|
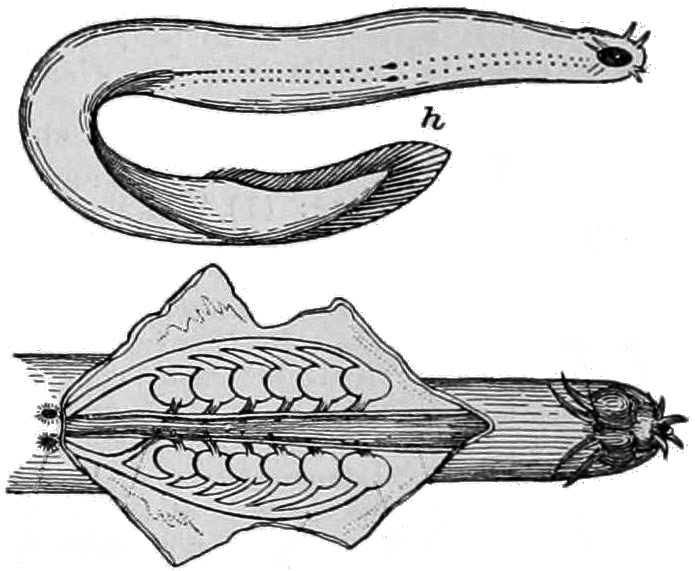
Eptatretus Deani
''Eptatretus deani'', the black hagfish, is a species of hagfish. Common to other species of hagfish, their unusual feeding habits and slime-producing capabilities have led members of the scientific and popular media to dub the hagfish as the most "disgusting" of all sea creatures. Although hagfish are sometimes called "slime eels", they are not eels at all. Description This eel-like species is uniform black, or dark brown. It can also appear prune-colored, and often piebald with light spots. The edges of the ventral finfolds and caudal may have a light colour. Unlike the Pacific hagfish, the black hagfish does not have a white ring around their gill pores. It has no true fins, but instead, one dorsal finfold, far back on its body. It has a moderately broad and round caudal, with ray-like markings. The ventral finfold is very low. The black hagfish is scaleless, and ranges from 30 - , with an average maximum overall length of . This species has four hearts, and 10 to 14 pairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagfish
Hagfish, of the class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped, slime-producing marine fish (occasionally called slime eels). They are the only known living animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, although hagfish do have rudimentary vertebrae. Along with lampreys, hagfish are jawless; the two form the sister group to jawed vertebrates, and living hagfish remain similar to hagfish from around 300 million years ago. The classification of hagfish had been controversial. The issue was whether the hagfish was a degenerate type of vertebrate-fish that through evolution had lost its vertebrae (the original scheme) and was most closely related to lampreys, or whether hagfish represent a stage that precedes the evolution of the vertebral column (the alternative scheme) as is the case with lancelets. Recent DNA evidence has supported the original scheme. The original scheme groups hagfish and lampreys together as cyclostomes (or historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barton Warren Evermann
Barton Warren Evermann (October 24, 1853 – September 27, 1932) was an American ichthyologist. Early life and education Evermann was born in Monroe County, Iowa in 1853. His family moved to Indiana while he was still a child and it was there that he grew up, completed his education, and married. Evermann graduated from Indiana University in 1886. Career For 10 years, he served as teacher and superintendent of schools in Indiana and California. While teaching in Carroll County, Indiana Evermann met fellow teacher Meadie Hawkins. They married on October 24, 1875 and had a son, Toxaway Bronte (born 1879) and a daughter, Edith (born). He was professor of biology at the Indiana State University in Terre Haute from 1886 to 1891. He lectured at Stanford University in 1893–1894, at Cornell University in 1900–1903, and at Yale University in 1903–1906. In the early 20th century, as director of the California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco, he promoted resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abyssal Zone
The abyssal zone or abyssopelagic zone is a layer of the pelagic zone of the ocean. "Abyss" derives from the Greek word , meaning bottomless. At depths of , this zone remains in perpetual darkness. It covers 83% of the total area of the ocean and 60% of Earth's surface. The abyssal zone has temperatures around through the large majority of its mass. Due to there being no light, there are no plants producing oxygen, which instead primarily comes from ice that had melted long ago from the polar regions. The water along the seafloor of this zone is actually devoid of oxygen, resulting in a death trap for organisms unable to quickly return to the oxygen-enriched water above. This region also contains a much higher concentration of nutrient salts, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and silica, due to the large amount of dead organic material that drifts down from the above ocean zones and decomposes. The water pressure can reach up to 76 megapascal. The area below the abyssal zone is the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scavengers
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feeding behavior. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by consuming dead animal and plant material. ''Decomposers'' and detritivores complete this process, by consuming the remains left by scavengers. Scavengers aid in overcoming fluctuations of food resources in the environment. The process and rate of scavenging is affected by both biotic and abiotic factors, such as carcass size, habitat, temperature, and seasons. Etymology Scavenger is an alteration of ''scavager,'' from Middle English ''skawager'' meaning "customs collector", from ''skawage'' meaning "customs", from Old North French ''escauwage'' meaning "inspection", from ''schauwer'' meaning "to inspect", of Germanic origin; akin to Old English ''scēawian'' and German ''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slime
Slime may refer to: Biology * Slime mold, a broad term often referring to roughly six groups of Eukaryotes * Biofilm, an aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other and/or to a surface * Slimy (fish), also known as the ponyfish * Snail slime, the mucus used by gastropods for locomotion * Subsurface Lithoautotrophic Microbial Ecosystem (SLiME), a biotope occupied by 'slime'. Chemistry *Gunge (UK) or Slime (US), a thick, gooey, yet runny substance used in children's TV programmes. *Flubber (material), a rubbery polymer commonly called slime. * Slimes, another name for tailings, a waste material left after the process of separation of ores Computing * SLIME, the Superior Lisp Interaction Mode for Emacs, an Emacs mode for developing Common Lisp applications Geography * Slime, a village, population 270, near Omiš, Croatia Fiction * "Slime" (short story) (Russian: тина), a short story by Anton Chekhov * "Slime", a novelette by Joseph Payne Brennan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hagfish, Eptatretus Deani Gonads 01
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and government officials in much of Europe. It became the color worn by English romantic poets, businessmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |