|
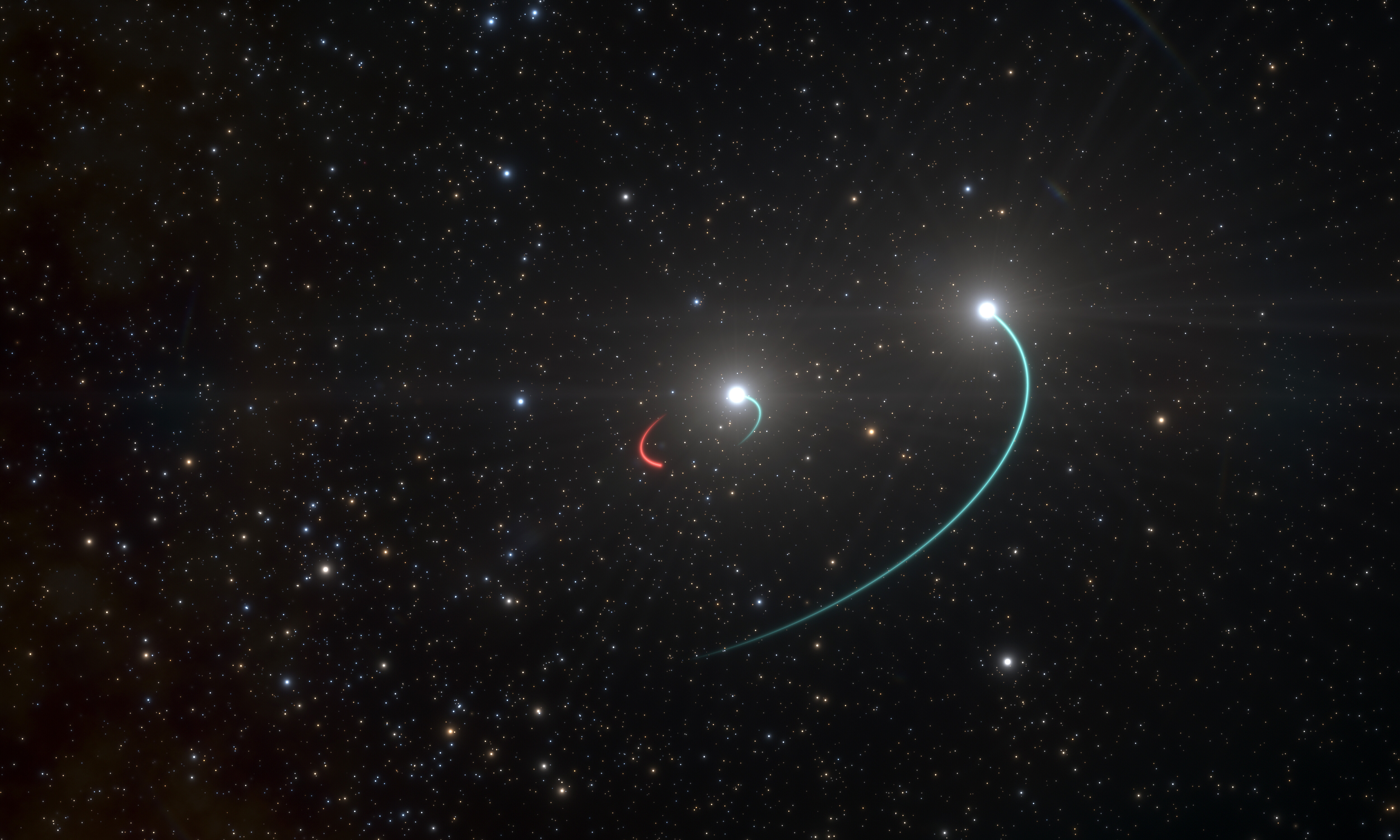
Epsilon Hydrae
Epsilon Hydrae (ε Hydrae, abbreviated Epsilon Hya, ε Hya) is a multiple star system of a combined third magnitude in the constellation of Hydra. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is located roughly distant from the Sun. The system consists of a binary pair designated Epsilon Hydrae AB, whose two components are themselves designated Epsilon Hydrae A (formally named Ashlesha ) and B, orbited by a spectroscopic binary designated Epsilon Hydrae C. A possible fourth component, designated Epsilon Hydrae D, shares a common proper motion with the other components and thus is most likely a gravitationally-bound member of the system. Nomenclature ''ε Hydrae'' ( Latinised to ''Epsilon Hydrae'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the three constituents as ''Epsilon Hydrae AB'', ''C'' and ''D'', and those of ''AB's'' components - ''Epsilon Hydrae A'' and ''B'' - derive from the convention used by the Washi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star System
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a '' binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Hydrae
Sigma Hydrae (σ Hydrae, abbreviated Sigma Hya, σ Hya), also named Minchir , is a solitary star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.48. The estimated distance to this star from the Sun, based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.75 mas, is around 370 light-years. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an interstellar extinction factor of 0.16, due to intervening dust. Nomenclature ''σ Hydrae'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Hydrae'') is the system's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Minchir'', appearing as ''Minchir es-schudscha'' in Bode's large star atlas, ''Uranographia''. The name which derived from the Arabic appelationمنخر الشجاع ''minkhar ash-shujāʽ'' "the nostril brave one" (the hydra) for this star. The name is erroneously spelt as ''Al Minliar al Shuja'' in the Yale ''Bright Star Catalogue''. In 2016, the IAU organized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Hydrae
Rho Hydrae, equally written ρ Hydrae, is a binary star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.34. The distance to this system, based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.21 mas, is about 354 light years. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an interstellar extinction of 0.06 magnitudes, due to intervening dust. The primary component is an A-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of A0 Vn. It has around double the radius of the Sun and 3.2 times the Sun's mass. Rho Hydrae is around 350 million years old and has a high rate of spin, with a projected rotational velocity of 128 km/s. It radiates 242 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 9,795 K. The companion is a magnitude 11.9 star at an angular separation of 12.1 arc seconds along a position angle of 146°, as of 2000. Name and etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Hydrae
Eta (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἦτα ''ē̂ta'' or ell, ήτα ''ita'' ) is the seventh letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the close front unrounded vowel . Originally denoting the voiceless glottal fricative in most dialects, its sound value in the classical Attic dialect of Ancient Greek was a long open-mid front unrounded vowel , raised to in hellenistic Greek, a process known as iotacism or itacism. In the ancient Attic number system (Herodianic or acrophonic numbers), the number 100 was represented by "", because it was the initial of , the ancient spelling of = "one hundred". In the later system of (Classical) Greek numerals eta represents 8. Eta was derived from the Phoenician letter heth . Letters that arose from eta include the Latin H and the Cyrillic letter И and Й. History Consonant h The letter shape 'H' was originally used in most Greek dialects to represent the voiceless glottal fricative . In this function, it was borrowed in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Hydrae
Zeta Hydrae (ζ Hya, ζ Hydrae) is a solitary star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. This is a generally faint constellation, so, at an apparent visual magnitude of +3.10, this is the third-brightest member after Alphard and Gamma Hydrae. Distance The distance to this star has been measured using the parallax technique, yielding a value of roughly . At this distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by 0.03 as a result of extinction from intervening gas and dust. Delta Hydrae is about from Zeta Hydrae and may be a largely co-moving object. The star has one of the lower-error margin readings among those of the Gaia spacecraft which computes a parallax of 20.7182 ± 0.3925 mas and, if correct, a distance of 157 ± 3 light years. Characteristics With a stellar classification of G9 II-III, this is an evolved giant star that is radiating 132 times the luminosity of the Sun from its outer envelope at an effective temperature of 4,925 K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Hydrae
Delta Hydrae, Latinized from δ Hydrae, is a double star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.146. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 20.34 mas, it is located about 160 light years from the Sun. This is a double star with an angular separation of along a position angle of , as of 2003. The brighter component is an A-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of A1 Vnn. It is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 285 km/s. This is giving the star an oblate shape with an equatorial bulge that is 20% larger than the polar radius. It has an estimated 2.88 times the mass of the Sun and 2.7 times the Sun's radius. The star is about 244 million years old and it radiates 42.7 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 11,055 K. The companion has a visual magnitude of 11.15. X-ray emissions have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Star
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a ''binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that appear f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Astrology
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The ''Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology Jyotisha, states Monier-Williams, is rooted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Mansion
Often called lunar mansion, a lunar station or lunar house is a segment of the ecliptic through which the Moon passes in its orbit around the Earth. The concept was used by several ancient cultures as part of their calendrical system. Stations in different cultures In general, though not always, the zodiac is divided into 27 or 28 segments relative to the vernal equinox point or the fixed stars – one for each day of the lunar month. (A sidereal month lasts about days.) The Moon's position is charted with respect to those fixed segments. Since the Moon's position at any given stage will vary according to Earth's position in its own orbit, lunar stations are an effective system for keeping track of the passage of seasons. Various cultures have used sets of lunar stations astrologically; for example, the Jyotisha astrological ''nakshatras'' of Hindu culture, the Arabic manzils (''manazil al-qamar''), the Twenty-Eight Mansions of Chinese astronomy, and the 36 ''d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakshatra
Nakshatra ( sa, नक्षत्रम्, translit=Nakṣatram) is the term for lunar mansion in Hindu astrology and Indian Astronomy. A nakshatra is one of 27 (sometimes also 28) sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or asterisms in or near the respective sectors. The starting point for the nakshatras according to Vedas is "Krittika" (it has been argued because the Pleiades may have started the year at the time the Vedas were compiled, presumably at the vernal equinox), but, in more recent compilations, the start of the nakshatras list is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite to the star Spica called ''Chitrā'' in Sanskrit, which would be Ashwinī, a part of the modern constellation Aries, and these compilations therefore may have been compiled during the centuries when the sun was passing through the area of the constellation Aries at the time of the vernal equinox. This version may have been called ''Meshādi'' or the " start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |