|
Erlanger's Lark
Erlanger's lark (''Calandrella blanfordi erlangeri'') is a small passerine bird of the lark family endemic to the highlands of Ethiopia. The name of this bird commemorates the German ornithologist Carlo von Erlanger Carlo von Erlanger (5 September 1872 – 4 September 1904) was a German ornithologist and explorer born in Ingelheim am Rhein. He was a cousin to musicologist Rodolphe d'Erlanger (1872-1932). ''(See: Erlanger family tree).'' He studied ornitholo .... It is considered to be a subspecies of Blanford's lark. Alternate names include Erlanger's red-capped lark, Erlanger's short-toed lark and Ethiopian short-toed lark. References Updates to ''Birds of the World: A Checklist'' by James F. Clements. Fifth Edition. 2000. {{alaudidae-stub Erlanger's lark Endemic birds of Ethiopia Erlanger's lark Taxa named by Oscar Neumann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscar Rudolph Neumann
Oscar Rudolph Neumann (3 September 1867 in Berlin – 17 May 1946 in Chicago) was a German ornithologist and naturalist who explored and collected specimens in Africa. He fled via Cuba and settled in the United States to escape Nazi persecution of Jews. Neumann's starling (''Onychognathus neumanni'') and several other species are named after him. Neumann was born in wealthy Jewish family, the son of Maximilian and Anna née Meyer. A younger sister of his was Elsa Neumann (1872-1902) who became one of the first physics doctorates from Berlin University. Another sister Alice was a sculptor. He travelled to German East Africa across Tanganyika, Uganda and Kenya in 1892 and collected for the Berlin Museum publishing descriptions. In 1899 he accompanied Baron Carlo von Erlanger through Somaliland and southern Ethiopia, collecting birds that went to Lord Walter Rothschild's bird collection in Tring. In 1915 he went to New Guinea and also made an expedition to Sulawesi in 1938 sponso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passerine
A passerine () is any bird of the order Passeriformes (; from Latin 'sparrow' and '-shaped'), which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines are distinguished from other orders of birds by the arrangement of their toes (three pointing forward and one back), which facilitates perching. With more than 140 families and some 6,500 identified species, Passeriformes is the largest clade of birds and among the most diverse clades of terrestrial vertebrates, representing 60% of birds.Ericson, P.G.P. et al. (2003Evolution, biogeography, and patterns of diversification in passerine birds ''J. Avian Biol'', 34:3–15.Selvatti, A.P. et al. (2015"A Paleogene origin for crown passerines and the diversification of the Oscines in the New World" ''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'', 88:1–15. Passerines are divided into three clades: Acanthisitti (New Zealand wrens), Tyranni (suboscines), and Passeri (oscines or songbirds). The passeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lark
Larks are passerine birds of the family Alaudidae. Larks have a cosmopolitan distribution with the largest number of species occurring in Africa. Only a single species, the horned lark, occurs in North America, and only Horsfield's bush lark occurs in Australia. Habitats vary widely, but many species live in dry regions. When the word "lark" is used without specification, it often refers to the Eurasian skylark ''(Alauda arvensis)''. Taxonomy and systematics The family Alaudidae was introduced in 1825 by the Irish zoologist Nicholas Aylward Vigors as a subfamily Alaudina of the finch family Fringillidae. Larks are a well-defined family, partly because of the shape of their . They have multiple scutes on the hind side of their tarsi, rather than the single plate found in most songbirds. They also lack a pessulus, the bony central structure in the syrinx of songbirds. They were long placed at or near the beginning of the songbirds or oscines (now often called Passeri), just afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Von Erlanger
Carlo von Erlanger (5 September 1872 – 4 September 1904) was a German ornithologist and explorer born in Ingelheim am Rhein. He was a cousin to musicologist Rodolphe d'Erlanger (1872-1932). ''(See: Erlanger family tree).'' He studied ornithology at the University of Lausanne, and performed wildlife studies in the Tunisian desert from 1893 to 1897. On his return to Europe he continued his studies at Cambridge and Berlin. In 1900 and 1901 with Oscar Rudolph Neumann, he went to East Africa (what is now Ethiopia and Somalia) and investigated and collected many thousands of insect and avian specimens. Erlanger died in an automobile accident in Salzburg on 4 September 1904, one day shy of his 32nd birthday. Erlanger is credited with naming 40 new ornithological taxa, and has several zoological species named after him, such as: * Erlanger's lark, ''Calandrella erlangeri'' () *'' Ptychadena erlangeri'' (), an Ethiopian frog *''Lamprophis erlangeri'' , an Ethiopian snake * Erlanger’s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
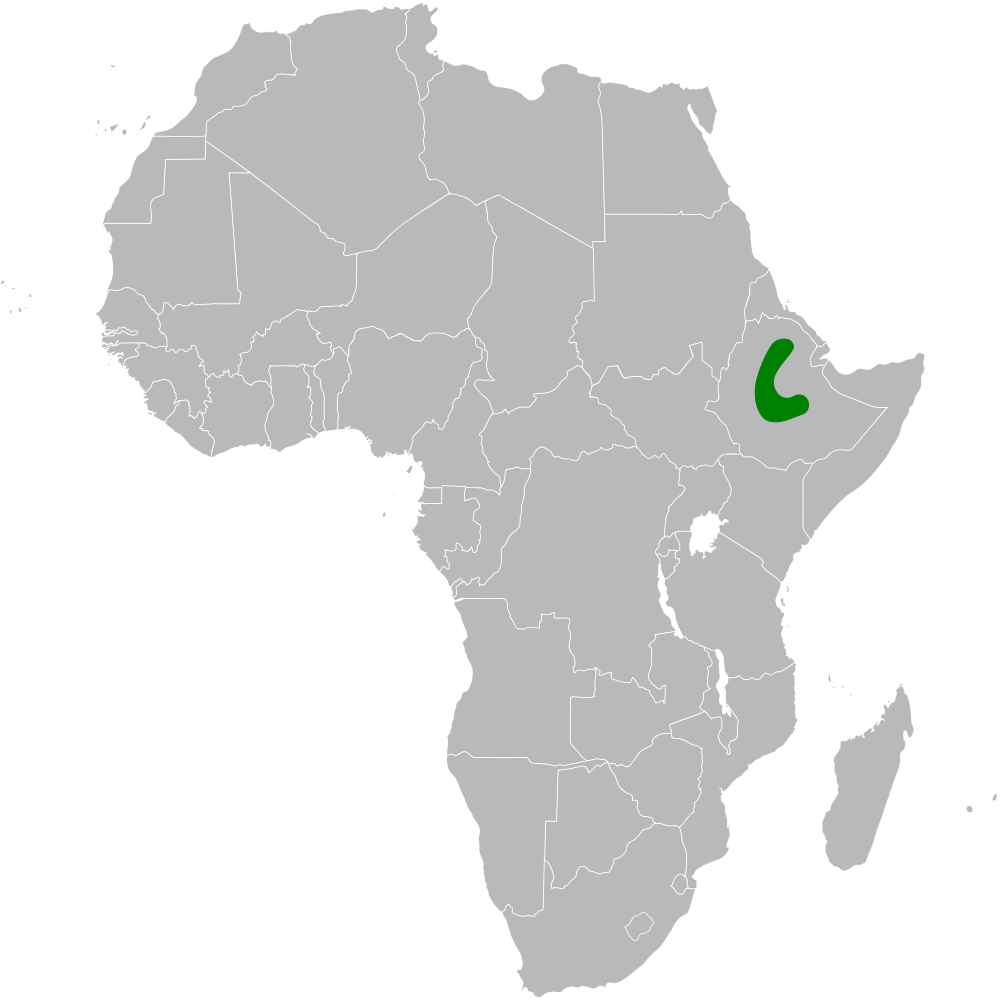
Calandrella Erlangeri Distribution Map
''Calandrella'' is a genus of larks in the family Alaudidae. Taxonomy and systematics The genus ''Calandrella'' was established by the German naturalist Johann Jakob Kaup in 1829 with the greater short-toed lark as the type species. The genus name is a diminutive of Ancient Greek ''kalandros'', the calandra lark. Four of the species in the genus use the shortened name of short-toed lark as an alternate name. Extant species Six species are recognized in the genus: Extinct species At least one fossil species is included in this genus: * †''Calandrella gali'' (late Miocene of Polgardi, Hungary) Former species Some authorities have classified the following species as belonging to the genus ''Calandrella'': * Buckley's lark (as ''Calandrella buckleyi'') * Obbia lark (as ''Calandrella obbiensis'') * Sclater's lark (as ''Calandrella sclateri'') * Stark's lark (as ''Calandrella starki'') * Masked lark (as ''Calandrella personata'') * Botha's lark (as ''Calandrella fringillaris'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanford's Lark
Blanford's lark or Blanford's short-toed lark (''Calandrella blanfordi'') is a small passerine bird of the lark family, Alaudidae, which is native to north-eastern Africa. Its common name commemorates the English zoologist William Thomas Blanford. Taxonomy and systematics Blanford's lark was formerly included in either the greater short-toed lark (''C. brachydactyla'') or the red-capped lark (''C. cinerea'') but is now commonly treated as a separate species. Alternate names for Blanford's lark include Blandford's lark, Blandford's short-toed lark and Blanford's red-capped lark. Subspecies Two subspecies are recognized: * ''C. b. blanfordi'' - ( Shelley, 1902): Found in northern Eritrea * ''C. b. erlangeri'' - Erlanger's lark- (Neumann, 1906): Found in Ethiopia Description Blanford's lark is 14–15 centimetres long. The upperparts are pale sandy-brown with some darker streaking and the crown is rufous. The underparts are pale and plain apart from a small dark patch on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calandrella
''Calandrella'' is a genus of larks in the family Alaudidae. Taxonomy and systematics The genus ''Calandrella'' was established by the German naturalist Johann Jakob Kaup in 1829 with the greater short-toed lark as the type species. The genus name is a diminutive of Ancient Greek ''kalandros'', the calandra lark. Four of the species in the genus use the shortened name of short-toed lark as an alternate name. Extant species Six species are recognized in the genus: Extinct species At least one fossil species is included in this genus: * †''Calandrella gali'' (late Miocene of Polgardi, Hungary) Former species Some authorities have classified the following species as belonging to the genus ''Calandrella'': * Buckley's lark (as ''Calandrella buckleyi'') * Obbia lark (as ''Calandrella obbiensis'') * Sclater's lark (as ''Calandrella sclateri'') * Stark's lark (as ''Calandrella starki'') * Masked lark (as ''Calandrella personata'') * Botha's lark (as ''Calandrella fringillaris'') * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Birds Of Ethiopia
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Described In 1906
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)

