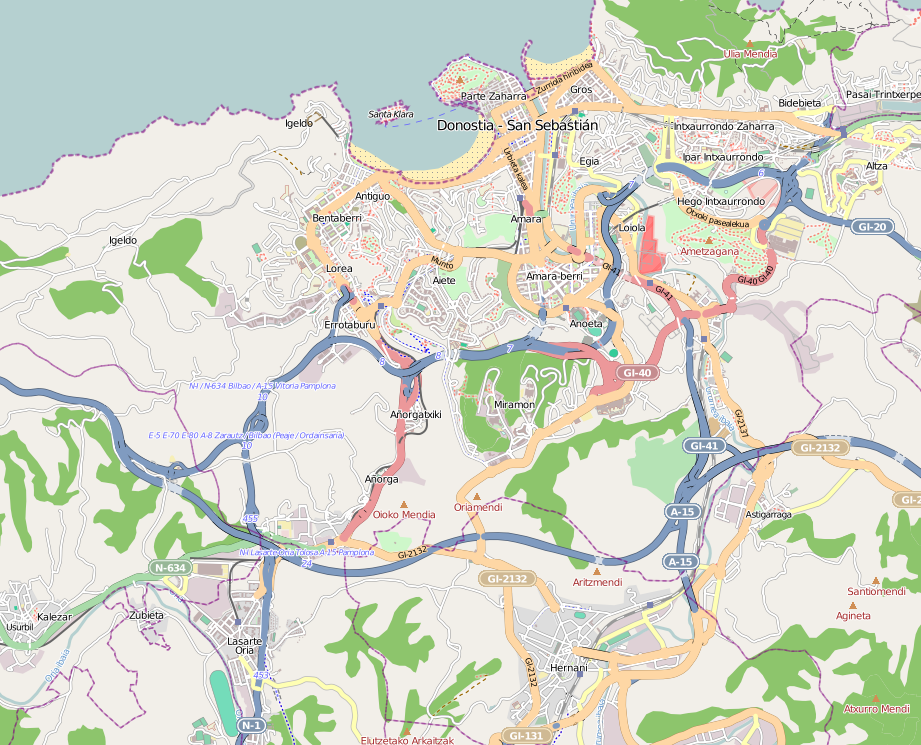
San Sebastián
San Sebastian, officially known as Donostia–San Sebastián (names in both local languages: ''Donostia'' () and ''San Sebastián'' ()) is a city and Municipalities of Spain, municipality located in the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Autonomous Community, Spain. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Biscay, from the France–Spain border. The capital city of the province of Gipuzkoa, the municipality's population is 188,102 as of 2021, with its metropolitan area reaching 436,500 in 2010. Locals call themselves ''donostiarra'' (singular), both in Spanish and Basque language, Basque. It is also a part of Basque Eurocity Bayonne-San Sebastián. The main economic activities are almost entirely service sector, service-based, with an emphasis on commerce and tourism, as it has long been one of the most famous tourist attraction, tourist destinations in Spain. Despite the city's small size, events such as the San Sebastián International Film Festival and the San Sebastia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Nationalism
The creation of the tradition of the political community of Spaniards as common destiny over other communities has been argued to trace back to the Cortes of Cádiz. Revisiting the history of Spain, after 1812 Spanish liberalism tended to take for granted the national conscience and the Spanish nation. During the first half of 20th century (notably during the dictatorship of Primo de Rivera), a new brand of Spanish nationalism with marked military flavour vouching for authoritarian stances (as well as promoting policies favouring the Spanish language against the other languages in the country) as means of country modernization was brought forward from the conservative camp, fusing regenerationist principles with traditional Spanish nationalism. The authoritarian national ideal resumed during the Francoist dictatorship, in the form of National-Catholicism, which was in turn complemented by the myth of the Hispanidad. Identified with Francoism, positive affirmation of Spanish nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |